|
Zenjibu-ji
Zenjibu-ji is a Shingon Buddhist Temple located in Nankoku, Kōchi, Japan. It is the 32nd temple of the Shikoku 88 Temple Pilgrimage The or is a multi-site pilgrimage of 88 temples associated with the Buddhist monk Kūkai (''Kōbō Daishi'') on the island of Shikoku, Japan. A popular and distinctive feature of the island's cultural landscape, and with a long history .... History According to the temple records, the temple hall was created under imperial decree from Emperor Shōmuin order to pray for the safety of Gyōki during a sea voyage. Later, Kūkai sensed that the hall was a sacred place, and carved Kannon as the honzon of the temple while performing a goma. Because the mountain the temple was located on was shaped like the eight-leafed lotus and Mount Potalaka, Kūkai prayed to Akasagarbha, and named the temple Gumonji-in Zenjibu-ji (求聞持院禅師峰寺). The Honzon is called Funadama Kannon (船魂(ふなだま)の観音 lit. ship spirit K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
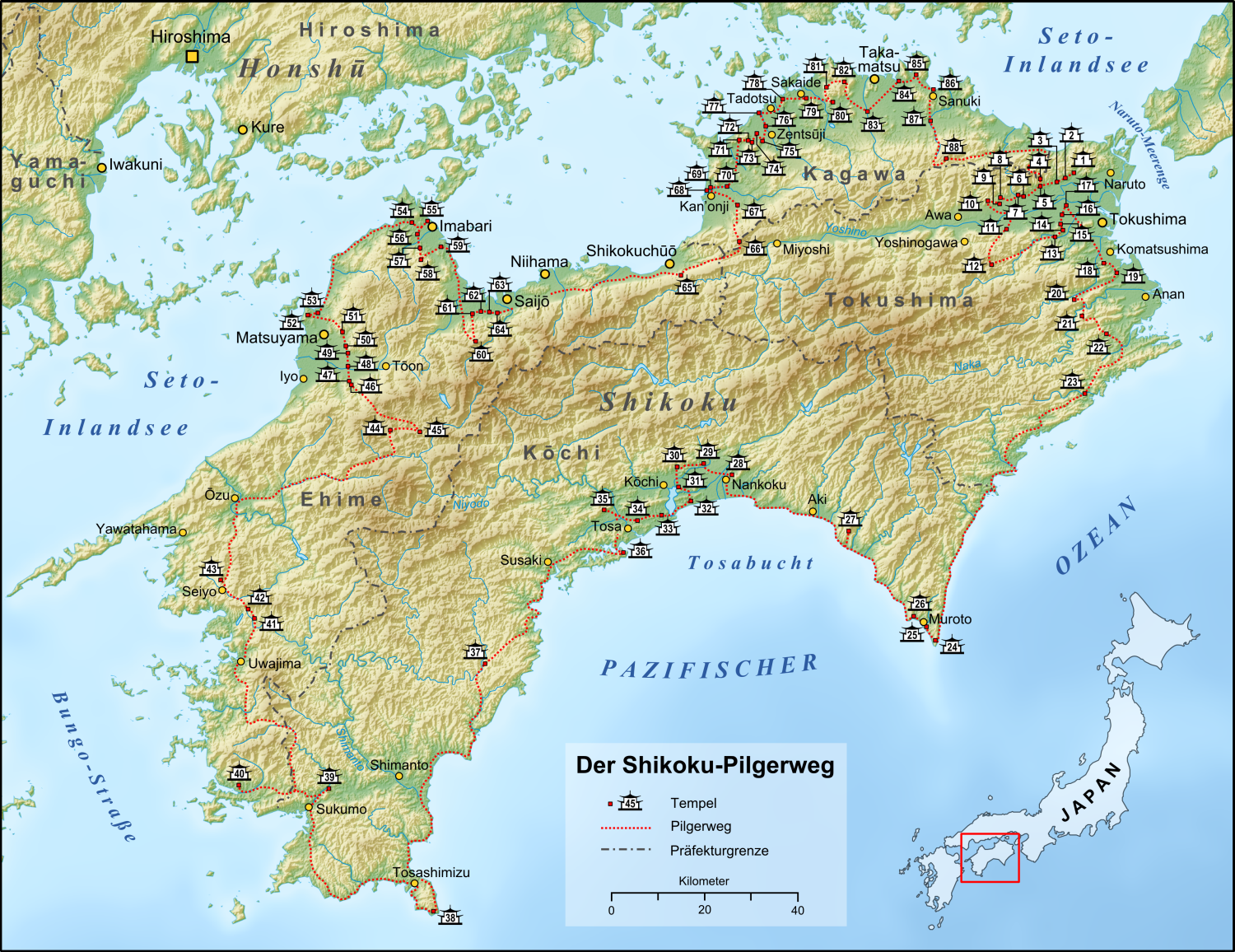
Shikoku Pilgrimage
The or is a multi-site pilgrimage of 88 temples associated with the Buddhist monk Kūkai (''Kōbō Daishi'') on the island of Shikoku, Japan. A popular and distinctive feature of the island's cultural landscape, and with a long history, large numbers of pilgrims, known as , still undertake the journey for a variety of ascetic, pious, and tourism-related purposes. The pilgrimage is traditionally completed on foot, but modern pilgrims use cars, taxis, buses, bicycles, or motorcycles, and often augment their travels with public transportation. The standard walking course is approximately long and can take anywhere from 30 to 60 days to complete. In addition to the 88 "official" temples of the pilgrimage, there are 20 ''bekkaku'' (別格) temples, which are officially associated with the Shikoku Pilgrimage (and hundreds more ''bangai'' (番外) temples, simply meaning "outside the numbers," which are not considered part of the official 88). To complete the pilgrimage, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nankoku, Kōchi
is a Cities of Japan, city located in Kōchi Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 46‚459 in 22499 households and a population density of 370 persons per km². The total area of the city is . Geography Nankoku is located in the center of Kochi Prefecture on the island of Shikoku. The northern part of the city is in the southern end of the Shikoku Mountains and the southern part has an eight kilometer long coastline on the Pacific Ocean. In between is the Kochi Plain, with the Mononobe River flowing from north to south on the border with Konan. About half of the municipality is forested. Neighbouring municipalities Kōchi Prefecture * Kōchi (city), Kōchi * Kami, Kōchi, Kami * Kōnan, Kōchi, Kōnan * Motoyama, Kōchi, Motoyama * Tosa, Kōchi (town), Tosa Climate Nankoku has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification ''Cfa'') with hot, humid summers and cool winters. There is significant precipitation throughout the year, especiall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kōchi Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located on the island of Shikoku. Kōchi Prefecture has a population of 757,914 (1 December 2011) and has a geographic area of 7,103 km2 (2,742 sq mi). Kōchi Prefecture borders Ehime Prefecture to the northwest and Tokushima Prefecture to the northeast. Kōchi is the capital and largest city of Kōchi Prefecture, with other major cities including Nankoku, Shimanto, and Kōnan. Kōchi Prefecture is located on Japan's Pacific coast surrounding a large bay in the south of Shikoku, with the southernmost point of the island located at Cape Ashizuri in Tosashimizu. Kōchi Prefecture is home to Kōchi Castle, considered the most intact Japanese castle, and the Shimanto River, one of the few undammed rivers in Japan. History Kōchi Prefecture was historically known as Tosa Province and was controlled by the Chōsokabe clan in the Sengoku period and the Yamauchi clan during the Edo period. Kōchi city is also the birthplace of noted revolutiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ākāśagarbha
Ākāśagarbha (, Standard Tibetan ''Namkha'i Nyingpo'', Vietnamese ''Hư Không Tạng Bồ Tát'') is a bodhisattva in Chinese, Japanese and Korean Buddhism who is associated with the great element (''mahābhūta'') of space ( ''ākāśa''). He is also sometimes called Gaganagañja, which means "sky-jewel." Overview Ākāśagarbha is regarded as one of the eight great bodhisattvas. His name can be translated as "boundless space treasury" or "void store" as his wisdom is said to be boundless as space itself. He is sometimes known as the twin brother of the "earth store" bodhisattva Kṣitigarbha, and is even briefly mentioned in the ''Kṣitigarbha Bodhisattva Pūrvapraṇidhāna Sūtra''. Kūkai, the founder of Shingon Buddhism, met a famous monk who is said to have repeatedly chanted a mantra of Ākāśagarbha as a young Buddhist acolyte. Kūkai took a tutorial with him on Kokuzou-Gumonji (a secret doctorine method, 虚空蔵求聞持法). As he chanted the mantra, he experienc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhist Temples In Japan
Buddhist temples or Buddhist monasteries together with Shinto shrines, are considered to be amongst the most numerous, famous, and important religious buildings in Japan.The term "Shinto shrine" is used in opposition to "Buddhist temple" to mirror in English the distinction made in Japanese between Shinto and Buddhist religious structures. In Japanese the first are called , the second . The shogunates or leaders of Japan have made it a priority to update and rebuild Buddhist temples since the Momoyama period. The Japanese word for a Buddhist monastery is ( ''kun'' reading) and the same kanji also has the pronunciation ''ji'' (''on'' reading), so that temple names frequently end in ''-dera'' or ''-ji''. Another ending, , is normally used to refer to minor temples. Such famous temples as Kiyomizu-dera, Enryaku-ji and Kōtoku-in are temples which use the described naming pattern. Etymology The Japanese word for a Buddhist temple was anciently also written phonetically 天良, ''ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shingon Buddhism
Shingon monks at Mount Koya is one of the major schools of Buddhism in Japan and one of the few surviving Vajrayana lineages in East Asia, originally spread from India to China through traveling monks such as Vajrabodhi and Amoghavajra. Known in Chinese as the Tangmi (; the Esoteric School in Tang Dynasty of China), these esoteric teachings would later flourish in Japan under the auspices of a Buddhist monk named Kūkai (), who traveled to Tang China to acquire and request transmission of the esoteric teachings. For that reason, it is often called Japanese Esoteric Buddhism, or Orthodox Esoteric Buddhism. The word ''shingon'' is the Japanese reading of the Chinese word ('), which is the translation of the Sanskrit word ("mantra"). History Shingon Buddhist doctrine and teachings arose during the Heian period (794-1185) after a Buddhist monk named Kūkai traveled to China in 804 to study Esoteric Buddhist practices in the city of Xi'an (), then called Chang-an, at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sekkei-ji
Sekkei-ji is a Shingon Buddhist Temple located in Kōchi, Kōchi, Japan. It is the 33rd temple of the Shikoku Pilgrimage. History According to the temple records, Kukai founded the temple, and named it ''Shourinsan Koufukuji'' (少林山高福寺 lit. Small Grove Mountain, Great Luck Temple). The statues that flank the main Honzon on the left and right are thought to be created by the great sculptor Tankei in the year at the beginning of the Karoku era, 1225. However there are no records of Tankei having any relation to the Tosa domain. There is also an explanation that sometime during the Kamakura period, Unkei along with his eldest son Tankei had arrived at the temple and renamed it “Keiun-ji” (慶運寺). Following the Kamakura period, the temple was in ruins, but during the Tensho era (1573-1593) a new priest that was a supporter of Chosokabe Motochika during the Sengoku period, revived the temple as a Rinzai Zen temple. During the fourth year of the Keicho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chikurin-ji (Kōchi)
is a Shingon temple in Kōchi, Kōchi Prefecture, Japan. Temple 31 on the Shikoku 88 temple pilgrimage, the main image is of Monju Bosatsu. The temple is said to have been founded by Gyōki in the early eighth century. The temple houses a number of important sculptures and its late Edo-period gardens are a Natural Monument. Buildings * Hondō, late Muromachi period, 5x5 bay, single storey, with a hip-and-gable shingle roof ( Important Cultural Property) * Reception hall, Edo period ( Prefectural Cultural Property) * Sanmon * Five-storey pagoda * Shōrō * Daishidō Treasures * Wooden pentad of Monju Bosatsu (late Heian period) (ICP) * Standing wooden statue of Amida Nyorai (late Heian period) (ICP) * Standing wooden statues of Tamonten and Zōjōten (late Heian period) (ICP) * Seated wooden statue of Yakushi (late Heian period) (ICP) * Standing wooden statue of Jūichimen Kannon (late Heian period) (ICP) * Seated wooden statue of Shaka Nyorai (late Heian period) (ICP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sankin-kōtai
''Sankin-kōtai'' ( ja, 参覲交代/参覲交替, now commonly written as ja, 参勤交代/参勤交替, lit=alternate attendance, label=none) was a policy of the Tokugawa shogunate during most of the Edo period of Japanese history.Jansen, Marius B. (2000). ''The Making of Modern Japan'', pp. 127–141. The purpose was to strengthen central control over the ''daimyōs'' (major feudal lords). It required feudal lords, ''daimyō'', to alternate living for a year in their domain and in Edo, the capital. History Toyotomi Hideyoshi had earlier established a similar practice of requiring his feudal lords to keep their wives and heirs at Osaka Castle or the nearby vicinity as hostages to ensure their loyalty. Following the Battle of Sekigahara and the establishment of the Tokugawa Shogunate, this practice was continued at the new capital of Edo as a matter of custom. It was made compulsory for the ''tozama daimyōs'' in 1635, and for the ''fudai daimyōs'' from 1642. Aside fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamauchi Kazutoyo
, also spelled Yamanouchi (1545/1546? – November 1, 1605). He was retainer of Oda Nobunaga and later Toyotomi Hideyoshi. His father Yamauchi Moritoyo, was a descendant of Fujiwara no Hidesato, a senior retainer of the Iwakura Oda clan (opposed to Oda Nobunaga), and lord of Kuroda castle in Owari Province at the end of the Sengoku period of Japan. He was famous as the husband of Yamauchi Chiyo. Military life When he was still a 400-Koku lord, many great people as children were entrusted to him, such as Kuroda Nagamasa when he was hostage of Oda Nobunaga and Toyotomi Hidetsugu were taught by him. He participated at Battle of Anegawa 1570 in the Oda's side. After the Siege of Odawara (1590) and the rise to power of Toyotomi Hideyoshi, Tokugawa Ieyasu was forced to trade his domains in the Tōkai region for the Kantō region instead. Kazutoyo was relinquished Kakegawa Castle from Hideyoshi. In 1600, Kazutoyo fought at the Battle of Sekigahara on Tokugawa Ieyasu's side. Aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
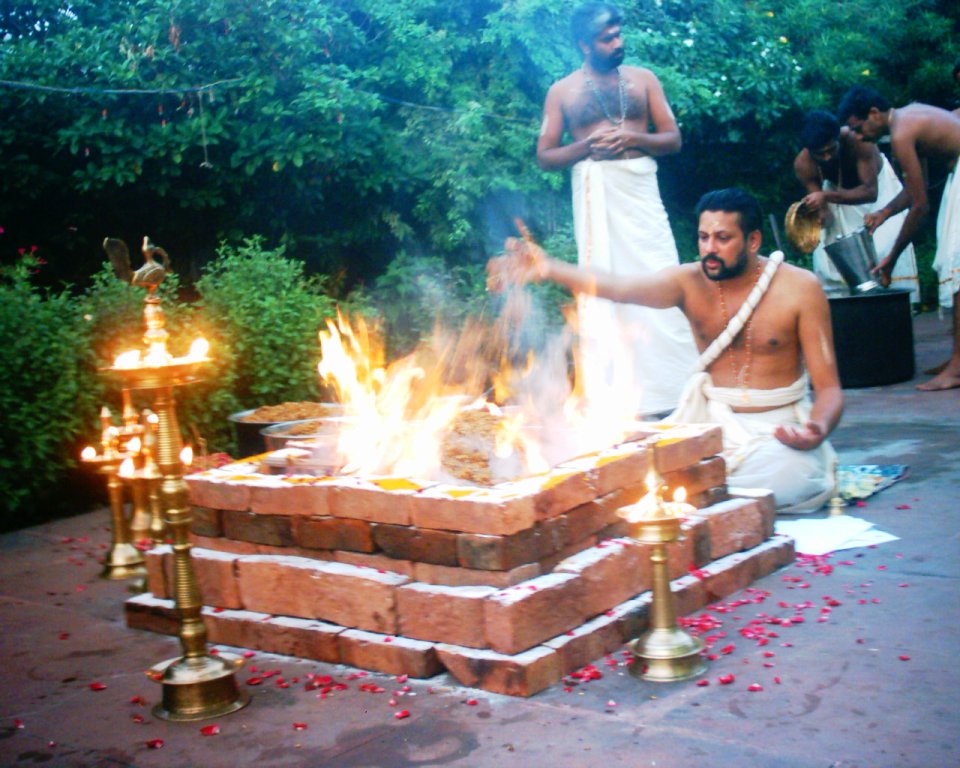
Homa (ritual)
In the Vedic Hinduism, a homa (Sanskrit: होम) also known as havan, is a fire ritual performed on special occasions by a Hindu priest usually for a homeowner (" grihastha": one possessing a home). The grihasth keeps different kinds of fire including one to cook food, heat his home, amongst other uses; therefore, a Yajna offering is made directly into the fire. A homa is sometimes called a "sacrifice ritual" because the fire destroys the offering, but a homa is more accurately a "votive ritual". The fire is the agent, and the offerings include those that are material and symbolic such as grains, ghee, milk, incense and seeds. It is rooted in the Vedic religion, and was adopted in ancient times by Buddhism and Jainism. The practice spread from India to Central Asia, East Asia and Southeast Asia. Homa rituals remain an important part of many Hindu ceremonies, and variations of homa continue to be practiced in current-day Buddhism, particularly in parts of Tibet and Japan. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Potalaka
Mount Potalaka (, Japanese: 補陀洛 ''Fudaraku-san''), which means "Brilliance", is the mythical dwelling of the Buddhist bodhisattva Avalokiteśvara, said to exist in the seas south of India. Origins The mountain is first mentioned in the final chapter of the '' Avataṃsaka Sūtra'', the '' Gaṇḍavyūha Sūtra'', where the chapter's protagonist journeys to seek the advice of Avalokiteśvara. The Japanese scholar Shu Hikosaka, on the basis of his study of Buddhist scriptures, ancient Tamil literary sources, as well as field survey, proposes the hypothesis that, the ancient mount Potalaka, the residence of Avalokiteśvara described in the ''Gaṇḍavyūha Sūtra'' and Xuanzang’s ''Great Tang Records on the Western Regions'', is the real mountain Potikai or Potiyil situated at Ambasamudram in Tirunelveli district, vast part of area comes under Singampatti zamindar forest, Tamil Nadu. Hikosaka, Shu. "The Potiyil Mountain in Tamil Nadu and the Origin of the Avalokiteśvar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |