|
Zenith Parsing Engine
ZPE Programming Environment (or simply ZPE), formerly the Zenith Parsing Engine, is a general-purpose compiler, parser and runtime environment for the YASS programming language designed for educational use as well as for its general use. The language it interprets, YASS, is an interpreted, high-level, general-purpose programming language. YASS is largely built upon making the language easy to read and use, with optional support for syntaxes such as curly-bracket syntax. YASS supports dynamic typing or static typing, as well as strong typing and weak typing. It was started in May 2015 as a planned university project but was later changed to be a replacement for another programming language developing at the time known as BlackRabbit Script, also built by Jamie Balfour. ZPE and YASS were designed to help with the automation of scripts by clearing up the inconsistent syntaxes of other scripting languages. The Zenith Parsing Engine (formerly ZenithParser) powers the underlying pars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Imperative Programming
In computer science, imperative programming is a programming paradigm of software that uses Statement (computer science), statements that change a program's state (computer science), state. In much the same way that the imperative mood in natural languages expresses commands, an imperative program consists of command (computing), commands for the computer to perform. Imperative programming focuses on describing ''how'' a program operates step by step (with general order of the steps being determined in source code by the placement of statements one below the other), rather than on high-level descriptions of its expected results. The term is often used in contrast to declarative programming, which focuses on ''what'' the program should accomplish without specifying all the details of ''how'' the program should achieve the result. Procedural programming Procedural programming is a type of imperative programming in which the program is built from one or more procedures (also termed s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sectors of the computing industry – Windows (unqualified) for a consumer or corporate workstation, Windows Server for a Server (computing), server and Windows IoT for an embedded system. Windows is sold as either a consumer retail product or licensed to Original equipment manufacturer, third-party hardware manufacturers who sell products Software bundles, bundled with Windows. The first version of Windows, Windows 1.0, was released on November 20, 1985, as a graphical operating system shell for MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces (GUIs). The name "Windows" is a reference to the windowing system in GUIs. The 1990 release of Windows 3.0 catapulted its market success and led to various other product families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
TOML
Tom's Obvious, Minimal Language (TOML, originally ''Tom's Own Markup Language'') is a file format for configuration files. It is intended to be easy to read and write due to obvious semantics which aim to be "minimal", and it is designed to map unambiguously to a dictionary. Originally created by Tom Preston-Werner, its specification is open source. TOML is used in a number of software projects and is implemented in many programming languages. Syntax TOML's syntax primarily consists of key = value pairs, ection names/code>, and # (for comments). TOML's syntax somewhat resembles that of .INI files, but it includes a formal specification, whereas the INI file format suffers from many competing variants. Its specification includes a list of supported data types: string, integer, float, boolean, datetime, array, and table. Example # This is a TOML document. title = "ImpalaPay Co." atabaseserver = "192.168.1.1" ports = 8000, 8001, 8002 connection_max = 5000 enabled = true # ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
JSON
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation, pronounced or ) is an open standard file format and electronic data interchange, data interchange format that uses Human-readable medium and data, human-readable text to store and transmit data objects consisting of name–value pairs and array data type, arrays (or other serialization, serializable values). It is a commonly used data format with diverse uses in electronic data interchange, including that of web applications with server (computing), servers. JSON is a Language-independent specification, language-independent data format. It was derived from JavaScript, but many modern programming languages include code to generate and parse JSON-format data. JSON filenames use the extension .json. Douglas Crockford originally specified the JSON format in the early 2000s. Transcript: He and Chip Morningstar sent the first JSON message in April 2001. Naming and pronunciation The 2017 international standard (ECMA-404 and ISO/IEC 21778:2017) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Comma-separated Values
Comma-separated values (CSV) is a text file format that uses commas to separate values, and newlines to separate records. A CSV file stores Table (information), tabular data (numbers and text) in plain text, where each line of the file typically represents one data record (computer science), record. Each record consists of the same number of field (computer science), fields, and these are separated by commas in the CSV file. If the field delimiter itself may appear within a field, fields can be surrounded with quotation marks. The CSV file format is one type of Delimiter-separated values, delimiter-separated file format. Delimiters frequently used include the comma, tab-separated values, tab, space, and semicolon. Delimiter-separated files are often given a ".csv" filename extension, extension even when the field separator is not a comma. Many applications or libraries that consume or produce CSV files have options to specify an alternative delimiter. The lack of adherence to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
List Of Programming Languages By Type
This is a list of notable programming languages, grouped by type. The groupings are overlapping; not mutually exclusive. A language can be listed in multiple groupings. Agent-oriented programming languages Agent-oriented programming allows the developer to build, extend and use software agents, which are abstractions of objects that can message other agents. * Clojure * F# * GOAL * SARL Array languages Array programming (also termed ''vector'' or ''multidimensional'') languages generalize operations on scalars to apply transparently to vectors, matrices, and higher-dimensional arrays. * A+ * Ada * Analytica * APL * Chapel * Dartmouth BASIC * Fortran (As of Fortran 90) * FreeMat * GAUSS * Interactive Data Language (IDL) * J * Julia * K * MATLAB * Octave * Q * R * Raku * S * Scilab * S-Lang * SequenceL * Speakeasy * Wolfram Mathematica (Wolfram language) * X10 * ZPL Aspect-oriented programming languages Aspect-oriented programming enable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Programming Language
A programming language is a system of notation for writing computer programs. Programming languages are described in terms of their Syntax (programming languages), syntax (form) and semantics (computer science), semantics (meaning), usually defined by a formal language. Languages usually provide features such as a type system, Variable (computer science), variables, and mechanisms for Exception handling (programming), error handling. An Programming language implementation, implementation of a programming language is required in order to Execution (computing), execute programs, namely an Interpreter (computing), interpreter or a compiler. An interpreter directly executes the source code, while a compiler produces an executable program. Computer architecture has strongly influenced the design of programming languages, with the most common type (imperative languages—which implement operations in a specified order) developed to perform well on the popular von Neumann architecture. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
General-purpose Programming Language
In computer software, a general-purpose programming language (GPL) is a programming language for building software in a wide variety of application Domain (software engineering), domains. Conversely, a Domain-specific language, domain-specific programming language (DSL) is used within a specific area. For example, Python (programming language), Python is a GPL, while SQL is a DSL for Query language, querying relational databases. History Early programming languages were designed for scientific computing (numerical calculations) or commercial data processing, as was computer hardware. Scientific languages such as Fortran and ALGOL, Algol supported floating-point calculations and multidimensional arrays, while business languages such as COBOL supported fixed-field file formats and record (computer science), data records. Much less widely used were specialized languages such as IPL-V and LISP for List (abstract data type), symbolic list processing; COMIT for string manipulation; APT ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
High-level Programming Language
A high-level programming language is a programming language with strong Abstraction (computer science), abstraction from the details of the computer. In contrast to low-level programming languages, it may use natural language ''elements'', be easier to use, or may automate (or even hide entirely) significant areas of computing systems (e.g. memory management), making the process of developing a program simpler and more understandable than when using a lower-level language. The amount of abstraction provided defines how "high-level" a programming language is. In the 1960s, a high-level programming language using a compiler was commonly called an ''autocode''. Examples of autocodes are COBOL and Fortran. The first high-level programming language designed for computers was Plankalkül, created by Konrad Zuse. However, it was not implemented in his time, and his original contributions were largely isolated from other developments due to World War II, aside from the language's influe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Interpreted Language
In computer science, an interpreter is a computer program that directly executes instructions written in a programming or scripting language, without requiring them previously to have been compiled into a machine language program. An interpreter generally uses one of the following strategies for program execution: # Parse the source code and perform its behavior directly; # Translate source code into some efficient intermediate representation or object code and immediately execute that; # Explicitly execute stored precompiled bytecode made by a compiler and matched with the interpreter's virtual machine. Early versions of Lisp programming language and minicomputer and microcomputer BASIC dialects would be examples of the first type. Perl, Raku, Python, MATLAB, and Ruby are examples of the second, while UCSD Pascal is an example of the third type. Source programs are compiled ahead of time and stored as machine independent code, which is then linked at run- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
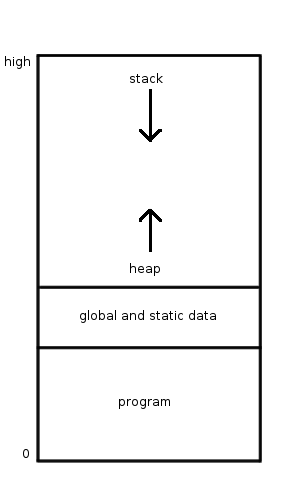
Runtime System
In computer programming, a runtime system or runtime environment is a sub-system that exists in the computer where a program is created, as well as in the computers where the program is intended to be run. The name comes from the compile time and runtime division from compiled languages, which similarly distinguishes the computer processes involved in the creation of a program (compilation) and its execution in the target machine (the runtime). Most programming languages have some form of runtime system that provides an environment in which programs run. This environment may address a number of issues including the management of application memory, how the program accesses variables, mechanisms for passing parameters between procedures, interfacing with the operating system (OS), among others. The compiler makes assumptions depending on the specific runtime system to generate correct code. Typically the runtime system will have some responsibility for setting up and managing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |