|
Zond 1968A , wind turbine developer
{{disambiguation ...
Zond may refer to * Zond program, Soviet unmanned space program undertaken from 1964 to 1970 **Zond 1, spacecraft **Zond 2, spacecraft **Zond 3, spacecraft **Zond 4, spacecraft **Zond 5, spacecraft ** Zond 3MV-1 No.2, spacecraft **Zond 7, spacecraft **Zond 8, spacecraft ** Zond 1964A, spacecraft ** Zond 1967A, spacecraft **Zond 1967B, spacecraft *Zond Corporation GE Wind Energy is a branch of GE Renewable Energy, a subsidiary of General Electric. The company manufactures and sells wind turbines to the international market. In 2018, GE was the fourth largest wind turbine manufacturer in the world. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zond Program
Zond (russian: Зонд, lit=probe) was the name given to two distinct series of Soviet robotic spacecraft launched between 1964 and 1970. The first series, based on the 3MV planetary probe, was intended to gather information about nearby planets. The second series of test spacecraft was intended as a precursor to remote-controlled robotic circumlunar loop flights, using a stripped-down variant of Soyuz spacecraft, consisting of the service and descent modules, but lacking the orbital module. Two tortoises and other lifeforms aboard Zond 5 were the first terrestrial organisms to travel around the Moon and return to Earth. Missions based on the 3MV planetary probe The first three missions were based on the model 3MV planetary probe, intended to explore Venus and Mars. After two failures, Zond 3 was sent on a test mission, becoming the second spacecraft to photograph the far side of the Moon (after Luna 3). It then continued out to the orbit of Mars in order to test telem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zond 1
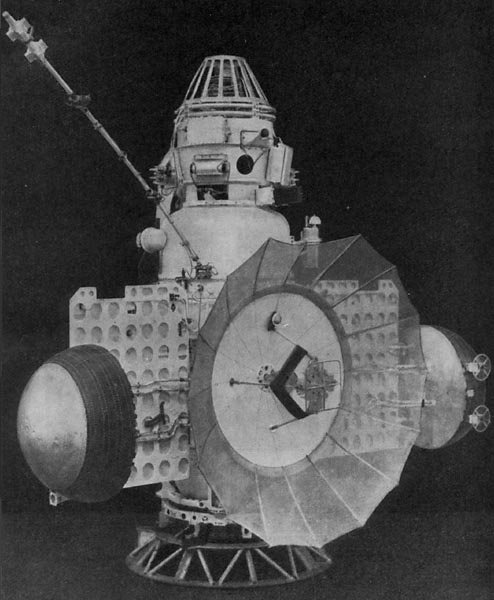
Zond 1 was a spacecraft of the Soviet Zond program. It was the second Soviet research spacecraft to reach Venus, although communications had failed by that time. It carried a 90 cm spherical landing capsule, containing experiments for chemical analysis of the atmosphere, gamma-ray measurements of surface rocks, a photometer, temperature and pressure gauges, and a motion/rocking sensor in case it landed in water. History At least three previous Soviet planetary probes had been lost due to malfunctions of the ullage rockets (BOZ) on the Blok L stage, but an investigation found that the problem was easily resolved. The spacecraft, a ''Venera 3MV-1'', was launched on April 2, 1964 from Tyuratam and this time the launch vehicle performed flawlessly. During the cruise phase, a slow leak from a cracked sensor window caused the electronics compartment to lose air pressure. This was a serious problem as Soviet electronics relied on vacuum tubes which would overheat without cooling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zond 2
Zond 2 was a Soviet space probe, a member of the Zond program, and was the sixth Soviet spacecraft to attempt a flyby of Mars. (See Exploration of Mars) It was launched on November 30, 1964 at 13:12 UTC onboard Molniya 8K78 launch vehicle from Baikonur Cosmodrome, Kazakhstan, USSR. The spacecraft was intended to survey Mars but lost communication before arrival. History Zond-2 carried a phototelevision camera of the same type later used to photograph the Moon on Zond 3. The camera system also included two ultraviolet spectrometers. As on Mars 1, an infrared spectrometer was installed to search for signs of methane on Mars. Zond 2 also carried six PPTs that served as actuators of the attitude control system. They were the first PPTs used on a spacecraft. The PPT propulsion system was tested during 70 minutes. Zond 2, a ''Mars 3MV-4A'' craft, was launched on November 30, 1964. During some maneuvering in early May 1965, communications were lost. Running on half power due to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zond 3
Zond 3 was a 1965 space probe which performed a flyby of the Moon far side, taking a number of quality photographs for its time. It was a member of the Soviet Zond program while also being part of the Mars 3MV project. It was unrelated to Zond spacecraft designed for manned circumlunar missions ( Soyuz 7K-L1). It is believed that Zond 3 was initially designed as a companion spacecraft to Zond 2 to be launched to Mars during the 1964 launch window. The opportunity to launch was missed, and the spacecraft was launched on a Mars-crossing trajectory as a spacecraft test, even though Mars was no longer attainable. Spacecraft design The spacecraft was of the 3MV-4 type, similar to Zond 2. In addition to a 106.4 mm focal length imaging system for visible light photography and ultraviolet spectrometry at 285-355 μm, it carried ultraviolet (190-275 μm) and infrared (3-4 μm) spectrophotometers, radiation sensors ( gas-discharge and scintillation counters), charged particle dete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zond 4
Zond 4, part of the Soviet Zond program and an uncrewed version of Soyuz 7K-L1 crewed Moon-flyby spacecraft, was one of the first Soviet experiments towards crewed circumlunar spaceflight. It was launched to test the spaceworthiness of the new capsule and to gather data about flights in circumterrestrial space. It was the first Soviet spacecraft to possess a computer, the 34 kg Argon 11. The spacecraft was successfully launched into a 354,000 km apogee orbit 180 degrees away from the Moon, It was launched away from the Moon probably to avoid trajectory complications with lunar gravity. However, on re-entry the L1's guidance system failed. It hit the atmosphere precisely at the calculated time, but was not guided to generate lift and fly out of the atmosphere again. A ballistic re-entry would mean no recovery on Soviet soil, so the APO destruct system automatically blew up the capsule at 10 to 15 km altitude, 180–200 km off the African coast at Guinea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zond 5
Zond 5 (russian: Зонд 5, lit=Probe 5) was a spacecraft of the Soviet Zond program. In September 1968 it became the first spaceship to travel to and circle the Moon, the first Moon mission to include animals, and the first to return safely to Earth. Zond 5 carried the first terrestrial organisms to the vicinity of the Moon, including two tortoises, fruit fly eggs, and plants. The Russian tortoise, Russian tortoises underwent biological changes during the flight, but it was concluded that the changes were primarily due to starvation and that they were little affected by space travel. A significant feature of travel to the Moon with terrestrial organisms, and their surviving the return trip, is that it establishes that transit through the Van Allen radiation belt may be less likely to be harmful for future space travelers. The Zond spacecraft was a version of the Soyuz 7K-L1 crewed lunar-flyby spacecraft. It was launched by a Proton-K carrier rocket with a Block D Multistage r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zond 3MV-1 No , wind turbine developer
{{disambiguation ...
Zond may refer to * Zond program, Soviet unmanned space program undertaken from 1964 to 1970 **Zond 1, spacecraft **Zond 2, spacecraft **Zond 3, spacecraft **Zond 4, spacecraft **Zond 5, spacecraft ** Zond 3MV-1 No.2, spacecraft **Zond 7, spacecraft **Zond 8, spacecraft ** Zond 1964A, spacecraft ** Zond 1967A, spacecraft **Zond 1967B, spacecraft *Zond Corporation GE Wind Energy is a branch of GE Renewable Energy, a subsidiary of General Electric. The company manufactures and sells wind turbines to the international market. In 2018, GE was the fourth largest wind turbine manufacturer in the world. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zond 7
Zond 7, a formal member of the Soviet Zond program and unmanned version of Soyuz 7K-L1 manned Moon-flyby spacecraft, the first truly successful test of L1, was launched towards the Moon on a Proton-K D rocket on August 7, 1969, on a mission of further studies of the Moon and circumlunar space, to obtain color photography of Earth and the Moon from varying distances, and to flight test the spacecraft systems. Earth photos were obtained on August 9, 1969. On August 11, 1969, the spacecraft flew past the Moon at a distance of 1984.6 km and conducted two picture taking sessions. On its way back from the moon the spacecraft tested its radio systems by transmitting recorded voices. Zond 7 reentered Earth's atmosphere on August 14, 1969, and achieved a soft landing in a preset region south of Kustanai, Kazakhstan. On its trip the craft carried 4 turtles. A human-like tissue-equivalent phantom for radiation measurements has been placed aboard. The phantom was equipped with 20 ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zond 8
Zond 8, also known as L-1 No.14, was the last in the series of circumlunar spacecraft, a member of the Soviet Zond program, designed to rehearse a piloted circumlunar flight, an uncrewed version of Soyuz 7K-L1 crewed circumlunar flight spacecraft. The project was initiated in 1965 to compete with the Americans in the race to the Moon but lost its importance once three astronauts circled the Moon on the Apollo 8 mission in December 1968. Mission Zond 8 was launched on 20 October 1970, at 19:55:39 GMT by a Proton-K / Blok D launcher from Site 81/23 of the Baikonur Cosmodrome, towards the Moon. Zond 8 had a mass of . The announced objectives of Zond 8 were investigations of the Moon and circumlunar space and testing of onboard systems and units. The spacecraft obtained photographs of Earth on 21 October from a distance of . After a mid-course correction on 22 October 1970 at a distance of from Earth. The spacecraft transmitted flight images of Earth for three days. Zond 8 reached ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zond 1964A
Zond program (Зонд; Russian for "probe") was a Soviet robotic spacecraft program launched between 1964 and 1970, using two spacecraft series, one for interplanetary exploration, and the other for lunar exploration. Program details The program had two series of spacecraft. The first series, based on the 3MV planetary probe, was intended to gather information about nearby planets. The second series of test spacecraft were intended as a precursor to crewed circumlunar loop flights, using a stripped-down variant of Soyuz spacecraft, consisting of the service and descent modules, but lacking the orbital module The Government of the Soviet Union had suppressed failed Space Race missions information to prevent bad publicity during the height of the Cold War and the Space Race. Since the fall of the Soviet Union in 1991, much previously restricted information became available. Zond 1964A Zond 1964A a SL-6/A-2-e launch vehicle launched 4 June 1964, failed to achieve Earth or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zond 1967A
Zond program (Зонд; Russian for "probe") was a Soviet robotic spacecraft program launched between 1964 and 1970, using two spacecraft series, one for interplanetary exploration, and the other for lunar exploration. Program details The program had two series of spacecraft. The first series, based on the 3MV planetary probe, was intended to gather information about nearby planets. The second series of test spacecraft were intended as a precursor to crewed circumlunar loop flights, using a stripped-down variant of Soyuz spacecraft, consisting of the service and descent modules, but lacking the orbital module The Government of the Soviet Union had suppressed failed Space Race missions information to prevent bad publicity during the height of the Cold War and the Space Race. Since the fall of the Soviet Union in 1991, much previously restricted information became available. Zond 1964A Zond 1964A a SL-6/A-2-e launch vehicle launched 4 June 1964, failed to achieve Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zond 1967B
Zond program (Зонд; Russian for "probe") was a Soviet robotic spacecraft program launched between 1964 and 1970, using two spacecraft series, one for interplanetary exploration, and the other for lunar exploration. Program details The program had two series of spacecraft. The first series, based on the 3MV planetary probe, was intended to gather information about nearby planets. The second series of test spacecraft were intended as a precursor to crewed circumlunar loop flights, using a stripped-down variant of Soyuz spacecraft, consisting of the service and descent modules, but lacking the orbital module The Government of the Soviet Union had suppressed failed Space Race missions information to prevent bad publicity during the height of the Cold War and the Space Race. Since the fall of the Soviet Union in 1991, much previously restricted information became available. Zond 1964A Zond 1964A a SL-6/A-2-e launch vehicle launched 4 June 1964, failed to achieve Earth o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)
