|
Accessory Drive
The accessory drive is a gearbox that forms part of a gas turbine engine. Although not part of the engine's core, it drives the accessories, fuel pumps, etc., that are otherwise essential for the operation of the engine or the aircraft on which it is mounted. Accessory drives on large engines handle between 400–500 hp. Components Power for the accessory drive is taken from the central shaft linking the turbine and compressor sections of the engine. This requires an internal gearbox that couples the drive to a radial driveshaft or ''towershaft'' that drives an external gearbox. Internal gearbox The design of the internal gearbox is complicated by the heat and small space available in which to connect the driveshaft. It is usually placed between the compressor outlet and the combustor. In turboprops or designs with centrifugal compressors, it may be placed ahead of the compressor. For two-shaft designs, an accessory drive will be taken from the high-pressure sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helical Gear
A gear is a rotating circular machine part having cut teeth or, in the case of a cogwheel or gearwheel, inserted teeth (called ''cogs''), which mesh with another (compatible) toothed part to transmit (convert) torque and speed. The basic principle behind the operation of gears is analogous to the basic principle of levers. A gear may also be known informally as a cog. Geared devices can change the speed, torque, and direction of a power source. Gears of different sizes produce a change in torque, creating a mechanical advantage, through their ''gear ratio'', and thus may be considered a simple machine. The rotational speeds, and the torques, of two meshing gears differ in proportion to their diameters. The teeth on the two meshing gears all have the same shape. Two or more meshing gears, working in a sequence, are called a gear train or a '' transmission''. The gears in a transmission are analogous to the wheels in a crossed, belt pulley system. An advantage of gears is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft Components
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines. Common examples of aircraft include airplanes, helicopters, airships (including blimps), gliders, paramotors, and hot air balloons. The human activity that surrounds aircraft is called ''aviation''. The science of aviation, including designing and building aircraft, is called ''aeronautics.'' Crewed aircraft are flown by an onboard pilot, but unmanned aerial vehicles may be remotely controlled or self-controlled by onboard computers. Aircraft may be classified by different criteria, such as lift type, aircraft propulsion, usage and others. History Flying model craft and stories of manned flight go back many centuries; however, the first manned ascent — and safe descent — in modern times took place by larger hot-air bal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Technologies Corporation
United Technologies Corporation (UTC) was an American multinational conglomerate headquartered in Farmington, Connecticut. It researched, developed, and manufactured products in numerous areas, including aircraft engines, aerospace systems, HVAC, elevators and escalators, fire and security, building automation, and industrial products, among others. UTC was also a large military contractor, getting about 10% of its revenue from the U.S. government. Gregory J. Hayes was the CEO and chairman. In April 2020 UTC merged with the Raytheon Company to form Raytheon Technologies. History Pre-1970s 1970s and 1980s In 1974, Harry Gray left Litton Industries to become the CEO of United Aircraft.. He pursued a strategy of growth and diversification, changing the parent corporation's name to United Technologies Corporation (UTC) in 1975 to reflect the intent to diversify into numerous high tech fields beyond aerospace.. (The change became official on May 1, 1975.) The diversificat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rolls-Royce Plc
Rolls-Royce Holdings plc is a British multinational aerospace and defence company incorporated in February 2011. The company owns Rolls-Royce, a business established in 1904 which today designs, manufactures and distributes power systems for aviation and other industries. Rolls-Royce is the world's second-largest maker of aircraft engines (after General Electric) and has major businesses in the marine propulsion and energy sectors. Rolls-Royce was the world's 16th largest defence contractor in 2018 when measured by defence revenues. Rolls-Royce Holdings plc is listed on the London Stock Exchange, where it is a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index. At the close of London trading on 28 August 2019, the company had a market capitalisation of £4.656bn, the 85th-largest of any company with a primary listing on the London Stock Exchange. The company's registered office is at Kings Place, near Kings Cross in London. History Ownership Rolls-Royce grew from the engineering business ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tachometer
A tachometer (revolution-counter, tach, rev-counter, RPM gauge) is an instrument measuring the rotation speed of a shaft or disk, as in a motor or other machine. The device usually displays the revolutions per minute (RPM) on a calibrated analogue dial, but digital displays are increasingly common. The word comes from Greek ''τάχος'' (''táchos'' "speed") and ''μέτρον'' (''métron'' "measure"). Essentially the words tachometer and speedometer have identical meaning: a device that measures speed. It is by arbitrary convention that in the automotive world one is used for engine revolutions and the other for vehicle speed. In formal engineering nomenclature, more precise terms are used to distinguish the two. History The first tachometer was described by an Donkin in a paper to the Royal Society of Arts in 1810 for which he was awarded the Gold medal of the society. This consisted of a bowl of mercury constructed in such a way that centrifugal force caused the level ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constant Speed Drive
A constant speed drive (CSD) also known as a constant speed generator, is a type of transmission that takes an input shaft rotating at a wide range of speeds, delivering this power to an output shaft that rotates at a constant speed, despite the varying input. They are used to drive mechanisms, typically electrical generators, that require a constant input speed. The term is most commonly applied to hydraulic transmissions found on the accessory drives of gas turbine engines, such as aircraft jet engines. On modern aircraft, the CSD is often combined with a generator into a single unit known as an integrated drive generator (IDG). Mechanism CSDs are mainly used on airliner and military aircraft jet engines to drive the alternating current (AC) electrical generator. In order to produce the proper voltage at a constant AC frequency, usually three-phase 115 VAC at 400 Hz, an alternator needs to spin at a constant specific speed (typically 6,000 RPM for air-cooled generators ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Generator
In electricity generation, a generator is a device that converts motive power (mechanical energy) or fuel-based power (chemical energy) into electric power for use in an external circuit. Sources of mechanical energy include steam turbines, gas turbines, water turbines, internal combustion engines, wind turbines and even hand cranks. The first electromagnetic generator, the Faraday disk, was invented in 1831 by British scientist Michael Faraday. Generators provide nearly all of the power for electric power grids. In addition to electromechanical designs, photovoltaic and fuel cell powered generators utilize solar power and hydrogen-based fuels, respectively, to generate electrical output. The reverse conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy is done by an electric motor, and motors and generators have many similarities. Many motors can be mechanically driven to generate electricity; frequently they make acceptable manual generators. Terminology Electromagnetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
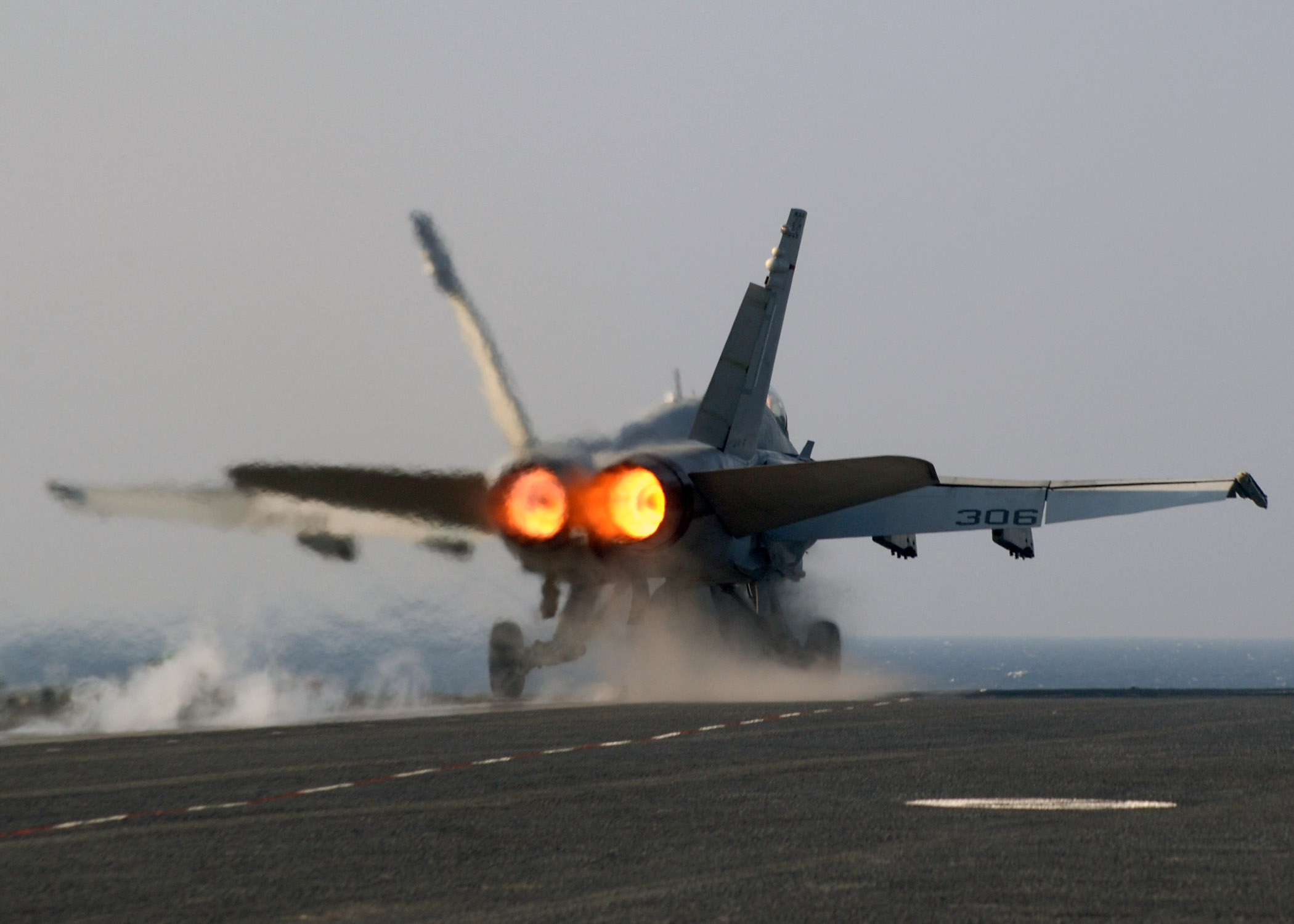
Afterburner
An afterburner (or reheat in British English) is an additional combustion component used on some jet engines, mostly those on military supersonic aircraft. Its purpose is to increase thrust, usually for supersonic flight, takeoff, and combat. The afterburning process injects additional fuel into a combustor in the jet pipe behind (''i.e.'', "after") the turbine, "reheating" the exhaust gas. Afterburning significantly increases thrust as an alternative to using a bigger engine with its attendant weight penalty, but at the cost of increased fuel consumption (decreased fuel efficiency) which limits its use to short periods. This aircraft application of "reheat" contrasts with the meaning and implementation of "reheat" applicable to gas turbines driving electrical generators and which reduces fuel consumption. Jet engines are referred to as operating ''wet'' when afterburning and ''dry'' when not. An engine producing maximum thrust wet is at ''maximum power,'' while an engine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cabin Air
Cabin may refer to: Buildings * Beach cabin, a small wooden hut on a beach * Log cabin, a house built from logs * Cottage, a small house * Chalet, a wooden mountain house with a sloping roof * Cabin, small free-standing structures that serve as individual lodging spaces of a motel Films * '' The Cabin'', 2018 Swedish-American horror film * '' The Cabin Movie'', 2005 Canadian comedy-drama film Places * Cabin, Shropshire, England * Cabins, West Virginia, US * Cabin Bluff, Georgia, in the List of places in Georgia (U.S. state) (A–D), US Transportation * Cabin (aircraft) * Cabin (ship) * Cabin (truck), an enclosed space where the driver is seated * Cabin car or caboose, a crewed rail transport vehicle at the end of a freight train * Cabin cruiser, a boat with enclosed accommodation * Cabin motorcycle, a fully or semi-enclosed motorcycle Other uses * Cabin (Ferris wheel), a passenger compartment * Cabin rights, an American frontier claim to land * Cabin (band) Cabin (styliz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
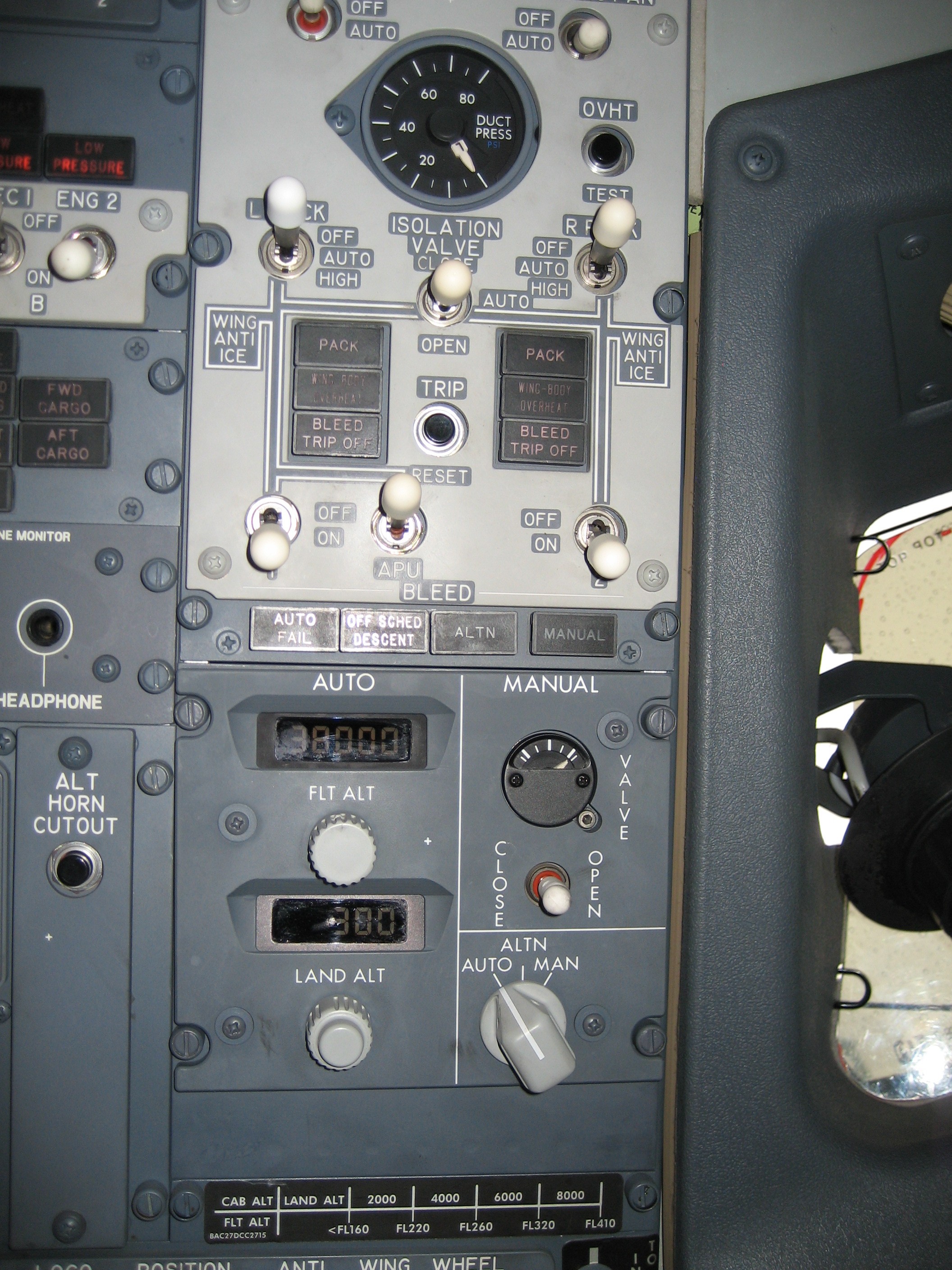
Bleed Air
Bleed air is compressed air taken from the compressor stage of a gas turbine upstream of its fuel-burning sections. Automatic air supply and cabin pressure controller (ASCPCs) valves bleed air from high or low stage engine compressor sections. Low stage air is used during high power setting operation, and high during descent and other low power setting operations. Bleed air from that system can be utilized for internal cooling of the engine, cross-starting another engine, engine and airframe anti-icing, cabin pressurization, pneumatic actuators, air-driven motors, pressurizing the hydraulic reservoir, and waste and water storage tanks. Some engine maintenance manuals refer to such systems as "customer bleed air". Bleed air is valuable in an aircraft for two properties: high temperature and high pressure (typical values are 200–250 °C and 275 kPa (40 PSI), for regulated bleed air exiting the engine pylon for use throughout the aircraft). Uses In civil aircraft, bleed air' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westinghouse J40
The Westinghouse J40 was an early high-performance afterburning turbojet engine designed by Westinghouse Aviation Gas Turbine Division starting in 1946 to a US Navy Bureau of Aeronautics (BuAer) request. BuAer intended to use the design in several fighter aircraft and a bomber. However, while an early low-power design was successful, attempts to scale it up to its full design power failed, and the design was finally abandoned, deemed a "fiasco" and a "flop". The design originally called for an engine of thrust at sea level static conditions without afterburner and 10,900 lbf thrust with afterburner. A more powerful model 9,500/13,700 lbf thrust version was intended to replace the earlier engines in the various airframes. In total, thirteen different variations were planned. The projected need for the higher-power engines led BuAer to place a second source production contract with Ford Motor Company, Lincoln Mercury Division for both J40-WE-10 and J40-WE-12 engines. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |