|
Zhu Yu (author)
Zhu Yu () was a Chinese maritime historian during the Song Dynasty (960–1279 AD). He retired in Huang Gang (黄岗) of the Hubei province, bought a country house and named it "Pingzhou". He called himself "Expert Vegetable Grower of Pingzhou (萍洲老圃)". Between 1111 and 1117 AD, Zhu Yu wrote the book ''Pingzhou Ketan'' (萍洲可談; Pingzhou Table Talks), published in 1119 AD.Needham, Volume 4, Part 3, 381. It covered a wide variety of maritime subjects and issues in China at the time. His extensive knowledge of maritime engagements, technologies, and practices were because his father, Zhu Fu, was the Port Superintendent of Merchant Shipping for Guangzhou from 1094 until 1099 AD, whereupon he was elevated to the status of governor there and served in that office until 1102 AD.Needham, Volume 4, Part 1, 279. ''Pingzhou Table Talks'' In terms of global significance, Zhu Yu's book was the first book in history to mention the use of the mariner's magnetic-needle compass for navi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Song Dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the rest of the Ten Kingdoms, ending the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. The Song often came into conflict with the contemporaneous Liao, Western Xia and Jin dynasties in northern China. After retreating to southern China, the Song was eventually conquered by the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The dynasty is divided into two periods: Northern Song and Southern Song. During the Northern Song (; 960–1127), the capital was in the northern city of Bianjing (now Kaifeng) and the dynasty controlled most of what is now Eastern China. The Southern Song (; 1127–1279) refers to the period after the Song lost control of its northern half to the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty in the Jin–Song Wars. At that time, the Song court retreated south o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
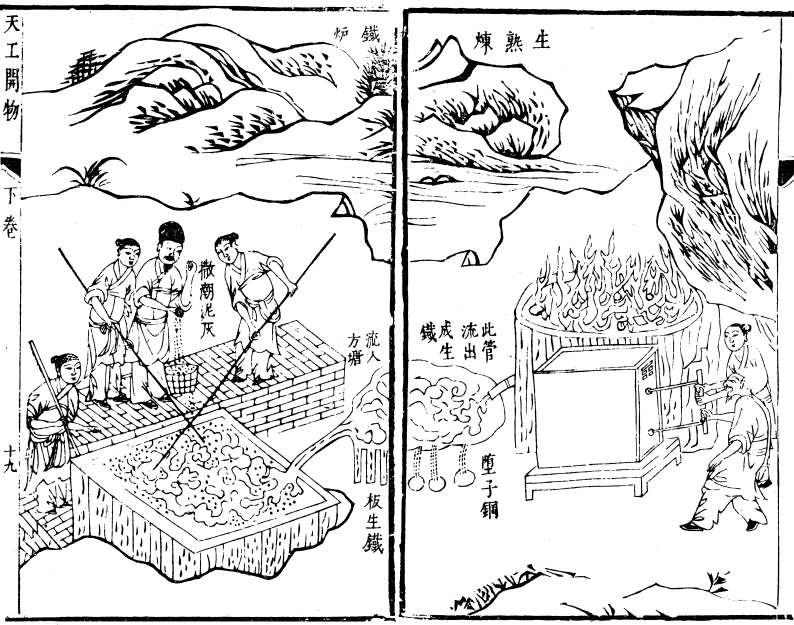
Song Yingxing
Song Yingxing ( Traditional Chinese: 宋應星; Simplified Chinese: 宋应星; Wade Giles: Sung Ying-Hsing; 1587-1666 AD) was a Chinese scientist and encyclopedist who lived during the late Ming Dynasty (1368–1644). He was the author of '' Tiangong Kaiwu'', an encyclopedia that covered a wide variety of technical subjects, including the use of gunpowder weapons.Needham, Volume 5, Part 7, 36. The British biochemist, sinologist, and historian Joseph Needham called Song Yingxing "The Diderot of China."Needham, Volume 5, Part 7, 102. Biography Song Yingxing was born in Yichun of Jiangxi in 1587 to a gentry family of reduced circumstances, he participated in the imperial examinations, and passed the provincial test in 1615, at the age of 28. He achieved only modest wealth and influence during his life. However, he was repeatedly unsuccessful in the metropolitan examination. Song sat for the test five times, the last being in 1631 at the age of 44. After this last failure, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
12th-century Chinese Historians
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Neckam
Alexander Neckam (8 September 115731 March 1217) was an English magnetician, poet, theologian, and writer. He was an abbot of Cirencester Abbey from 1213 until his death. Early life Born on 8 September 1157 in St Albans, Alexander shared his birthday with King Richard I. For this reason, his mother, Hodierna of St Albans, was hired by the royal household under Henry II to serve as a wet nurse for the future monarch. As a result, Alexander was raised as Richard's foster-brother in their early years. Works ''Speculum speculationum'' The ''Speculum speculationum'' (edited by Rodney M. Thomson, 1988) is Neckam's major surviving contribution to the science of theology. It is unfinished in its current form, but covers a fairly standard range of theological topics derived from Peter Lombard's ''Sentences'' and Augustine. Neckam is not regarded as an especially innovative or profound theologian, although he is notable for his early interest in the ideas of St. Anselm of Canterb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South-pointing Chariot
The south-pointing chariot (or carriage) was an ancient Chinese two-wheeled vehicle that carried a movable pointer to indicate the south, no matter how the chariot turned. Usually, the pointer took the form of a doll or figure with an outstretched arm. The chariot was supposedly used as a compass for navigation and may also have had other purposes. The ancient Chinese invented a mobile-like armored cart in the 5th century BC called the Dongwu Che (). It was used for the purpose of protecting warriors on the battlefield. The Chinese war wagon was designed as a kind of mobile protective cart with a shed-like roof. It would serve to be rolled up to city fortifications to provide protection for sappers digging underneath to weaken a wall's foundation. The early Chinese war wagon became the basis of technologies for the making of ancient Chinese south-pointing chariots. There are legends of earlier south-pointing chariots, but the first reliably documented one was created by the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wujing Zongyao
The ''Wujing Zongyao'' (), sometimes rendered in English as the ''Complete Essentials for the Military Classics'', is a Chinese military compendium written from around 1040 to 1044. The book was compiled during the Northern Song dynasty by Zeng Gongliang (曾公亮), Ding Du (丁度) and Yang Weide (楊惟德), whose writing influenced many later Chinese military writers. The compendium was published under the auspices of Emperor Renzong of Song, who also authored the book's preface. The book covers a wide range of subjects, including everything from naval warships to different types of catapults. It contains the earliest known written chemical formulas for gunpowder, made from saltpeter, sulphur and charcoal along with many added ingredients. In addition to formulas for gunpowder, the compendium also contains details on various other gunpowder weapons such as fire arrows, incendiary bombs and projectiles, and grenades and smoke bombs. It also describes an early for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technology Of The Song Dynasty
The Song dynasty (; 960–1279 CE) invented some technological advances in Chinese history, many of which came from talented statesmen drafted by the government through imperial examinations. The ingenuity of advanced mechanical engineering had a long tradition in China. The Song engineer Su Song admitted that he and his contemporaries were building upon the achievements of the ancients such as Zhang Heng (78–139), an astronomer, inventor, and early master of mechanical gears.Needham, Volume 4, Part 2, 466. The application of movable type printing advanced the already widespread use of woodblock printing to educate and amuse Confucian students and the masses. The application of new weapons employing the use of gunpowder enabled the Song to ward off its militant enemies—the Liao, Western Xia, and Jin with weapons such as cannons—until its collapse to the Mongol forces of Kublai Khan in the late 13th century. Notable advances in civil engineering, nautics, and metallurgy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Song Dynasty
The Song dynasty ( Chinese: 宋朝; pinyin: Sòng cháo; 960–1279) of China was an imperial dynasty that ruled most of China proper and southern China from the middle of the 10th century into the last quarter of the 13th century. The dynasty was established by Emperor Taizu of Song with his usurpation of the throne of Later Zhou, ending the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. The Song is considered a high point of classical Chinese innovation in science and technology, an era that featured prominent intellectual figures such as Shen Kuo and Su Song and the revolutionary use of gunpowder weapons. However, it was also a period of political and military turmoil, with opposing and often aggressive political factions formed at court that impeded political, social, and economic progress. The frontier management policies of the Chancellor Wang Anshi exacerbated hostile conditions along the Chinese-Vietnamese border. This sparked a border war with Vietnam's Lý dynasty, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waterproof
Waterproofing is the process of making an object or structure waterproof or water-resistant so that it remains relatively unaffected by water or resisting the ingress of water under specified conditions. Such items may be used in wet environments or underwater to specified depths. ''Water-resistant'' and ''waterproof'' often refer to resistance to penetration of water in its liquid state and possibly under pressure, whereas '' damp proof'' refers to resistance to humidity or dampness. Permeation of water vapour through a material or structure is reported as a moisture vapor transmission rate (MVTR). The hulls of boats and ships were once waterproofed by applying tar or pitch. Modern items may be waterproofed by applying water-repellent coatings or by sealing seams with gaskets or o-rings. Waterproofing is used in reference to building structures (such as basements, decks, or wet areas), watercraft, canvas, clothing (raincoats or waders), electronic devices and paper packa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tang Dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Historians generally regard the Tang as a high point in Chinese civilization, and a golden age of cosmopolitan culture. Tang territory, acquired through the military campaigns of its early rulers, rivaled that of the Han dynasty. The Lǐ family () founded the dynasty, seizing power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire and inaugurating a period of progress and stability in the first half of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty was formally interrupted during 690–705 when Empress Wu Zetian seized the throne, proclaiming the Wu Zhou dynasty and becoming the only legitimate Chinese empress regnant. The devastating An Lushan Rebellion (755–763) shook the nation and led to the decline of central authority in the dynas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)



