|
Agriculture (Chinese Mythology)
Agriculture is an important theme in Chinese mythology. There are many myths about the invention of agriculture that have been told or written about in China. Chinese mythology refers to those myths found in the historical geographic area of China. This includes myths in Chinese and other languages, as transmitted by Han Chinese as well as other ethnic groups (of which fifty-six are officially recognized by the current administration of China). Many of the myths about agriculture involve its invention by such deities or cultural heroes such as Shennong, Houji, Houtu, and Shujun: of these Shennong is the most famous, according to Lihui Yang. There are also many other myths. Myths related to agriculture include how humans learned the use of fire, cooking, animal husbandry and the use of draft animals, inventions of various agricultural tools and implements, the domestication of various species of plants such as ginger and radishes, the evaluation and uses of various types of soi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
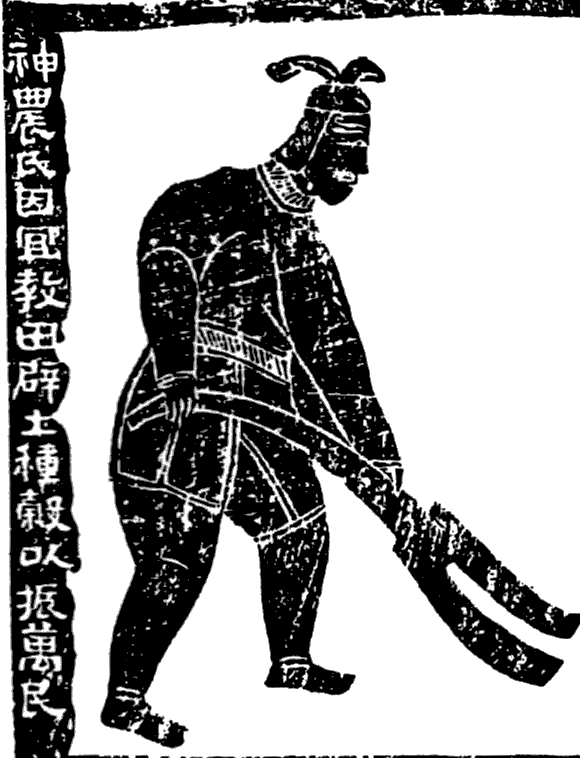
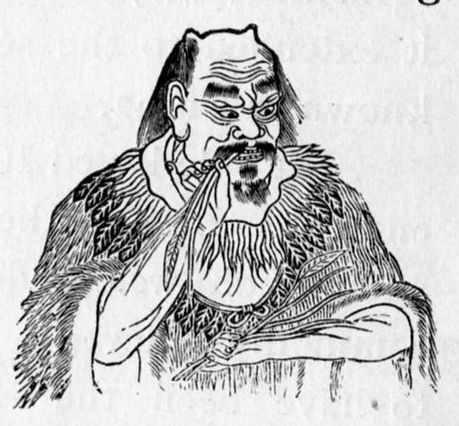
Shennong2
Shennong (), variously translated as "Divine Farmer" or "Divine Husbandman", born Jiang Shinian (), was a mythological Chinese sovereign, Chinese ruler known as the first Yan Emperor who has become a deity in Chinese folk religion, Chinese and Vietnamese folk religion. He is venerated as a culture hero in China and Vietnam. In Vietnamese he is referred to as :vi:Thần_Nông, Thần Nông. Shennong has at times been counted amongst the Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors, Three Sovereigns (also known as "Three Kings" or "Three Patrons"), a group of ancient deities or deified kings of prehistoric China. Shennong has been thought to have taught the ancient Chinese not only their practices of agriculture, but also the use of herbal drugs. Shennong was credited with various inventions: these include the Hoe (tool), hoe, plow (both ''leisi'' () style and the plowshare), axe, digging Water well, wells, agricultural irrigation, preserving stored seeds by using boiled horse urine, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bigu (avoiding Grains)
''Bigu'' () is a Daoist fasting technique associated with achieving '' xian'' "transcendence; immortality". Grain avoidance is related to multifaceted Chinese cultural beliefs. For instance, ''bigu'' fasting was the common medical cure for expelling the ''sanshi'' "Three Corpses", the malevolent, grain-eating spirits that live in the human body (along with the hun and po souls), report their host's sins to heaven every 60 days, and carry out punishments of sickness and early death. Avoiding "grains" has been diversely interpreted to mean not eating particular foodstuffs (food grain, cereal, the Five Grains, ''wugu'', or staple food), or not eating any food (inedia). In the historical context of traditional Chinese culture within which the concept of ''bigu'' developed, there was great symbolic importance connected with the five grains and their importance in sustaining human life, exemplified in various myths and legends from ancient China and throughout subsequent history. The c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhurong
Zhurong (), also known as Chongli (), is an important personage in Chinese mythology and Chinese folk religion. According to the ''Huainanzi'' and the philosophical texts of Mozi and his followers, Zhurong is a god of fire and of the south. The ''Shanhaijing'' gives alternative genealogies for Zhurong, including descent from both the Yan Emperor and Yellow Emperor. Some sources associate Zhurong with some of the principal early and ancient myths of China, such as those of Nüwa (Nüwa Mends the Heavens), Gonggong, and the Great Flood. Chinese mythology has in the past been believed to be, at least in part, a factual recording of history. Thus, in the study of historical Chinese culture, many of the stories that have been told regarding characters and events which have been written or told of the distant past have a double tradition: one tradition which presents a more historicised and one which presents a more mythological version. This is also true in the case of Zhurong. In Sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow Emperor
The Yellow Emperor, also known as the Yellow Thearch or by his Chinese name Huangdi (), is a deity ('' shen'') in Chinese religion, one of the legendary Chinese sovereigns and culture heroes included among the mytho-historical Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors and cosmological Five Regions' Highest Deities (). Calculated by Jesuit missionaries on the basis of Chinese chronicles and later accepted by the twentieth-century promoters of a universal calendar starting with the Yellow Emperor, Huangdi's traditional reign dates are 2697–2597 or 2698–2598 BC. Huangdi's cult became prominent in the late Warring States and early Han dynasty, when he was portrayed as the originator of the centralized state, as a cosmic ruler, and as a patron of esoteric arts. A large number of texts – such as the ''Huangdi Neijing'', a medical classic, and the '' Huangdi Sijing'', a group of political treatises – were thus attributed to him. Having waned in influence during most of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traditional Chinese Medicine
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is an alternative medical practice drawn from traditional medicine in China. It has been described as "fraught with pseudoscience", with the majority of its treatments having no logical mechanism of action. Medicine in traditional China encompassed a range of sometimes competing health and healing practices, folk beliefs, literati theory and Confucian philosophy, herbal remedies, food, diet, exercise, medical specializations, and schools of thought. In the early twentieth century, Chinese cultural and political modernizers worked to eliminate traditional practices as backward and unscientific. Traditional practitioners then selected elements of philosophy and practice and organized them into what they called "Chinese medicine" (''Zhongyi''). In the 1950s, the Chinese government sponsored the integration of Chinese and Western medicine, and in the Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution of the 1960s, promoted Chinese medicine as inexpensive a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil And Grain
__NOTOC__ Soil and grain was a common political term in the Sinosphere for the state. Shejitan, the altars of soil and grain, were constructed alongside ancestral altars. Chinese monarchs of the Ming and Qing dynasties performed ceremonies of soil and grain to affirm their sovereignty at the Beijing Shejitan, while Korean monarchs of the Joseon dynasty did so at the Seoul Sajikdan. It has also been rendered "gods of soil and grain" in English, owing to its associations of prayer and supernatural possibilities. In Vietnam, corresponding soil and grain altars () were established at historical capital of Hoa Lư, Thăng Long (Hanoi) and Huế. During the Chinese Warring States period, ministers defied their rulers by claiming a greater loyalty to the "soil and grain". A similar concept to ''sheji'' is that of the earth deities Tudi and Houtu.Yang, 97 See also * Tian & Di * Tudigong & Houtu * Agriculture in Chinese mythology * Chinese spiritual world concepts References Citations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ox In Chinese Mythology
Oxen, cows, beef cattle, buffalo and so on are an important motif in Chinese mythology. There are many myths about the oxen or ox-like beings, including both celestial and earthly varieties. The myths range from ones which include oxen or composite beings with ox characteristics as major actors to ones which focus on human or divine actors, in which the role of the oxen are more subsidiary. In some cases, Chinese myths focus on oxen-related subjects, such as plowing and agriculture or ox-powered carriage. Another important role for beef cattle is in the religious capacity of sacrificial offerings. Terminology The Chinese character 牛 () used for "ox" is rather non-specific. It can refer to a male, castrate or not, or to a female, young or old, of various species of the bovine family which have been domesticated for use as draft animals, with their strength being harnessed for various purposes, especially carting loads and various types of farm work, such as plowing. ''Niú'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
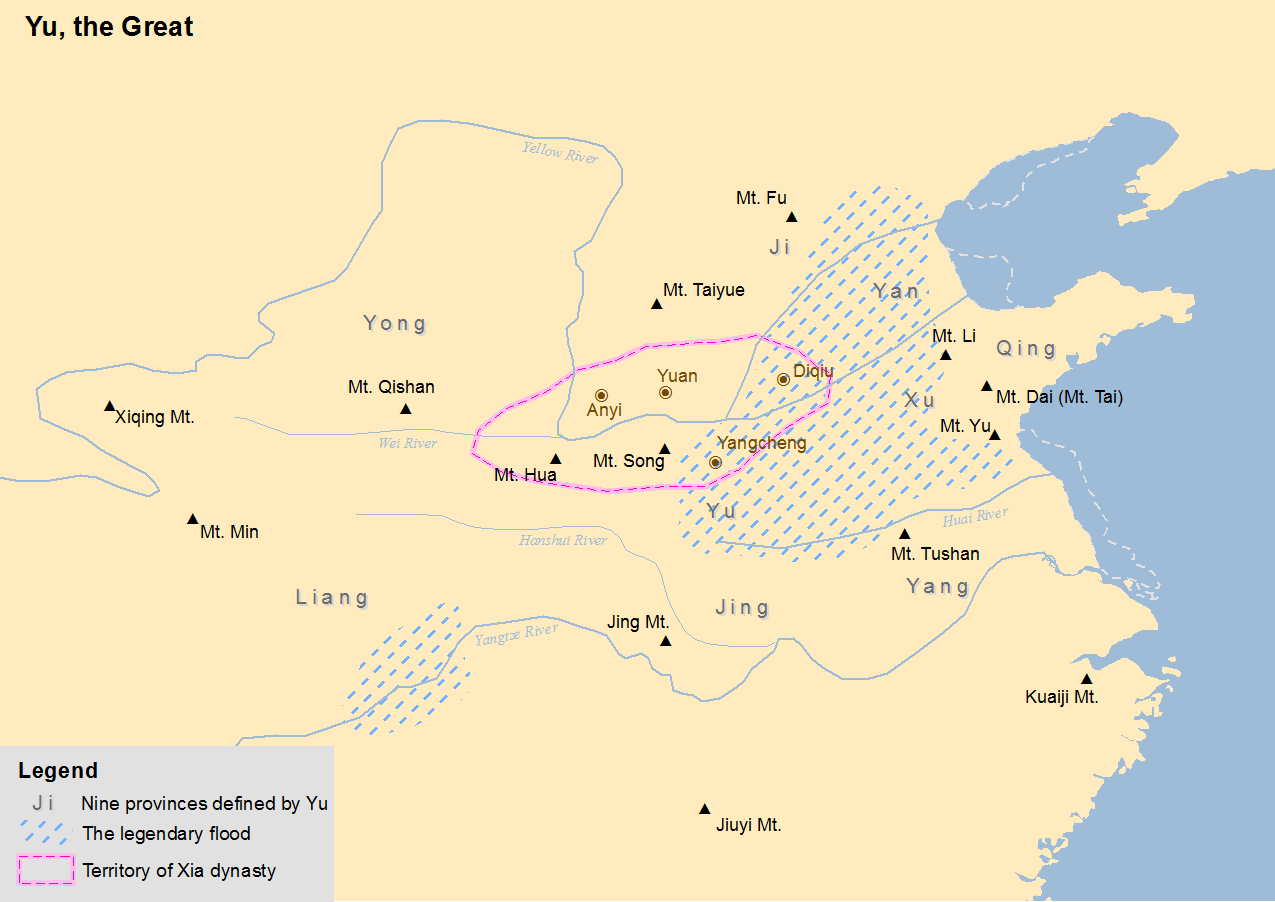
Great Flood (China)
The Great Flood of Gun-Yu (), also known as the Gun-Yu myth, was a major flood in ancient China that allegedly continued for at least two generations, which resulted in great population displacements among other disasters, such as storms and famine. People left their homes to live on the high hills and mounts, or nest on the trees. According to mythological and historical sources, it is traditionally dated to the third millennium BCE, or about 2300-2200 BCE, during the reign of Emperor Yao. However, archaeological evidence of an outburst flood at Jishi Gore on the Yellow River, comparable to similar severe events in the world in the past 10,000 years, has been dated to about 1920 BCE (a few centuries later than the traditional beginning of the Xia dynasty which came after Emperors Shun and Yao), and is suggested to have been the basis for the myth. Treated either historically or mythologically, the story of the Great Flood and the heroic attempts of the various human charact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Five Grains
The Five Grains or Cereals () are a grouping (or set of groupings) of five farmed crops that were all important in ancient China. Sometimes the crops themselves were regarded as sacred; other times, their cultivation was regarded as a sacred boon from a mythological or supernatural source. More generally, ''wǔgǔ'' can be employed in Chinese as a synecdoche referring to ''all'' grains or staple crops of which the end produce is of a granular nature. The identity of the five grains has varied over time, with different authors identifying different grains or even categories of grains. Holiness The sense of holiness or sacredness regarding the Five Grains proceeds from their traditional ascription to the saintly rulers credited with creating China's civilization. They were seen not merely as five crops chosen from many options but as the source permitting agrarian society and civilization itself. "Squandering the Five Grains" was seen as a sin worthy of torment in ''Diyu'', the Chin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Di Ku
Kù (, variant graph ), usually referred to as Dì Kù (), also known as Gaoxin or Gāoxīn Shì () or Qūn (), was a descendant of the Yellow Emperor. He went by the name Gaoxin until receiving imperial authority, when he took the name Ku and the title Di, thus being known as Di Ku. He is considered the ancestor of the ruling families of certain subsequent dynasties. Some sources treat Ku as a semi-historical figure, while others make fantastic mythological or religious claims about him. Besides varying in their degree of historicizing Ku, the various sources also differ in what specific stories about him they focus on, so that putting together the various elements of what is known regarding Ku results in a multifaceted story. Di Ku was (according to many versions of the list) one of the Five Emperors of the Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors of Chinese mythology. Ku, or Gaoxin, is also known as the "White Emperor". Birth Ku's lineage is derived from descent from the legendary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dog In Chinese Mythology
Dogs are an important motif in Chinese mythology. These motifs include a particular dog which accompanies a hero, the dog as one of the twelve totem creatures for which years are named, a dog giving first provision of grain which allowed current agriculture, and claims of having a magical dog as an original ancestor in the case of certain ethnic groups. Myth versus history Chinese mythology includes myths in Chinese and other languages, as transmitted by Han Chinese as well as other ethnic groups (of which fifty-six are officially recognized by the current administration of China). (Yang 2005:4) In the study of historical Chinese culture, many of the stories that have been told regarding characters and events which have been written or told of the distant past have a double tradition: one which tradition which presents a more historicized and one which presents a more mythological version.(Yang 2005: 12–13) This is also true of some accounts related to mythological dogs in China ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |