|
Zhongshu Sheng
The Zhongshu Sheng (), also known as the Palace Secretariat or Central Secretariat, was one of the departments of the Three Departments and Six Ministries government structure in imperial China from Cao Wei (220–266) until the early Ming dynasty. As one of the Three Departments, the Zhongshu Sheng was primarily a policy-formulating agency responsible for proposing and drafting all imperial decrees, but its actual function varied at different times. The department traces its origins back to the Han dynasty. History Origins: Han dynasty and Cao Wei The Central Secretariat originated during the reign of Emperor Wu of Han (r. 141-87 BC) to handle documents. The chief steward for writing (''shangshu'' 尚書), aided by eunuch secretary-receptionists (''zhongshu yezhe'' 中書謁者)), forwarded documents to the inner palace. This organization was headed by a Secretariat Director (''zhongshu ling'' 中書令) assisted by a Vice Director (''zhongshu puye'' 中書仆射). These two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
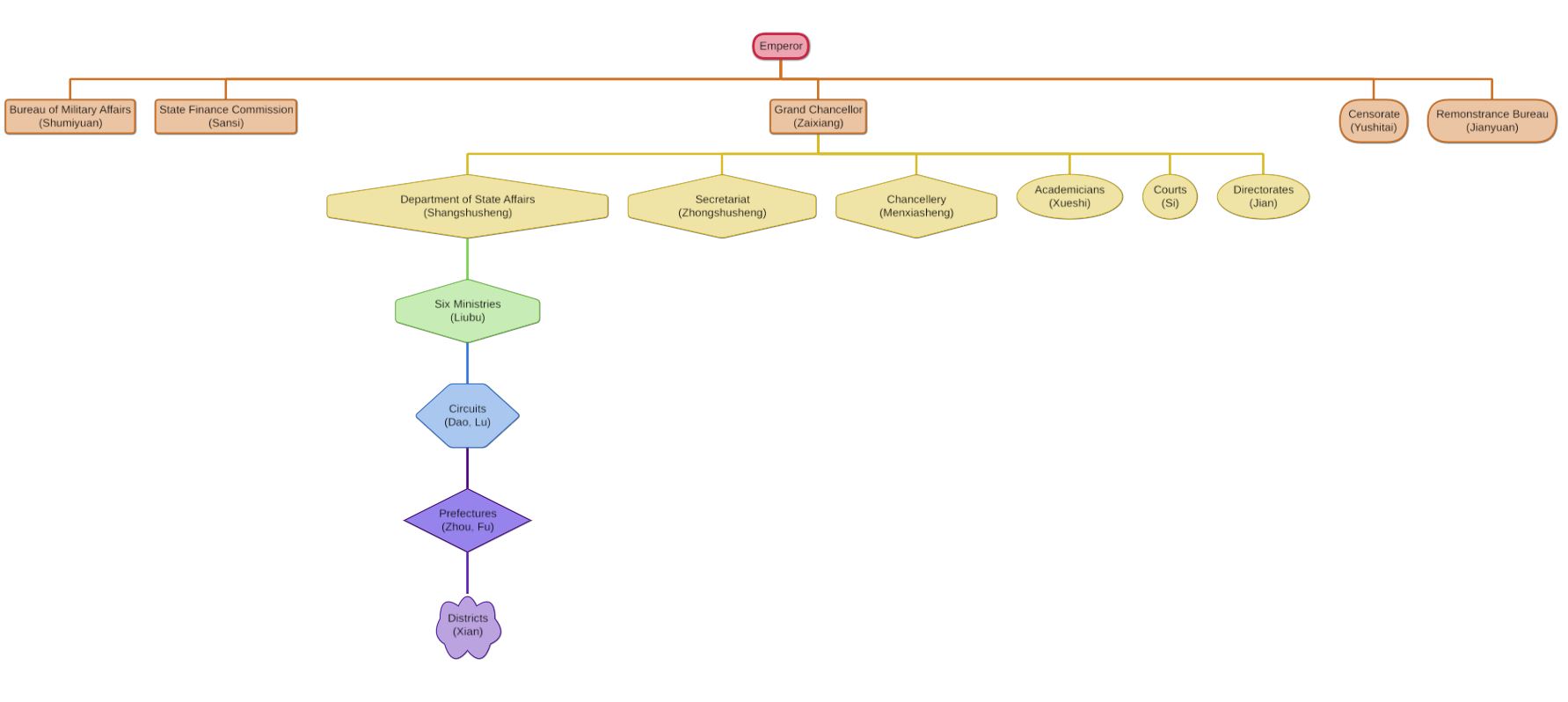
Three Departments And Six Ministries
The Three Departments and Six Ministries () system was the primary administrative structure in imperial China from the Sui dynasty (581–618) to the Yuan dynasty (1271–1368). It was also used by Balhae (698–926) and Goryeo (918–1392) and various other kingdoms in Manchuria, Korea and Vietnam. The Three Departments were three top-level administrative structures in imperial China. They were the Central Secretariat, responsible for drafting policy, the Chancellery, responsible for reviewing policy and advising the emperor, and the Department of State Affairs, responsible for implementing policy. The former two were loosely joined as the Secretariat-Chancellery during the late Tang dynasty, Song dynasty and in the Korean kingdom of Goryeo. The Six Ministries (also translated as Six Boards) were direct administrative organs of the state under the authority of the Department of State Affairs. They were the Ministries of Personnel, Rites, War, Justice, Works, and Revenue. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Chancellor (China)
The grand chancellor (''zaixiang, tsai-hsiang''), also translated as counselor-in-chief, chancellor, chief councillor, chief minister, imperial chancellor, lieutenant chancellor and prime minister, was the highest-ranking executive official in the imperial Chinese government. The term was known by many different names throughout Chinese history, and the exact extent of the powers associated with the position fluctuated greatly, even during a particular dynasty. During the Six Dynasties period, the term denoted a number of power-holders serving as chief administrators, including ''zhongshun jian'' (Inspector General of the Secretariat), ''zhongshu ling'' (President of the Secretariat), ''shizhong'' (Palace Attendant), ''shangshu ling'' and ''puye'' (president and vice-president of the Department of State Affairs). History In the Spring and Autumn period, Guan Zhong was the first chancellor in China, who became chancellor under the state of Qi in 685 BC. In Qin, during the Warring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khanbaliq
Khanbaliq or Dadu of Yuan () was the winter capital of the Yuan dynasty of China in what is now Beijing, also the capital of the People's Republic of China today. It was located at the center of modern Beijing. The Secretariat directly administered the Central Region () of the Yuan Empire (comprising present-day Beijing, Hebei, Shandong, Shanxi, and parts of Henan and Inner Mongolia) and dictated policies for the other provinces. Kublai and his successors also claimed supremacy over the entire Mongol Empire following the death of Möngke (Kublai's brother and predecessor) in 1259. Over time the unified empire gradually fragmented into a number of khanates. Khanbaliq is the direct predecessor to modern Beijing. Several stations of Line 10 and Line 13 are named after the gates of Dadu. Name The name Khanbaliq comes from the Mongolian and Old Uyghur words '' khan'' and ''balik'' ("town", "permanent settlement"): "City of the Khan". It was actually in use among the Turks an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Six Ministries
The Three Departments and Six Ministries () system was the primary administrative structure in imperial China from the Sui dynasty (581–618) to the Yuan dynasty (1271–1368). It was also used by Balhae (698–926) and Goryeo (918–1392) and various other kingdoms in Manchuria, Korea and Vietnam. The Three Departments were three top-level administrative structures in imperial China. They were the Central Secretariat, responsible for drafting policy, the Chancellery, responsible for reviewing policy and advising the emperor, and the Department of State Affairs, responsible for implementing policy. The former two were loosely joined as the Secretariat-Chancellery during the late Tang dynasty, Song dynasty and in the Korean kingdom of Goryeo. The Six Ministries (also translated as Six Boards) were direct administrative organs of the state under the authority of the Department of State Affairs. They were the Ministries of Personnel, Rites, War, Justice, Works, and Revenue. Duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuan Dynasty
The Yuan dynasty (), officially the Great Yuan (; xng, , , literally "Great Yuan State"), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after its division. It was established by Kublai, the fifth khagan-emperor of the Mongol Empire from the Borjigin clan, and lasted from 1271 to 1368. In orthodox Chinese historiography, the Yuan dynasty followed the Song dynasty and preceded the Ming dynasty. Although Genghis Khan had been enthroned with the Han-style title of Emperor in 1206 and the Mongol Empire had ruled territories including modern-day northern China for decades, it was not until 1271 that Kublai Khan officially proclaimed the dynasty in the traditional Han style, and the conquest was not complete until 1279 when the Southern Song dynasty was defeated in the Battle of Yamen. His realm was, by this point, isolated from the other Mongol-led khanates and controlled most of modern-day China and its surrounding areas, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family of Mongolic peoples. The Oirats in Western Mongolia as well as the Buryats and Kalmyks of Russia are classified either as distinct ethno-linguistic groups or subgroups of Mongols. The Mongols are bound together by a common heritage and ethnic identity. Their indigenous dialects are collectively known as the Mongolian language. The ancestors of the modern-day Mongols are referred to as Proto-Mongols. Definition Broadly defined, the term includes the Mongols proper (also known as the Khalkha Mongols), Buryats, Oirats, the Kalmyk people and the Southern Mongols. The latter comprises the Abaga Mongols, Abaganar, Aohans, Baarins, Chahars, Eastern Dorbets, Gorlos Mongols, Jalaids, Jaruud, Kharchins, Khishig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wanyan Liang
Digunai (24 February 1122 – 15 December 1161), also known by his sinicised name Wanyan Liang (完顏亮) and his formal title Prince of Hailing (海陵王, ''Hǎilíng Wáng''), was the fourth emperor of the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty of China. He was the second son of Wanyan Zonggan, the eldest son of Aguda (Emperor Taizu) (the founder of the Jin dynasty). He came to power in 1150 after overthrowing and murdering his predecessor, Emperor Xizong, in a ''coup d'état''. During his reign, he moved the Jin capital from Shangjing (present-day Acheng District, Harbin, Heilongjiang Province) to Yanjing (present-day Beijing), and introduced a policy of sinicisation. In 1161, after the Jin dynasty lost the Battle of Caishi against the Southern Song dynasty, Digunai's subordinates rebelled against him and assassinated him. After his death, even though he ruled as an emperor during his lifetime, he was posthumously demoted to the status of a prince – "Prince Yang of Hailing" (海陵煬� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jin Dynasty (1115–1234)
The Jin dynasty (, ; ) or Jin State (; Jurchen: Anchun Gurun), officially known as the Great Jin (), was an imperial dynasty of China that existed between 1115 and 1234. Its name is sometimes written as Kin, Jurchen Jin, Jinn, or Chin in English to differentiate it from an earlier Jìn dynasty whose name is rendered identically in Hanyu Pinyin without the tone marking. It is also sometimes called the "Jurchen dynasty" or the "Jurchen Jin", because members of the ruling Wanyan clan were of Jurchen descent. The Jin emerged from Wanyan Aguda's rebellion against the Liao dynasty (916–1125), which held sway over northern China until the nascent Jin drove the Liao to the Western Regions, where they became known in historiography as the Western Liao. After vanquishing the Liao, the Jin launched a century-long campaign against the Han-led Song dynasty (960–1279), which was based in southern China. Over the course of their rule, the ethnic Jurchen emperors of the Jin dynas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jurchen People
Jurchen (Manchu: ''Jušen'', ; zh, 女真, ''Nǚzhēn'', ) is a term used to collectively describe a number of East Asian Tungusic-speaking peoples, descended from the Donghu people. They lived in the northeast of China, later known as Manchuria, before the 18th century. The Jurchens were renamed Manchus in 1635 by Hong Taiji. Different Jurchen groups lived as hunter-gatherers, pastoralist semi-nomads, or sedentary agriculturists. Generally lacking a central authority, and having little communication with each other, many Jurchen groups fell under the influence of neighbouring dynasties, their chiefs paying tribute and holding nominal posts as effectively hereditary commanders of border guards. Chinese officials of the Ming dynasty (1368-1644) classified them into three groups, reflecting relative proximity to China: # Jianzhou (Chinese: 建州) Jurchens, some of whom were mixed with Korean and Chinese populations, lived in the proximity of the Mudan river, the Changbai mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liao Dynasty
The Liao dynasty (; Khitan: ''Mos Jælud''; ), also known as the Khitan Empire (Khitan: ''Mos diau-d kitai huldʒi gur''), officially the Great Liao (), was an imperial dynasty of China that existed between 916 and 1125, ruled by the Yelü clan of the Khitan people. Founded around the time of the collapse of the Tang dynasty, at its greatest extent it ruled over Northeast China, the Mongolian Plateau, the northern part of the Korean Peninsula, southern portions of the Russian Far East, and the northern tip of the North China Plain. The dynasty had a history of territorial expansion. The most important early gains was the Sixteen Prefectures (including present-day Beijing and part of Hebei) by fueling a proxy war that led to the collapse of the Later Tang dynasty (923–936). In 1004, the Liao dynasty launched an imperial expedition against the Northern Song dynasty. After heavy fighting and large casualties between the two empires, both sides worked out the Chanyuan Trea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khitan People
The Khitan people (Khitan small script: ; ) were a historical nomadic people from Northeast Asia who, from the 4th century, inhabited an area corresponding to parts of modern Mongolia, Northeast China and the Russian Far East. As a people descended from the proto-Mongols through the Xianbei, Khitans spoke the Khitan language, a Para-Mongolic language related to the Mongolic languages. During the Liao dynasty, they dominated a vast area of Siberia and Northern China. After the fall of the Liao dynasty in 1125 following the Jurchen invasion, many Khitans followed Yelü Dashi's group westward to establish the Qara Khitai or Western Liao dynasty, in Central Asia, which lasted nearly a century before falling to the Mongol Empire in 1218. Other regimes founded by the Khitans included the Northern Liao, Eastern Liao and Later Liao in China, as well as the Qutlugh-Khanid dynasty in Persia. Etymology There is no consensus on the etymology of the name of Khitan. There are basica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Song
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the rest of the Ten Kingdoms, ending the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. The Song often came into conflict with the contemporaneous Liao dynasty, Liao, Western Xia and Jin dynasty (1115–1234), Jin dynasties in northern China. After retreating to southern China, the Song was eventually conquered by the Mongols, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The dynasty is divided into History of the Song dynasty, two periods: Northern Song and Southern Song. During the Northern Song (960–1127), Northern Song (; 960–1127), the capital was in the northern city of Kaifeng, Bianjing (now Kaifeng) and the dynasty controlled most of what is now Eastern China. The #Southern Song, 1127–1279, Southern Song (; 1127–1279) refers to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |