|
Acoustic Attenuation
Acoustic attenuation is a measure of the energy loss of sound propagation in media. Most media have viscosity and are therefore not ideal media. When sound propagates in such media, there is always thermal consumption of energy caused by viscosity. This effect can be quantified through the Stokes's law of sound attenuation. Sound attenuation may also be a result of heat conductivity in the media as has been shown by G. Kirchhoff in 1868. The Stokes-Kirchhoff attenuation formula takes into account both viscosity and thermal conductivity effects. For heterogeneous media, besides media viscosity, acoustic scattering is another main reason for removal of acoustic energy. Acoustic attenuation in a lossy medium plays an important role in many scientific researches and engineering fields, such as medical ultrasonography, vibration and noise reduction. Power-law frequency-dependent acoustic attenuation Many experimental and field measurements show that the acoustic attenuation coeffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J). Common forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, and the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system. All living organisms constantly take in and release energy. Due to mass–energy equivalence, any object that has mass whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
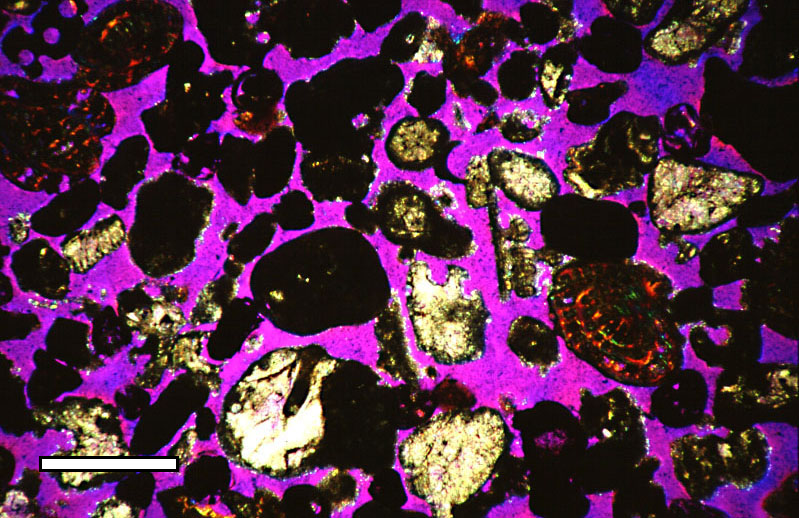
Porous Rock
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void (i.e. "empty") spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0 and 1, or as a percentage between 0% and 100%. Strictly speaking, some tests measure the "accessible void", the total amount of void space accessible from the surface (cf. closed-cell foam). There are many ways to test porosity in a substance or part, such as industrial CT scanning. The term porosity is used in multiple fields including pharmaceutics, ceramics, metallurgy, materials, manufacturing, petrophysics, hydrology, earth sciences, soil mechanics, and engineering. Void fraction in two-phase flow In gas-liquid two-phase flow, the void fraction is defined as the fraction of the flow-channel volume that is occupied by the gas phase or, alternatively, as the fraction of the cross-sectional area of the channel that is occupied by the gas phase. Void fraction usually varies from location to location in the flow cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sound Measurements
In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave, through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid. In human physiology and psychology, sound is the ''reception'' of such waves and their ''perception'' by the brain. Only acoustic waves that have frequencies lying between about 20 Hz and 20 kHz, the audio frequency range, elicit an auditory percept in humans. In air at atmospheric pressure, these represent sound waves with wavelengths of to . Sound waves above 20 kHz are known as ultrasound and are not audible to humans. Sound waves below 20 Hz are known as infrasound. Different animal species have varying hearing ranges. Acoustics Acoustics is the interdisciplinary science that deals with the study of mechanical waves in gasses, liquids, and solids including vibration, sound, ultrasound, and infrasound. A scientist who works in the field of acoustics is an ''acoustician'', while someone working in the field of acoustical e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
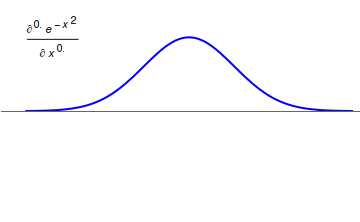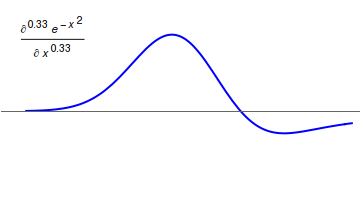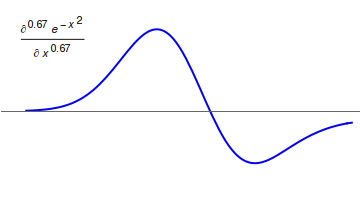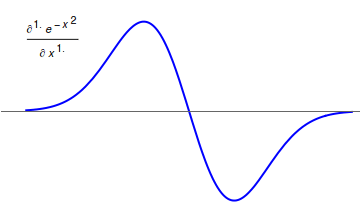
Fractional Calculus
Fractional calculus is a branch of mathematical analysis that studies the several different possibilities of defining real number powers or complex number powers of the differentiation operator D :D f(x) = \frac f(x)\,, and of the integration operator J The symbol J is commonly used instead of the intuitive I in order to avoid confusion with other concepts identified by similar I–like glyphs, such as identities. :J f(x) = \int_0^x f(s) \,ds\,, and developing a calculus for such operators generalizing the classical one. In this context, the term ''powers'' refers to iterative application of a linear operator D to a function f, that is, repeatedly composing D with itself, as in D^n(f) = (\underbrace_n)(f) = \underbrace_n (f)\cdots))). For example, one may ask for a meaningful interpretation of :\sqrt = D^\frac12 as an analogue of the functional square root for the differentiation operator, that is, an expression for some linear operator that, when applied ''twice'' to any ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absorption (acoustics)
Acoustic absorption refers to the process by which a material, structure, or object takes in sound energy when sound waves are encountered, as opposed to reflecting the energy. Part of the absorbed energy is transformed into heat and part is transmitted through the absorbing body. The energy transformed into heat is said to have been 'lost'.Acoustic Absorbers and Diffusers: Theory, Design and Applicatio.CRC Press .2009.Peter D'Antoni When sound from a loudspeaker collides with the walls of a room part of the sound's energy is reflected, part is transmitted, and part is absorbed into the walls. Just as the acoustic energy was transmitted through the air as pressure differentials (or deformations), the acoustic energy travels through the material which makes up the wall in the same manner. Deformation causes mechanical losses via conversion of part of the sound energy into heat, resulting in acoustic attenuation, mostly due to the wall's viscosity. Similar attenuation mechanisms ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks. Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates) because they are the most resistant minerals to weathering processes at the Earth's surface. Like uncemented sand, sandstone may be any color due to impurities within the minerals, but the most common colors are tan, brown, yellow, red, grey, pink, white, and black. Since sandstone beds often form highly visible cliffs and other topographic features, certain colors of sandstone have been strongly identified with certain regions. Rock formations that are primarily composed of sandstone usually allow the percolation of water and other fluids and are porous enough to store large quantities, making them valuable aquifers and petroleum reservoirs. Quartz-bearing sandstone can be changed into quartzite through metamorphism, usually related to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedimentary Rocks
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles to settle in place. The particles that form a sedimentary rock are called sediment, and may be composed of geological detritus (minerals) or biological detritus (organic matter). The geological detritus originated from weathering and erosion of existing rocks, or from the solidification of molten lava blobs erupted by volcanoes. The geological detritus is transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice or mass movement, which are called agents of denudation. Biological detritus was formed by bodies and parts (mainly shells) of dead aquatic organisms, as well as their fecal mass, suspended in water and slowly piling up on the floor of water bodies (marine snow). Sedimentation may also occur as dissolved minerals precipitate from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porosity
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void (i.e. "empty") spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0 and 1, or as a percentage between 0% and 100%. Strictly speaking, some tests measure the "accessible void", the total amount of void space accessible from the surface (cf. closed-cell foam). There are many ways to test porosity in a substance or part, such as industrial CT scanning. The term porosity is used in multiple fields including pharmaceutics, ceramics, metallurgy, materials, manufacturing, petrophysics, hydrology, earth sciences, soil mechanics, and engineering. Void fraction in two-phase flow In gas-liquid two-phase flow, the void fraction is defined as the fraction of the flow-channel volume that is occupied by the gas phase or, alternatively, as the fraction of the cross-sectional area of the channel that is occupied by the gas phase. Void fraction usually varies from location to location in the flow ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acoustical Society Of America Press
The Acoustical Society of America (ASA) is an international scientific society founded in 1929 dedicated to generating, disseminating and promoting the knowledge of acoustics and its practical applications. The Society is primarily a voluntary organization of about 7500 members and attracts the interest, commitment, and service of many professionals. History In the summer of 1928, (See Wallace Clement Sabine.) Floyd R. Watson and Wallace Waterfall (1900–1974), a former doctoral student of Watson, were invited by UCLA's Vern Oliver Knudsen to an evening dinner at Knudsen's beach club in Santa Monica. The three physicists decided to form a society of acoustical engineers interested in architectural acoustics. In the early part of December 1928, Wallace Waterfall sent letters to sixteen people inquiring about the possibility of organizing such a society. Harvey Fletcher offered the use of the Bell Telephone Laboratories at 463 West Street in Manhattan as a meeting place for an orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springer (publisher)
Springer Science+Business Media, commonly known as Springer, is a German multinational publishing company of books, e-books and peer-reviewed journals in science, humanities, technical and medical (STM) publishing. Originally founded in 1842 in Berlin, it expanded internationally in the 1960s, and through mergers in the 1990s and a sale to venture capitalists it fused with Wolters Kluwer and eventually became part of Springer Nature in 2015. Springer has major offices in Berlin, Heidelberg, Dordrecht, and New York City. History Julius Springer founded Springer-Verlag in Berlin in 1842 and his son Ferdinand Springer grew it from a small firm of 4 employees into Germany's then second largest academic publisher with 65 staff in 1872.Chronology ". Springer Science+Business Media. In 1964, Springer expanded its business internationally, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from ''angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is equal to one event per second. The period is the interval of time between events, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency. For example, if a heart beats at a frequency of 120 times a minute (2 hertz), the period, —the interval at which the beats repeat—is half a second (60 seconds divided by 120 beats). Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio signals (sound), radio waves, and light. Definitions and units For cyclical phenomena such as oscillations, waves, or for examples of simple harmonic motion, the term ''frequency'' is defined as the number of cycles or vibrations per unit of time. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Law
In statistics, a power law is a Function (mathematics), functional relationship between two quantities, where a Relative change and difference, relative change in one quantity results in a proportional relative change in the other quantity, independent of the initial size of those quantities: one quantity varies as a Exponentiation, power of another. For instance, considering the area of a square in terms of the length of its side, if the length is doubled, the area is multiplied by a factor of four. Empirical examples The distributions of a wide variety of physical, biological, and man-made phenomena approximately follow a power law over a wide range of magnitudes: these include the sizes of craters on the moon and of solar flares, the foraging pattern of various species, the sizes of activity patterns of neuronal populations, the frequencies of words in most languages, frequencies of family names, the species richness in clades of organisms, the sizes of power outages, volcanic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



Saunders_Quarry-1.jpg)
