|
Zofia Poznańska
Zofia Poznańska, also known as Zosia, Zosha, or Sophia (8 June 190629 September 1942) was a Polish antifascist and resistance fighter of the Soviet-affiliated espionage group that the German Abwehr intelligence service later called the " Red Orchestra". Life Zofia Poznańska was born in Łódź, Congress Poland, Russian Empire, into the prosperous Jewish family of Mosze Poznański and Hana Poznańska, née Basz. She later grew up in Kalisz, after Poland regained its independence in 1918. As a youth she was a member of the left-wing Hashomer Hatzair Socialist-Zionist secular Jewish youth movement. In 1925, when she was 19, Poznańska emigrated to Palestine to live and work at the Mishmar HaEmek kibbutz, laying gravel to create roads. After becoming disillusioned with the kibbutz and struggling to reconcile her Socialist-Zionist politics with the displacement of Arab farmers, whose land was being purchased, Poznańska moved to Tel Aviv. There she met Leopold Trepper and joined h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Łódź
Łódź, also rendered in English as Lodz, is a city in central Poland and a former industrial centre. It is the capital of Łódź Voivodeship, and is located approximately south-west of Warsaw. The city's coat of arms is an example of canting arms, canting, as it depicts a boat ( in Polish language, Polish), which alludes to the city's name. As of 2022, Łódź has a population of 670,642 making it the country's List of cities and towns in Poland, fourth largest city. Łódź was once a small settlement that first appeared in 14th-century records. It was granted city rights, town rights in 1423 by Polish King Władysław II Jagiełło and it remained a private town of the Kuyavian bishops and clergy until the late 18th century. In the Second Partition of Poland in 1793, Łódź was annexed to Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia before becoming part of the Napoleonic Duchy of Warsaw; the city joined Congress Poland, a Russian Empire, Russian client state, at the 1815 Congress of Vien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewish Land Purchase In Palestine
Jewish land purchase in Palestine was the acquisition of land in Ottoman and Mandatory Palestine by Jews from the 1880s until the establishment of the State of Israel in 1948. By far the largest such arrangement was known as the Sursock Purchase. As of 1944, Jews had acquired 6% of the land in Palestine. Background Towards the end of the 19th-century, the creation of the Zionist movement resulted in many European Jews immigrating to Palestine. Most land purchases between the late 1880s and the 1930s were located in the coastal plain area, including "Acre to the North and Rehovoth to the South, the Esdraelon (Jezreel) and Jordan Valleys and to the lesser extent in Galilee". Porath (1977), p. 80. The migration affected Palestine in many ways, including economically, socially, and politically. The Talmud mentions the religious duty of settling the Land of Israel. It allows for the lifting of certain religious restrictions of Sabbath observance to further its acquisition and settl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Vauck
Wilhelm Vauck (born 8 October 1896 in Neustadt, Dresden; died 8 December 1968 in Bautzen) was a German mathematician, physicist and university lecturer in physics and electrical engineering. During World War II, Vauck was the director of the agents Referat within the Funkabwehr, the German Armies radio counter-intelligence organisation. As an anti-nazi, Vauck's work on the discovery of the Rote Kapelle anti-fascist resistance group during World War II, burdened him deeply until the end of his life. Life After World War I finished, Vauck undertook study of mathematics and physics at the Technical University of Dresden. In 1922, he passed the exam for a higher education office, and two years later, under supervision of Gerhard Kowalewski, Vauck was promoted to Dr. phil with a thesis titled ''A generalisation of Bolzano's continuous but non-differentiable function'' (german: Versuch einer Verallgemeinerung der stetigen nirgends differenzierbaren Funktion Bolzanos) which is within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brussels
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Brussels Hoofdstedelijk Gewest), is a region of Belgium comprising 19 municipalities, including the City of Brussels, which is the capital of Belgium. The Brussels-Capital Region is located in the central portion of the country and is a part of both the French Community of Belgium and the Flemish Community, but is separate from the Flemish Region (within which it forms an enclave) and the Walloon Region. Brussels is the most densely populated region in Belgium, and although it has the highest GDP per capita, it has the lowest available income per household. The Brussels Region covers , a relatively small area compared to the two other regions, and has a population of over 1.2 million. The five times larger metropolitan area of Brusse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
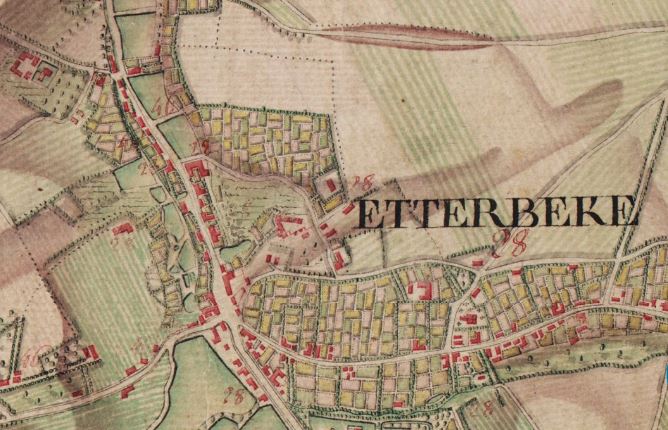
Etterbeek
Etterbeek ( French: ; Dutch: ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the eastern part of the region, it is bordered by the municipalities of Auderghem, the City of Brussels, Ixelles, Schaerbeek, Woluwe-Saint-Lambert and Woluwe-Saint-Pierre. In common with all of Brussels' municipalities, it is legally bilingual (French–Dutch). The main university campus of Vrije Universiteit Brussel (VUB) is called ''Campus Etterbeek'', although it is geographically not within Etterbeek but in the adjacent Ixelles. History Origins and etymology According to legend, Saint Gertrude of Nivelles, daughter of Pippin of Landen, founded a chapel there in the 8th century. A document by Holy Roman Emperor Otto I, dated 966, mentions the church of ''Iatrebache''. The name ''Ietrebecca''—possibly from the Celtic root ''ett'' meaning "rapid movement" and the Dutch word ''beek'' meaning "stream"—is found for the first time in a document dated 1127. The cur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rita Arnould
Rita Arnould ( – 20 August 1943) was a housekeeper and courier of the Red Orchestra resistance group in Belgium during World War II. She was captured when the Funkabwehr raided an apartment at 101 Rue des Atrébates in Brussels on 12 December 1941 at 2 pm. from which a Soviet clandestine radio station was being run. Early years Arnould was born in Frankfurt am Main to a Jewish family. She studied philosophy at Frankfurt am Main University, where she became the companion of Isidor Springer. He convinced her to become a Communist activist. In 1933 the couple moved to Brussels after Hitler had seized power since it was now dangerous in Germany to be either a Jew or Communist. Soon after reaching Brussels, she married A. M. Arnould, a well-to-do Dutch textile salesman who was over twice her age, and settled into a domestic routine. During World War II (1939–45) the Germans invaded Belgium in May 1940. Rita's husband died soon after, leaving her with no money. She asked Isidor Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikhail Makarov (spy)
Mikhail Varfolomeevich Makarov (* 2 January 1915 in Leningrad; † circa 1942) was a Russian national and career Soviet GRU (G.U.), GRU officer with rank of lieutenant, who was one of the organizers of a Soviet intelligence network in Belgium and Netherlands, that was later called the Red Orchestra (espionage), Red Orchestra by the Abwehr. His aliases were ''Alamo'', ''Carlos Alamo'' and ''Chemnitz''. In March 1939, Makarov became associated with Leopold Trepper, a Soviet intelligence agent who would later run a large espionage network in Europe. Makarov was captured on the 13 December 1941 by the Abwehr and later executed in Plötzensee Prison in 1942. Life Makarov was born into a poor family and lost his father at an early age. He went to school in his hometown for seven years and then studied French and Spanish at the Moscow State Linguistic University. He initially worked as a translator. and after the first delivery of the Polikarpov I-16 fighter planes to the Spanish Rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Main Intelligence Directorate (GRU)
Main Intelligence Directorate ( rus, Главное разведывательное управление, Glavnoye razvedyvatel'noye upravleniye, ˈglavnəjə rɐzˈvʲɛdɨvətʲɪlʲnəjə ʊprɐˈvlʲenʲɪjə), abbreviated GRU ( rus, ГРУ, p=geeˈru), was the foreign military intelligence agency of the Soviet Army General Staff of the Soviet Union until 1991. For a few months it was also the foreign military intelligence agency of the newly established Russian Federation until 7 May 1992 when it was dissolved and the GRU (Russian Federation), Russian GRU took over its activities. History The GRU's first predecessor in Russia formed on October 21, 1918 by secret order under the sponsorship of Leon Trotsky (then the civilian leader of the Red Army), signed by Jukums Vācietis, the first commander-in-chief of the Red Army (RKKA), and by Ephraim Sklyansky, deputy to Trotsky; it was originally known as the Registration Directorate (''Registrupravlenie'', or RU). Semyon Ara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national republics; in practice, both its government and its economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kiev (Ukrainian SSR), Minsk ( Byelorussian SSR), Tashkent (Uzbek SSR), Alma-Ata (Kazakh SSR), and Novosibirsk (Russian SFSR). It was the largest country in the world, covering over and spanning eleven time zones. The country's roots lay in the October Revolution of 1917, when the Bolsheviks, under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin, overthrew the Russian Provisional Government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yehudit Kafri
Yehudit Kafri Meiri ( he, יהודית כפרי מאירי; born 1935) is a 20th–21st century Israeli poet and a writer, as well as editor and translator. Biography She was born in 1935 and lived as a child in Kibbutz Ein HaHoresh, where her parents were founding members. Yehudit belonged to the first group of children born in this kibbutz. After she got married, she moved to Kibbutz Sasa, where she wrote her first book, ''The Time Will Have Mercy'' (Hebrew: הזמן ירחם), which was published in 1962, one year after she moved to Kibbutz Shoval with her family. In Kibbutz Shoval she published a few more poetry books and children's books and made her first attempt at writing prose including a book describing her childhood memories, ''All The Summer We Went Barefoot'' (Hebrew: כל הקיץ הלכנו יחפים), which was successful and sold several editions. Yehudit Kafri, mother of three and grandmother of four, has lived since 1989 with her husband in Mazkeret Batya, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palestine Communist Party
The Palestine Communist Party ( yi, פאלעסטינישע קומוניסטישע פארטיי, ''Palestinische Komunistische Partei'', abbreviated PKP; ar, الحزب الشيوعي الفلسطيني) was a political party in British Mandate of Palestine formed in 1923 through the merger of the Palestinian Communist Party and the Communist Party of Palestine. In 1924 the party was recognized as the Palestinian section of the Communist International.''Early Communism in Palestine'', Fred Halliday, Journal of Palestine Studies, Vol. 7, No. 2 (Winter, 1978), pp. 162-169 In its early years, the party was predominantly Jewish, but nevertheless held an anti-Zionist position. History In 1923, at the party congress, a position of support was adopted in favour of the Arab national movement as a movement "opposed to British imperialism and denounced Zionism as a movement of the Jewish bourgeoisie allied to British imperialism", a move that won it membership of the Comintern. The Party ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ihud
Ihud ( he, איחוד, 'Unity') was a small binationalist Zionist political party founded by Judah Leon Magnes, Martin Buber, Ernst Simon and Henrietta Szold, former supporters of Brit Shalom, in 1942"The History of the original Brit Shalom, founded 1925" britshalom.org following the . Other prominent members were , agronomist (1868–1947), and Judge Joseph Moshe Valero. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |