|
Access Type
Ada is a structured, statically typed, imperative, and object-oriented high-level programming language, extended from Pascal and other languages. It has built-in language support for '' design by contract'' (DbC), extremely strong typing, explicit concurrency, tasks, synchronous message passing, protected objects, and non-determinism. Ada improves code safety and maintainability by using the compiler to find errors in favor of runtime errors. Ada is an international technical standard, jointly defined by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). , the standard, called Ada 2012 informally, is ISO/IEC 8652:2012. Ada was originally designed by a team led by French computer scientist Jean Ichbiah of CII Honeywell Bull under contract to the United States Department of Defense (DoD) from 1977 to 1983 to supersede over 450 programming languages used by the DoD at that time. Ada was named after Ada Lovelace (18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multi-paradigm Programming Language
Programming paradigms are a way to classify programming languages based on their features. Languages can be classified into multiple paradigms. Some paradigms are concerned mainly with implications for the execution model of the language, such as allowing Side effect (computer science), side effects, or whether the sequence of operations is defined by the execution model. Other paradigms are concerned mainly with the way that code is organized, such as grouping a code into units along with the state that is modified by the code. Yet others are concerned mainly with the style of syntax and grammar. Common programming paradigms include: * imperative programming, imperative in which the programmer instructs the machine how to change its state, ** procedural programming, procedural which groups instructions into procedures, ** object-oriented programming, object-oriented which groups instructions with the part of the state they operate on, * declarative programming, declarative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
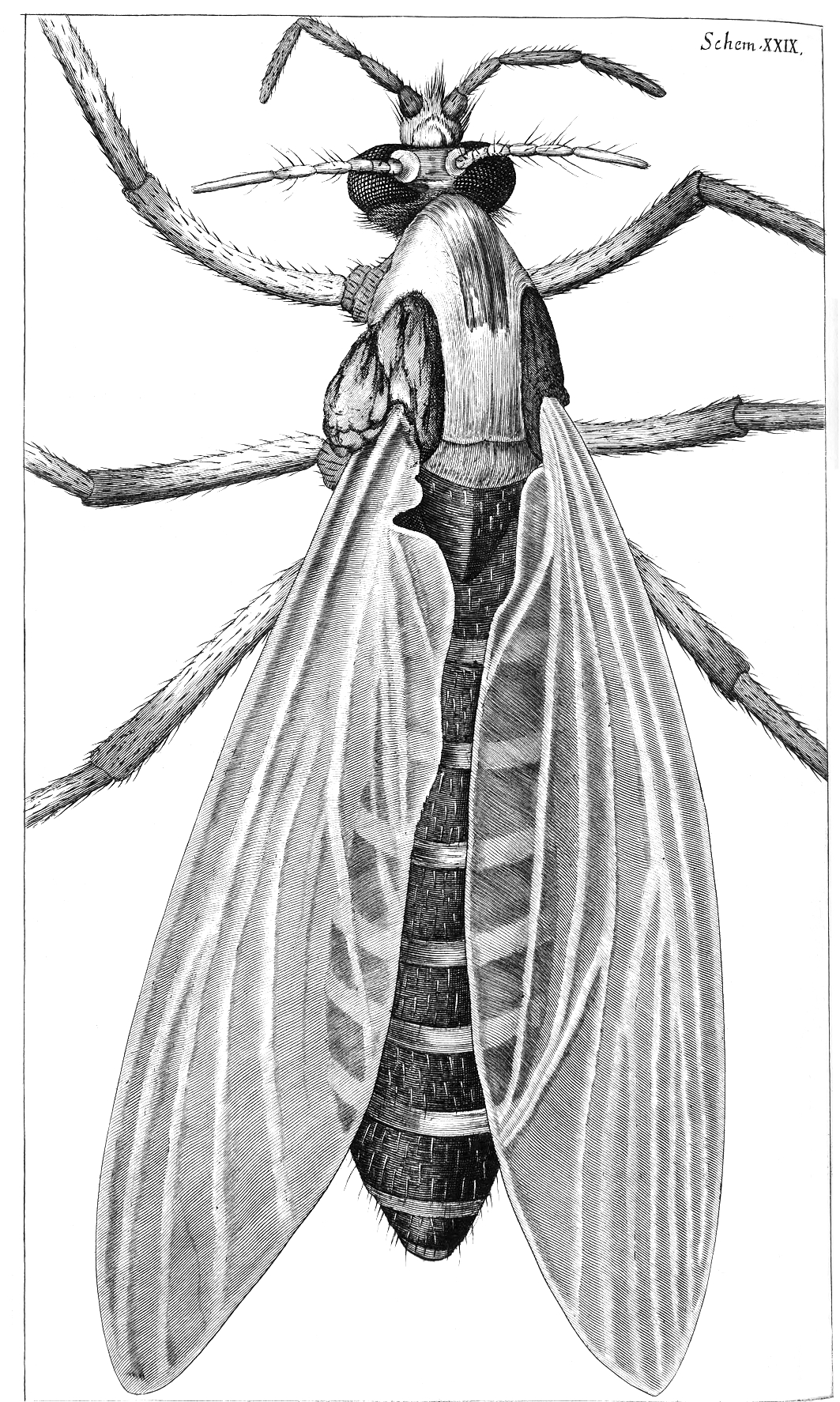
GNAT
A gnat () is any of many species of tiny flying insects in the dipterid suborder Nematocera, especially those in the families Mycetophilidae, Anisopodidae and Sciaridae. They can be both biting and non-biting. Most often they fly in large numbers, called clouds. "Gnat" is a loose descriptive category rather than a phylogenetic or other technical term, so there is no scientific consensus on what constitutes a gnat. Some entomologists consider only non-biting flies to be gnats. Certain universities and institutes also distinguish eye gnats: the Smithsonian Institution describes them as "non-biting flies, no bigger than a few grains of salt, ... attracted to fluids secreted by your eyes". Description As nematoceran flies, adult gnats have antennae with at least six segments that are often long and slender. They are generally slender-bodied with long and narrow wings. Black fly (Simuliidae) and biting midges (Ceratopogonidae), also belonging to the gnat category, are small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PL/SQL
PL/SQL (Procedural Language for SQL) is Oracle Corporation's procedural extension for SQL and the Oracle relational database. PL/SQL is available in Oracle Database (since version 6 - stored PL/SQL procedures/functions/packages/triggers since version 7), Times Ten in-memory database (since version 11.2.1), and IBM Db2 (since version 9.7). Oracle Corporation usually extends PL/SQL functionality with each successive release of the Oracle Database. PL/SQL includes procedural language elements such as conditions and loops. It allows declaration of constants and variables, procedures and functions, types and variables of those types, and triggers. It can handle exceptions (run-time errors). Arrays are supported involving the use of PL/SQL collections. Implementations from version 8 of Oracle Database onwards have included features associated with object-orientation. One can create PL/SQL units such as procedures, functions, packages, types, and triggers, which are stored ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ParaSail (programming Language)
Parallel Specification and Implementation Language (ParaSail) is an object-oriented parallel programming language. Its design and ongoing implementation is described in a blog and on its official website. ParaSail uses a pointer-free programming model, where objects can grow and shrink, and value semantics are used for assignment. It has no global garbage collected heap. Instead, region-based memory management is used throughout. Types can be recursive, so long as the recursive components are declared ''optional''. There are no global variables, no parameter aliasing, and all subexpressions of an expression can be evaluated in parallel. Assertions, preconditions, postconditions, class invariants, etc., are part of the standard syntax, using a Hoare-like notation. Any possible race conditions are detected at compile time. Initial design of ParaSail began in September 2009, by S. Tucker Taft. Both an interpreter using the ParaSail virtual machine, and an LLVM-based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nim (programming Language)
Nim is a general-purpose, multi-paradigm, statically typed, compiled systems programming language, designed and developed by a team around Andreas Rumpf. Nim is designed to be "efficient, expressive, and elegant", supporting metaprogramming, functional, message passing, procedural, and object-oriented programming styles by providing several features such as compile time code generation, algebraic data types, a foreign function interface (FFI) with C, C++, Objective-C, and JavaScript, and supporting compiling to those same languages as intermediate representations. Description Nim was created to be a language as fast as C, as expressive as Python, and as extensible as Lisp. Nim is statically typed. It supports compile-time metaprogramming features such as syntactic macros and term rewriting macros. Term rewriting macros enable library implementations of common data structures, such as bignums and matrices, to be implemented efficiently, as if they were built-in language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Java (programming Language)
Java is a high-level, class-based, object-oriented programming language that is designed to have as few implementation dependencies as possible. It is a general-purpose programming language intended to let programmers ''write once, run anywhere'' ( WORA), meaning that compiled Java code can run on all platforms that support Java without the need to recompile. Java applications are typically compiled to bytecode that can run on any Java virtual machine (JVM) regardless of the underlying computer architecture. The syntax of Java is similar to C and C++, but has fewer low-level facilities than either of them. The Java runtime provides dynamic capabilities (such as reflection and runtime code modification) that are typically not available in traditional compiled languages. , Java was one of the most popular programming languages in use according to GitHub, particularly for client–server web applications, with a reported 9 million developers. Java was originally de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eiffel (programming Language)
Eiffel is an object-oriented programming language designed by Bertrand Meyer (an object-orientation proponent and author of '' Object-Oriented Software Construction'') and Eiffel Software. Meyer conceived the language in 1985 with the goal of increasing the reliability of commercial software development; the first version becoming available in 1986. In 2005, Eiffel became an ISO-standardized language. The design of the language is closely connected with the Eiffel programming method. Both are based on a set of principles, including design by contract, command–query separation, the uniform-access principle, the single-choice principle, the open–closed principle, and option–operand separation. Many concepts initially introduced by Eiffel later found their way into Java, C#, and other languages. New language design ideas, particularly through the Ecma/ ISO standardization process, continue to be incorporated into the Eiffel language. Characteristics The key characte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D (programming Language)
D, also known as dlang, is a multi-paradigm system programming language created by Walter Bright at Digital Mars and released in 2001. Andrei Alexandrescu joined the design and development effort in 2007. Though it originated as a re-engineering of C++, D is a profoundly different language —features of D can be considered streamlined and expanded-upon ideas from C++, however D also draws inspiration from other high-level programming languages, notably Java, Python, Ruby, C#, and Eiffel. D combines the performance and safety of compiled languages with the expressive power of modern dynamic and functional programming languages. Idiomatic D code is commonly as fast as equivalent C++ code, while also being shorter. The language as a whole is not memory-safe but includes optional attributes designed to guarantee memory safety of either subsets of or the whole program. Type inference, automatic memory management and syntactic sugar for common types allow faster ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drago (programming Language)
Drago may refer to: People * Drago (given name) * Drago (surname) * Drago (wrestler), Mexican professional wrestler Víctor Soto * Drago Dumbovic, Croatian footballer known simply as Drago * Drago, nickname of Alexander Volkov * Prince del Drago, 1860–1956, Italian noble and New York socialite Fictional characters * Ivan Drago, a boxer in the film ''Rocky IV'' * Blackie Drago, a supervillain from Marvel Comics * Drago, a character from ''Jackie Chan Adventures'' * Dragos, dinosaur-like creatures in the video game ''Mother 3'' * Drago, the Dragonoid from ''Bakugan'' series Other uses * Drago (fabric mill) * Drago (publisher), International publishing house of contemporary art * Drago (river), Sicily * Drago Doctrine, announced in 1902 by the Argentine Minister of Foreign Affairs, Luis María Drago * Drago restaurants of California * Drago Tree, common name for the species ''Dracaena draco'' See also * * * * Proper names derived from Drag- * Proper names derived fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chapel (programming Language)
Chapel, the Cascade High Productivity Language, is a parallel programming language that was developed by Cray, and later by Hewlett Packard Enterprise which acquired Cray. It was being developed as part of the Cray Cascade project, a participant in DARPA's High Productivity Computing Systems (HPCS) program, which had the goal of increasing supercomputer productivity by 2010. It is being developed as an open source project, under version 2 of the Apache license. The Chapel compiler is written in C and C++ (C++14). The backend (i.e. the optimizer) is LLVM, written in C++. Python 3.7 or newer is required for some optional components such Chapel’s test system and c2chapel, a tool to generate C bindings for Chapel. By default Chapel compiles to binary expendables, but it can also compile to C code, and then LLVM is not used. Chapel code can be compiled to libraries to be callable from C, or Fortran or e.g. Python also supported. Chapel includes preliminary work to target NVidia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ravenscar Profile
The Ravenscar profile is a subset of the Ada tasking features designed for safety-critical hard real-time computing. It was defined by a separate technical report in Ada 95; it is now part of the Ada 2012 Standard. It has been named after the English village of Ravenscar, the location of the 8th International Real-Time Ada Workshop (IRTAW 8). Restrictions of the profile A Ravenscar Ada application uses the following compiler directive: pragma Profile (Ravenscar); This is the same as writing the following set of configuration pragmas: pragma Task_Dispatching_Policy (FIFO_Within_Priorities); pragma Locking_Policy (Ceiling_Locking); pragma Detect_Blocking; pragma Restrictions ( No_Abort_Statements, No_Calendar, No_Dynamic_Attachment, No_Dynamic_Priorities, No_Implicit_Heap_Allocations, No_Local_Protected_Objects, No_Local_Timing_Events, No_Prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SPARK (programming Language)
SPARK is a formally defined computer programming language based on the Ada programming language, intended for the development of high integrity software used in systems where predictable and highly reliable operation is essential. It facilitates the development of applications that demand safety, security, or business integrity. Originally, there were three versions of the SPARK language (SPARK83, SPARK95, SPARK2005) based on Ada 83, Ada 95 and Ada 2005 respectively. A fourth version of the SPARK language, SPARK 2014, based on Ada 2012, was released on April 30, 2014. SPARK 2014 is a complete re-design of the language and supporting verification tools. The SPARK language consists of a well-defined subset of the Ada language that uses contracts to describe the specification of components in a form that is suitable for both static and dynamic verification. In SPARK83/95/2005, the contracts are encoded in Ada comments and so are ignored by any standard Ada compiler, but ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |