|
Zieria
''Zieria'' is a genus of plants in the family, Rutaceae. About sixty species have been formally described, all of which are endemic to Australia except for one species which is found in New Caledonia. They occur in all Australian states except Western Australia but the genus is under review and a number of species are yet to be described or the description published. Zierias are similar to the better known genus ''Boronia'' but can be distinguished by the number of stamens in the flowers. The name ''Zieria'' honours the Polish botanist John Zier. Description Plants in the genus ''Zieria'' are shrubs or small trees. The leaves are arranged in opposite pairs and are usually compound with three leaflets similar in shape but the middle leaflet slightly larger. The flowers are arranged in groups in the leaf axils and have four fused sepals and four petals alternating with the sepals. There are four stamens (eight in ''Boronia'') and four carpels with their styles fused. The fruit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zieria Prostrata
''Zieria prostrata '' commonly known as headland zieria, is a plant in the citrus Family (biology), family Rutaceae and is endemism, endemic to the Coffs Harbour district in New South Wales. It is a wikt:prostrate, prostrate shrub with leaves composed of three leaflets, and flowers with four pink to white petals. It is only known from four headlands and is classified as an endangered species. Description ''Zieria prostrata'' is a prostrate or low, scrambling shrub with wikt:glabrous, glabrous, ridged branches and which grows to a height of . Its leaves are composed of three narrow oval leaflets with the middle leaflet long and wide and the others smaller. Both surfaces of the leaf are the same colour, dotted with oil glands and glabrous, with a stalk long. The flowers are pink in the bud stage but turn white as they open. They are arranged in groups of mostly 3 to 7 (sometimes up to 32) in leaf wikt:axil, axils and the groups are usually much shorter than the leaves. The four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zieria Smithii
''Zieria smithii'', commonly known as sandfly zieria, lanoline bush or Smithian zieria, is a plant in the citrus family Rutaceae and is endemic to eastern and south-eastern Australia. It is a robust shrub with its leaves composed of three leaflets, and groups of flowers with four white petals, the groups usually shorter than the leaves. It is common and widespread along the coast and adjacent ranges. Description ''Zieria smithii'' is a shrub which grows to a height of and is sometimes robust or at other times spindly. Its leaves are composed of three leaflets with the middle leaflet oblong to lance-shaped long, and wide with a pointed tip. The upper surface of the leaflets is a darker green than the lower side, dotted with oil glands and mostly glabrous. The leaf stalk is long and the leaves are strongly aromatic when crushed. The flowers are usually white and are arranged in groups of up to 60 in upper leaf axils, the groups shorter than the leaves and each flower in dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zieria Involucrata
''Zieria involucrata'' is a plant in the citrus family Rutaceae and is endemic to New South Wales. It is a sparse, erect shrub with mostly three-part leaves and groups of up to 21 small white flowers, the groups shorter than the leaves. It mostly occurs in the lower Blue Mountains, but is also known from other areas around Sydney. Description ''Zieria involucrata '' is a sparse, erect shrub that grows to a height of with its branches and leaves densely covered with soft, velvety leaves. The leaves have a petiole long and are mostly composed of three elliptic to lance-shaped leaflets long and wide, although some leaves may have only one leaflet. The leaflets are more or less flat, dark green on the upper surface and light greyish-green below. The flowers are white, sometimes with a pink tinge and arranged in groups of between three and 21, the groups mostly shorter than the leaves. Hairy, leaf-like bracts surround the flowers and usually remain on the plant during flowering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zieria Compacta (habit)
''Zieria compacta '' is a plant in the citrus family Rutaceae and is endemic to eastern Australia. It is an erect, bushy shrub with leaves composed of three leaflets, and white flowers with four petals and four stamens. It usually grows in rocky places on steep hills. Description ''Zieria compacta'' is an erect, bushy shrub which grows to a height of about . The branches are smooth and lack obvious glands but are covered with a dense layer of hairs, especially when young. Its leaves are composed of three elliptic to egg-shaped leaflets with the middle leaflet long and wide and the others smaller. The leaf stalk is long. The upper surface of the leaves is glabrous and dark green while the lower surface is a paler green, covered with a thin, dense layer of hairs and has an obvious mid-vein. The flowers are white to pale pink and are arranged in groups of mostly six flowers (but sometimes as few as one or as many as 35) in leaf axils. The groups are usually about as long as the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zieria Chevalieri
''Zieria chevalieri'' is a species of plant in the family Rutaceae. It is endemic to New Caledonia ) , anthem = "" , image_map = New Caledonia on the globe (small islands magnified) (Polynesia centered).svg , map_alt = Location of New Caledonia , map_caption = Location of New Caledonia , mapsize = 290px , subdivision_type = Sovereign st .... References Endemic flora of New Caledonia chevalieri Vulnerable plants Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{Rutaceae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boronia
''Boronia'' is a genus of about 160 species of flowering plants in the citrus family Rutaceae. Most are endemic to Australia with a few species in New Caledonia, which were previously placed in the genus ''Boronella''. They occur in all Australian states but the genus is under review and a number of species are yet to be described or have the description published. Boronias are similar to familiar plants in the genera ''Zieria'', ''Eriostemon'' and '' Correa'' but can be distinguished from them by the number of petals or stamens. Some species have a distinctive fragrance and are popular garden plants. Description Plants in the genus ''Boronia'' are nearly always shrubs although a very small number occur as herbs or as small trees. The leaves are usually arranged in opposite pairs and may be simple leaves or compound leaves with up to nineteen or more leaflets, in either a pinnate or bipinnate arrangement. The flowers are arranged in groups in the leaf axils or on the ends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family ( la, familia, plural ') is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". What belongs to a family—or if a described family should be recognized at all—are proposed and determined by practicing taxonomists. There are no hard rules for describing or recognizing a family, but in plants, they can be characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Taxonomists often take different positions about descriptions, and there may be no broad consensus across the scientific community for some time. The publishing of new data and opini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linnean Society Of London
The Linnean Society of London is a learned society dedicated to the study and dissemination of information concerning natural history, evolution, and taxonomy. It possesses several important biological specimen, manuscript and literature collections, and publishes academic journals and books on plant and animal biology. The society also awards a number of prestigious medals and prizes. A product of the 18th-century enlightenment, the Society is the oldest extant biological society in the world and is historically important as the venue for the first public presentation of the theory of evolution by natural selection on 1 July 1858. The patron of the society was Queen Elizabeth II. Honorary members include: King Charles III of Great Britain, Emeritus Emperor Akihito of Japan, King Carl XVI Gustaf of Sweden (both of latter have active interests in natural history), and the eminent naturalist and broadcaster Sir David Attenborough. History Founding The Linnean Society ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monophyly
In cladistics for a group of organisms, monophyly is the condition of being a clade—that is, a group of taxa composed only of a common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population) and all of its lineal descendants. Monophyletic groups are typically characterised by shared derived characteristics ( synapomorphies), which distinguish organisms in the clade from other organisms. An equivalent term is holophyly. The word "mono-phyly" means "one-tribe" in Greek. Monophyly is contrasted with paraphyly and polyphyly as shown in the second diagram. A ''paraphyletic group'' consists of all of the descendants of a common ancestor minus one or more monophyletic groups. A '' polyphyletic group'' is characterized by convergent features or habits of scientific interest (for example, night-active primates, fruit trees, aquatic insects). The features by which a polyphyletic group is differentiated from others are not inherited from a common ancestor. These definitions have taken ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cynthia Morton
Cynthia Casson Morton (born August 1, 1955) is an American geneticist, professor at Harvard Medical School, and director of cytogenetics at Brigham and Women's Hospital. Biography Morton graduated in 1973 from Maryland's Easton High School and in 1977 from the College of William and Mary with a bachelor's degree in biology. In 1982 she received her Ph.D. in human genetics from the Medical College of Virginia. As a postdoc she worked at Children's Hospital of Boston and then for three-and-a-half years in Philip Leder's laboratory in Harvard Medical School's department of genetics. In 1987, the eminent pathologist Ramzi Cotran recruited her to become the Director of Cytogenetics at Brigham and Women's Hospital. At Harvard Medical School she is now the William Lambert Richardson Professor of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproductive Medicine as well as a professor of pathology. At Brigham and Women's Hospital she also holds the Keneth J. Ryan, M.D., Distinguished Chair in Obstetrics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
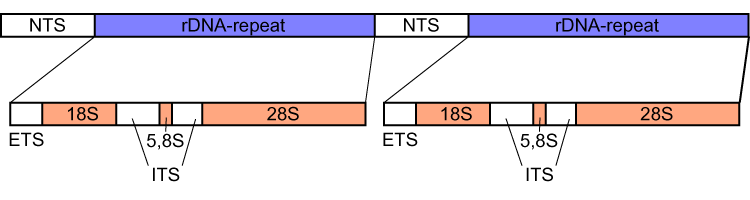
Internal Transcribed Spacer
Internal transcribed spacer (ITS) is the spacer DNA situated between the small-subunit ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and large-subunit rRNA genes in the chromosome or the corresponding transcribed region in the polycistronic rRNA precursor transcript. ITS across life domains In bacteria and archaea, there is a single ITS, located between the 16S and 23S rRNA genes. Conversely, there are two ITSs in eukaryotes: ITS1 is located between 18S and 5.8S rRNA genes, while ITS2 is between 5.8S and 28S (in opisthokonts, or 25S in plants) rRNA genes. ITS1 corresponds to the ITS in bacteria and archaea, while ITS2 originated as an insertion that interrupted the ancestral 23S rRNA gene. Organization In bacteria and archaea, the ITS occurs in one to several copies, as do the flanking 16S and 23S genes. When there are multiple copies, these do not occur adjacent to one another. Rather, they occur in discrete locations in the circular chromosome. It is not uncommon in bacteria to carry tRN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in the energy-storage molecules ATP and NADPH while freeing oxygen from water in the cells. The ATP and NADPH is then used to make organic molecules from carbon dioxide in a process known as the Calvin cycle. Chloroplasts carry out a number of other functions, including fatty acid synthesis, amino acid synthesis, and the immune response in plants. The number of chloroplasts per cell varies from one, in unicellular algae, up to 100 in plants like ''Arabidopsis'' and wheat. A chloroplast is characterized by its two membranes and a high concentration of chlorophyll. Other plastid types, such as the leucoplast and the chromoplast, contain little chlorophyll and do not carry out photosynthesis. Chloroplasts are highly dynamic—they circulat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

.jpg)