|
Agatoxin
Agatoxins are a class of chemically diverse polyamine and peptide toxins which are isolated from the venom of various spiders. Their mechanism of action includes blockade of glutamate -gated ion channels, voltage-gated sodium channels, or voltage-dependent calcium channels. Agatoxin is named after the funnel web spider (''Agelenopsis aperta'') which produces a venom containing several agatoxins. There are different agatoxins. The ω-agatoxins are approximately 100 amino acids in length and are antagonists of voltage-sensitive calcium channels and also block the release of neurotransmitters. For instance, the ω-agatoxin 1A is a selective blocker and will block L-type calcium channels whereas the ω-agatoxin 4B will inhibit voltage sensitive P-type calcium channels. The μ-agatoxins only act on insect voltage-gated sodium channels. Isolation The venom of the ''Agelenopsis aperta'' is located in two glands, which are located in the two fang bases. Ejection of the venom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agelenopsis Aperta
''Agelenopsis aperta'', also known as the desert grass spider or funnel-web spider, is a species of spider belonging to the family Agelenidae and the genus ''Agelenopsis''. It is found in dry and arid regions across the southern United States and into northwestern Mexico. Their body is about 13–18 mm long and they have relatively long legs in order to run after their prey. Desert grass spiders can withstand very low temperatures even though they do not Cold hardening, cold harden. It constructs the characteristic funnel-shaped webs in crevices where the funnel will fit, where they wait in the tube for prey which they can run after using their long legs. They often hunt for their prey at night. ''A. aperta'' is known for its territoriality and will fight intruders to protect their space. ''A. aperta'' are mainly monogamous, and the male performs an elaborate courtship ritual that involves swaying his abdomen and releasing pheromones. The male's pheromones induce a cataplec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AG 489
AG 489 (or agatoxin 489) is a component of the venom produced by Agelenopsis aperta, a North American funnel web spider. It inhibits the ligand gated ion channel TRPV1 through a pore blocking mechanism. To identify new inhibitors, capsaicin receptor channels (TRPV1) were screened from a venom library for activity against these channels. In result, the robust inhibitory activity was found in the venom. Venom fractionation utilizing a reversed phase HPLC which led to the purification of the two acylpolyamine toxins, AG489 and AG505. Both of these inhibit the TRPV1 channels from the extracellular membrane side. From the pore blocking mechanism, the pore mutations that change toxic affinity were identified. As a result, the four mutants decreased toxic affinity and several mutants increased it. Therefore, this was consistent with the scanned TM5-TM6 linker region being the outer vestibule of the channels and further confirming that AG489 is a pore blocker. See also * Agatoxin Ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P-type Calcium Channel
The P-type calcium channel is a type of voltage-dependent calcium channel. Similar to many other high-voltage-gated calcium channels, the α1 subunit determines most of the channel's properties. The 'P' signifies cerebellar Purkinje cells, referring to the channel's initial site of discovery. P-type calcium channels play a similar role to the N-type calcium channel in neurotransmitter release at the presynaptic terminal and in neuronal integration in many neuronal types. History The calcium channel experiments that led to the discovery of P-type calcium channels were initially completed by Rodolfo Llinas, Llinás and Sugimori in 1980. P type calcium channels were named in 1989 because they were discovered within mammalian Purkinje neurons. They were able to use an ''in vitro'' preparation to examine the ionic currents that account for Purkinje cells' electrophysiology, electrophysiological properties. They found that there are calcium dependent action potentials which rise slowly a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NMDA Receptor
The ''N''-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (also known as the NMDA receptor or NMDAR), is a glutamate receptor and ion channel found in neurons. The NMDA receptor is one of three types of ionotropic glutamate receptors, the other two being AMPA receptor, AMPA and kainate receptors. Depending on its subunit composition, its Ligand (biochemistry), ligands are glutamate and glycine (or D-Serine, D-serine). However, the binding of the ligands is typically not sufficient to open the channel as it may be blocked by Magnesium, Mg2+ ions which are only removed when the neuron is sufficiently depolarized. Thus, the channel acts as a “coincidence detector” and only once both of these conditions are met, the channel opens and it allows cation, positively charged ions (cations) to flow through the cell membrane. The NMDA receptor is thought to be very important for controlling synaptic plasticity and mediating learning and memory functions. The NMDA receptor is ionotropic, meaning it is a pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excitatory Junctional Potential
In neuroscience, an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) is a postsynaptic potential that makes the postsynaptic neuron more likely to fire an action potential. This temporary depolarization of postsynaptic membrane potential, caused by the flow of positively charged ions into the postsynaptic cell, is a result of opening ligand-gated ion channels. These are the opposite of inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs), which usually result from the flow of ''negative'' ions into the cell or positive ions ''out'' of the cell. EPSPs can also result from a decrease in outgoing positive charges, while IPSPs are sometimes caused by an increase in positive charge outflow. The flow of ions that causes an EPSP is an excitatory postsynaptic current (EPSC). EPSPs, like IPSPs, are graded (i.e. they have an additive effect). When multiple EPSPs occur on a single patch of postsynaptic membrane, their combined effect is the sum of the individual EPSPs. Larger EPSPs result in greater membrane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R-type Calcium Channel
The R-type calcium channel is a type of voltage-dependent calcium channel. Like the others of this class, the α1 subunit forms the pore through which calcium enters the cell and determines most of the channel's properties. This α1 subunit is also known as the calcium channel, voltage-dependent, R type, alpha 1E subunit (CACNA1E) or Cav2.3 which in humans is encoded by the ''CACNA1E'' gene. They are strongly expressed in cortex, hippocampus, striatum, amygdala and interpeduncular nucleus. They are poorly understood, but like Q-type calcium channels, they appear to be present in cerebellum, cerebellar granule cells. They have a high threshold of activation and relatively slow kinetics. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * * {{Ion channels, g1 Ion channels Electrophysiology Integral membrane proteins Calcium channels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-type Calcium Channel
N-type calcium channels also called Cav2.2 channels are voltage gated calcium channels that are localized primarily on the nerve terminals and dendrites as well as neuroendocrine cells. The calcium N-channel consists of several subunits: the primary subunit α1B and the auxiliary subunits α2δ and β. The α1B subunit forms the pore through which the calcium enters and helps to determine most of the channel's properties. These channels play an important role in the neurotransmission during development. In the adult nervous system, N-type calcium channels are critically involved in the release of neurotransmitters, and in pain pathways. N-type calcium channels are the target of ziconotide, the drug prescribed to relieve intractable cancer pain. There are many known N-type calcium channel blockers that function to inhibit channel activity, although the most notable blockers are ω-conotoxins. Structure N-type calcium channels are categorized as high threshold-activated channels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
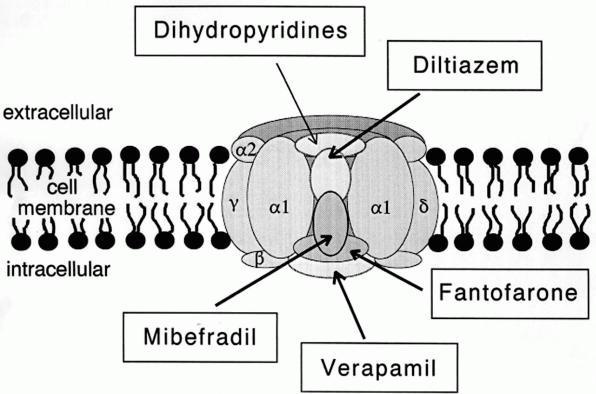
L-type Calcium Channel
The L-type calcium channel (also known as the dihydropyridine channel, or DHP channel) is part of the high-voltage activated family of voltage-dependent calcium channel. "L" stands for long-lasting referring to the length of activation. This channel has four isoforms: Cav1.1, Cav1.2, Cav1.3, and Cav1.4. L-type calcium channels are responsible for the excitation-contraction coupling of skeletal, smooth, cardiac muscle, and for aldosterone secretion in endocrine cells of the adrenal cortex. They are also found in neurons, and with the help of L-type calcium channels in endocrine cells, they regulate neurohormones and neurotransmitters. They have also been seen to play a role in gene expression, mRNA stability, neuronal survival, ischemic-induced axonal injury, synaptic efficacy, and both activation and deactivation of other ion channels. In cardiac myocytes, the L-type calcium channel passes inward Ca2+ current (ICaL) and triggers calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Q-type Calcium Channel
The Q-type calcium channel is a type of voltage-dependent calcium channel. Like the others of this class, the α1 subunit is the one that determines most of the channel's properties. They are poorly understood, but like R-type calcium channels, they appear to be present in cerebellar The cerebellum (Latin for "little brain") is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as or even larger. In humans, the cerebel ... granule cells. They have a high threshold of activation and relatively slow kinetics. External links * {{Ion channels, g1 Ion channels Electrophysiology Membrane biology Integral membrane proteins Calcium channels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Channel
A calcium channel is an ion channel which shows selective permeability to calcium ions. It is sometimes synonymous with voltage-gated calcium channel, although there are also ligand-gated calcium channels. Comparison tables The following tables explain gating, gene, location and function of different types of calcium channels, both voltage and ligand-gated. Voltage-gated Ligand-gated *the ''receptor-operated calcium channels'' (in vasoconstriction) **P2X receptors Page 479 Pharmacology L-type calcium channel blockers are used to treat hypertension. In most areas of the body, depolarization is mediated by sodium influx into a cell; changing the calcium permeability has little effect on action potentials. However, in many smooth muscle tissues, depolarization is mediated primarily by calcium influx into the cell. L-type calcium channel blockers selectively inhibit these action potentials in smooth muscle which leads to dilation of blood vessels; this in turn corrects hypert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Channels
Sodium channels are integral membrane proteins that form ion channels, conducting sodium ions (Na+) through a cell's membrane. They belong to the superfamily of cation channels and can be classified according to the trigger that opens the channel for such ions, i.e. either a voltage-change ("voltage-gated", "voltage-sensitive", or "voltage-dependent" sodium channel; also called "VGSCs" or "Nav channel") or a binding of a substance (a ligand) to the channel (ligand-gated sodium channels). In excitable cells such as neurons, myocytes, and certain types of glia, sodium channels are responsible for the rising phase of action potentials. These channels go through three different states called resting, active and inactive states. Even though the resting and inactive states would not allow the ions to flow through the channels the difference exists with respect to their structural conformation. Selectivity Sodium channels are highly selective for the transport of ions across cell membr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |