|
Abstract Factory
The abstract factory pattern in software engineering is a design pattern that provides a way to create families of related objects without imposing their concrete classes, by encapsulating a group of individual factories that have a common theme without specifying their concrete classes. According to this pattern, a client software component creates a concrete implementation of the abstract factory and then uses the generic interface of the factory to create the concrete objects that are part of the family. The client does not know which concrete objects it receives from each of these internal factories, as it uses only the generic interfaces of their products. This pattern separates the details of implementation of a set of objects from their general usage and relies on object composition, as object creation is implemented in methods exposed in the factory interface. Use of this pattern enables interchangeable concrete implementations without changing the code that uses them, ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abstract Factory UML
Abstract may refer to: *"Abstract", a 2017 episode of the animated television series ''Adventure Time'' * ''Abstract'' (album), 1962 album by Joe Harriott * Abstract algebra, sets with specific operations acting on their elements * Abstract of title, a summary of the documents affecting the title to a parcel of land * Abstract (law), a summary of a legal document * Abstract (summary), in academic publishing * Abstract art, artistic works that do not attempt to represent reality or concrete subjects * '' Abstract: The Art of Design'', 2017 Netflix documentary series * Abstract music, music that is non-representational * Abstract object in philosophy * Abstract structure in mathematics * Abstract type in computer science * The property of an abstraction * Q-Tip (musician), also known as "The Abstract" * Abstract and concrete In philosophy and the arts, a fundamental distinction exists between abstract and concrete entities. While there is no universally accepted definition, comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abstract Class
In object-oriented programming, a class defines the shared aspects of objects created from the class. The capabilities of a class differ between programming languages, but generally the shared aspects consist of state ( variables) and behavior ( methods) that are each either associated with a particular object or with all objects of that class. Object state can differ between each instance of the class whereas the class state is shared by all of them. The object methods include access to the object state (via an implicit or explicit parameter that references the object) whereas class methods do not. If the language supports inheritance, a class can be defined based on another class with all of its state and behavior plus additional state and behavior that further specializes the class. The specialized class is a ''sub-class'', and the class it is based on is its ''superclass''. Attributes Object lifecycle As an instance of a class, an object is constructed from a class via '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C++23
C++23, formally ISO/IEC 14882:2024, is the current open standard for the C++ programming language that follows C++20. The final draft of this version is N4950. In February 2020, at the final meeting for C++20 in Prague, an overall plan for C++23 was adopted: planned features for C++23 were library support for coroutines, a modular standard library, executors, and networking. The first WG21 meeting focused on C++23 was intended to take place in Varna in early June 2020, but was cancelled due to the COVID-19 pandemic, as was the November 2020 meeting in New York and the February 2021 meeting in Kona, Hawaii. All meetings until November 2022 were virtual while the November 2022 meeting until the final meeting in February 2023 was hybrid. The standard was technically finalized by WG21 at the hybrid meeting in Issaquah in February 2023. Modern "Hello, world" Example After many library changes applied to the working draft, the new "Hello, world" program will be import std; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequence Diagram
In software engineering, a sequence diagram shows process interactions arranged in time sequence. This diagram depicts the processes and objects involved and the sequence of messages exchanged as needed to carry out the functionality. Sequence diagrams are typically associated with use case realizations in the 4+1 architectural view model of the system under development. Sequence diagrams are sometimes called event diagrams or event scenarios. For a particular scenario of a use case, the diagrams show the events that external actors generate, their order, and possible inter-system events. The diagram emphasizes events that cross the system boundary from actors to systems. A system sequence diagram should be done for the main success scenario of the use case, and frequent or complex alternative scenarios. There are two kinds of sequence diagrams: * Sequence Diagram (SD): A regular version of sequence diagram describes how the system operates, and every object within a system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Class Diagram
In software engineering, a class diagram in the Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a type of static structure diagram that describes the structure of a system by showing the system's classes, their attributes, operations (or methods), and the relationships among objects. The class diagram is the main building block of object-oriented modeling. It is used for general conceptual modeling of the structure of the application, and for detailed modeling, translating the models into programming code. Class diagrams can also be used for data modeling Data modeling in software engineering is the process of creating a data model for an information system by applying certain formal techniques. It may be applied as part of broader Model-driven engineering (MDE) concept. Overview Data modeli .... The classes in a class diagram represent both the main elements, interactions in the application, and the classes to be programmed. In the diagram, classes are represented with boxes that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
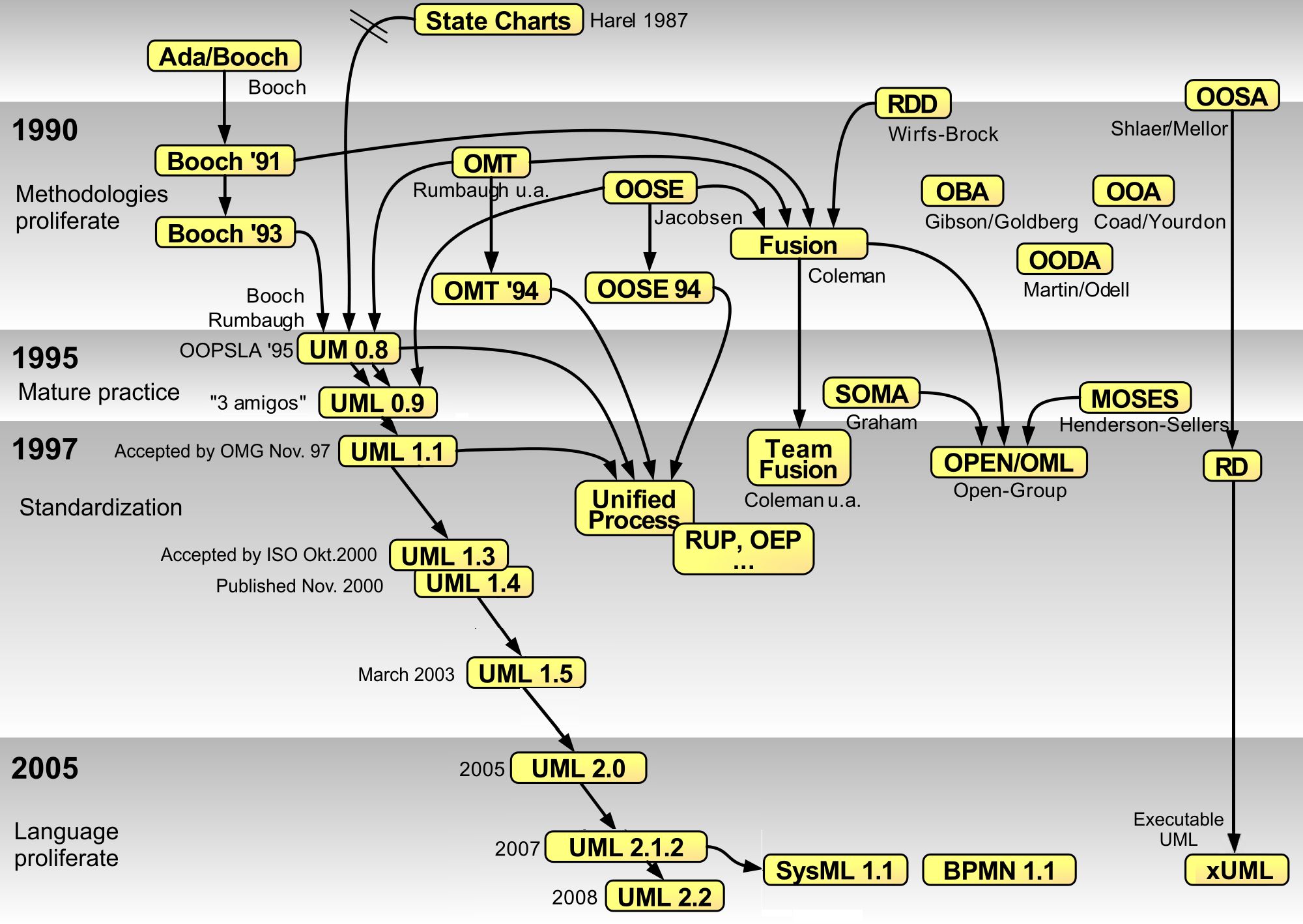
Unified Modeling Language
The Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a general-purpose visual modeling language that is intended to provide a standard way to visualize the design of a system. UML provides a standard notation for many types of diagrams which can be roughly divided into three main groups: behavior diagrams, interaction diagrams, and structure diagrams. The creation of UML was originally motivated by the desire to standardize the disparate notational systems and approaches to software design. It was developed at Rational Software in 1994–1995, with further development led by them through 1996. In 1997, UML was adopted as a standard by the Object Management Group (OMG) and has been managed by this organization ever since. In 2005, UML was also published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) as the ISO/IEC 19501 standard. Since then the standard has been periodically revised to cover the latest revision of UML. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Singleton Pattern
In object-oriented programming, the singleton pattern is a software design pattern that restricts the instantiation of a class to a singular instance. It is one of the well-known "Gang of Four" design patterns, which describe how to solve recurring problems in object-oriented software. The pattern is useful when exactly one object is needed to coordinate actions across a system. More specifically, the singleton pattern allows classes to: * Ensure they only have one instance * Provide easy access to that instance * Control their instantiation (for example, hiding the constructors of a class) The term comes from the mathematical concept of a singleton. Common uses Singletons are often preferred to global variables because they do not pollute the global namespace (or their containing namespace). Additionally, they permit lazy allocation and initialization, whereas global variables in many languages will always consume resources. The singleton pattern can also be used as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abstract Interface
In computing, an abstraction layer or abstraction level is a way of hiding the working details of a subsystem. Examples of software models that use layers of abstraction include the OSI model for network protocols, OpenGL, and other graphics libraries, which allow the separation of concerns to facilitate interoperability and platform independence. In computer science, an abstraction layer is a generalization of a conceptual model or algorithm, away from any specific implementation. These generalizations arise from broad similarities that are best encapsulated by models that express similarities present in various specific implementations. The simplification provided by a good abstraction layer allows for easy reuse by distilling a useful concept or design pattern so that situations, where it may be accurately applied, can be quickly recognized. Just composing lower-level elements into a construct doesn't count as an abstraction layer unless it shields users from its underlying co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Declaration (computer Science)
In computer programming, a declaration is a language construct specifying identifier properties: it declares a word's (identifier's) meaning."A declaration specifies the interpretation and attributes of a set of identifiers. A ''definition'' of an identifier is a declaration for that identifier that: * for an object ariable or constant causes storage to be reserved for that object; * for a function, includes the function body; * for an enumeration constant, is the (only) declaration of the identifier; * for a typedef name, is the first (or only) declaration of the identifier." C11 specification, 6.7: Declarations, paragraph 5. Declarations are most commonly used for functions, variables, constants, and classes, but can also be used for other entities such as enumerations and type definitions. Beyond the name (the identifier itself) and the kind of entity (function, variable, etc.), declarations typically specify the data type (for variables and constants), or the type sign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Class (computer Science)
In object-oriented programming, a class defines the shared aspects of objects created from the class. The capabilities of a class differ between programming languages, but generally the shared aspects consist of state ( variables) and behavior ( methods) that are each either associated with a particular object or with all objects of that class. Object state can differ between each instance of the class whereas the class state is shared by all of them. The object methods include access to the object state (via an implicit or explicit parameter that references the object) whereas class methods do not. If the language supports inheritance, a class can be defined based on another class with all of its state and behavior plus additional state and behavior that further specializes the class. The specialized class is a ''sub-class'', and the class it is based on is its ''superclass''. Attributes Object lifecycle As an instance of a class, an object is constructed from a class via '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Header File
An include directive instructs a text file processor to replace the directive text with the content of a specified file. The act of including may be logical in nature. The processor may simply process the include file content at the location of the directive without creating a combined file. Different processors may use different syntax. The C preprocessor (used with C, C++ and in other contexts) defines an include directive as a line that starts #include and is followed by a file specification. COBOL defines an include directive indicated by copy in order to include a copybook. Generally, for C/C++ the include directive is used to include a header file, but can include any file. Although relatively uncommon, it is sometimes used to include a body file such as a .c file. The include directive can support encapsulation and reuse. Different parts of a system can be segregated into logical groupings yet rely on one another via file inclusion. C and C++ are designed to leverag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |