|
Zarya Spacecraft
The Zarya spacecraft () was a secret Soviet project of the late 1980s aiming to design and build a large crewed vertical-takeoff, vertical-landing (VTVL) reusable space capsule, a much larger replacement for the Soyuz (spacecraft). The project was developed during 1985–1989 years by Energia corporation until it was shelved in 1989, "on the eve of the Soviet Union's collapse" due to lack of funding. The name of the project was later reused by the Zarya space station module which served as the first component of International Space Station in 1998. Design The Zarya spacecraft would have differed from all previous spacecraft by having an array of a dozen rocket engines for making a soft landing upon return to Earth, without using a parachute. Mission Zarya spacecraft would have brought crew and supplies to ''Mir'' or supplies only in automated mode. It would have had a normal crew of one or two and offered the possibility of carrying a maximum of eight to twelve if used as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national republics; in practice, both its government and its economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kiev ( Ukrainian SSR), Minsk ( Byelorussian SSR), Tashkent (Uzbek SSR), Alma-Ata (Kazakh SSR), and Novosibirsk (Russian SFSR). It was the largest country in the world, covering over and spanning eleven time zones. The country's roots lay in the October Revolution of 1917, when the Bolsheviks, under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin, overthrew the Russian Provisional Gove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronaut
An astronaut (from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'star', and (), meaning 'sailor') is a person trained, equipped, and deployed by a human spaceflight program to serve as a commander or crew member aboard a spacecraft. Although generally reserved for professional space travelers, the term is sometimes applied to anyone who travels into space, including scientists, politicians, journalists, and tourists. "Astronaut" technically applies to all human space travelers regardless of nationality. However, astronauts fielded by Russia or the Soviet Union are typically known instead as cosmonauts (from the Russian "kosmos" (космос), meaning "space", also borrowed from Greek). Comparatively recent developments in crewed spaceflight made by China have led to the rise of the term taikonaut (from the Mandarin "tàikōng" (), meaning "space"), although its use is somewhat informal and its origin is unclear. In China, the People's Liberation Army Astronaut Corps astronauts and their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Space Program
The Soviet space program (russian: Космическая программа СССР, Kosmicheskaya programma SSSR) was the national space program of the former Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), active from 1955 until the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. Soviet investigations in rocketry began with the formation of a research laboratory in 1921, but these efforts were hampered by the devastating war with Germany. Competing in the Space Race with the United States and later with the European Union and China, the Soviet program was notable in setting many records in space exploration, including the first intercontinental missile that launched the first satellite and sent the first animal into Earth orbit in 1957, and placed the first human in space in 1961. In addition, the Soviet program also saw the first woman in space in 1963 and a cosmonaut performing the first spacewalk in 1965. Other milestones included computerized robotic missions exploring t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low Earth Orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an orbit around Earth with a period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial objects in outer space are in LEO, with an altitude never more than about one-third of the radius of Earth. The term ''LEO region'' is also used for the area of space below an altitude of (about one-third of Earth's radius). Objects in orbits that pass through this zone, even if they have an apogee further out or are sub-orbital, are carefully tracked since they present a collision risk to the many LEO satellites. All crewed space stations to date have been within LEO. From 1968 to 1972, the Apollo program's lunar missions sent humans beyond LEO. Since the end of the Apollo program, no human spaceflights have been beyond LEO. Defining characteristics A wide variety of sources define LEO in terms of altitude. The altitude of an object in an elliptic orbit can vary significantly along the orbit. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
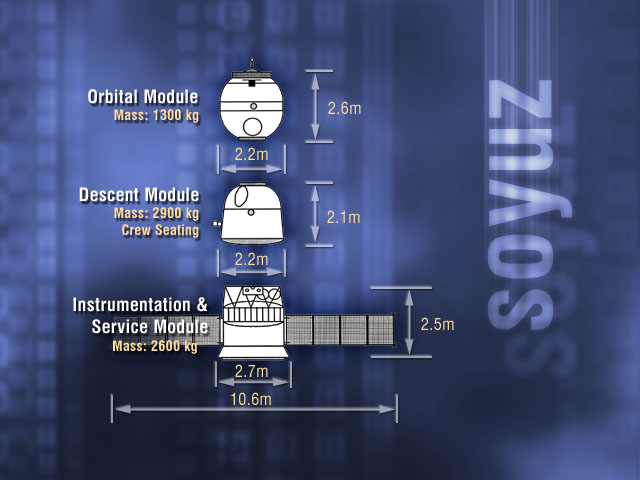
Soyuz (spacecraft)
Soyuz () is a series of spacecraft which has been in service since the 1960s, having made more than 140 flights. It was designed for the Soviet space program by the Korolev Design Bureau (now Energia). The Soyuz succeeded the Voskhod spacecraft and was originally built as part of the Soviet crewed lunar programs. It is launched on a Soyuz rocket from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Between the 2011 retirement of the Space Shuttle and the 2020 demo flight of SpaceX Crew Dragon, the Soyuz served as the only means to ferry crew to or from the International Space Station, for which it remains heavily used. Although China did launch crewed Shenzhou flights during this time, none of them docked with the ISS. History The first Soyuz flight was uncrewed and started on 28 November 1966. The first Soyuz mission with a crew, Soyuz 1, launched on 23 April 1967 but ended with a crash due to a parachute failure, killing cosmonaut Vladimir Komarov. The following flight was uncrew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VTVL
Vertical takeoff, vertical landing (VTVL) is a form of takeoff and landing for rockets. Multiple VTVL craft have flown. The most widely known and commercially successful VTVL rocket is SpaceX's Falcon 9 first stage. VTVL technologies were developed substantially with small rockets after 2000, in part due to incentive prize competitions like the Lunar Lander Challenge. Successful small VTVL rockets were developed by Masten Space Systems, Armadillo Aerospace, and others. Starting in the mid-2010s, VTVL was under intense development as a technology for reusable rockets large enough to transport people. In 2013, SpaceX demonstrated vertical landing on a Falcon 9 prototype after climbing 744 meters in the air. Later, Blue Origin (New Shepard) and SpaceX (Falcon 9), both demonstrated recovery of launch vehicles after return to the launch site (RTLS) operations, with Blue Origin's New Shepard booster rocket making the first successful vertical landing on November 23, 2015, followi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reusable Launch System
A reusable launch vehicle have parts that can be recovered and reflown, while carrying payloads from the surface to outer space. Rocket stages are the most common launch vehicle parts aimed for reuse. Smaller parts such as rocket engines and boosters can also be reused, though reusable spacecraft may be launched on top of an expendable launch vehicle. Reusable launch vehicles do not need to make these parts for each launch, therefore reducing its launch cost significantly. However, these benefits are diminished by the cost of recovery and refurbishment. Reusable launch vehicles may contain additional avionics and propellant, making them heavier than their expendable counterparts. Reused parts may need to enter the atmosphere and navigate through it, so they are often equipped with heat shields, grid fins, and other flight control surfaces. By modifying their shape, spaceplanes can leverage aviation mechanics to aid in its recovery, such as gliding or lift. In the atmosphere, par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Capsule
A space capsule is an often-crewed spacecraft that uses a blunt-body reentry capsule to reenter the Earth's atmosphere without wings. Capsules are distinguished from other satellites primarily by the ability to survive reentry and return a payload to the Earth's surface from orbit. Capsule-based crewed spacecraft such as Soyuz or Orion are often supported by a service or adapter module, and sometimes augmented with an extra module for extended space operations. Capsules make up the majority of crewed spacecraft designs, although one crewed spaceplane, the Space Shuttle, has flown in orbit. Current examples of crewed space capsules include Soyuz, Shenzhou, and Dragon 2. Examples of new crew capsules currently in development include NASA's Orion, Boeing's Starliner, Russia's Orel, India's Gaganyaan, and China's next-generation crewed spacecraft. Historic examples of crewed capsules include Vostok, Mercury, Voskhod, Gemini, and Apollo, and active programs include the New She ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energia (corporation)
PAO S. P. Korolev Rocket and Space Corporation Energia (russian: Ракетно-космическая корпорация «Энергия» им. С. П. Королёва, Raketno-kosmicheskaya korporatsiya "Energiya" im. S. P. Korolyova), also known as RSC Energia (, RKK "Energiya"), is a Russian manufacturer of spacecraft and space station components. The company is the prime developer and contractor of the Russian crewed spaceflight program; it also owns a majority of Sea Launch. Its name is derived from Sergei Korolev, the first chief of its design bureau, and the Russian word for energy. Overview Energia is the largest company of the Russian space industry and one of its key players. It is responsible for all operations involving human spaceflight and is the lead developer of the Soyuz and Progress spacecraft, and the lead developer of the Russian end of the International Space Station (ISS). In the mid-2000s, the company employed 22,000–30,000 people. The ent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zarya (ISS Module)
''Zarya'' (russian: Заря, , Dawn), also known as the Functional Cargo Block or FGB (from the russian: "Функционально-грузовой блок", , ''Funktsionalno-gruzovoy blok'' or ''ФГБ''), is the first module of the International Space Station to have been launched.NASA, International Space StationZarya(accessed 19 Apr. 2014) The FGB provided electrical power, storage, propulsion, and guidance to the ISS during the initial stage of assembly. With the launch and assembly in orbit of other modules with more specialized functionality, it is primarily used for storage, both inside the pressurized section and in the externally mounted fuel tanks. The ''Zarya'' is a descendant of the TKS spacecraft designed for the Russian ''Salyut'' program. The name ''Zarya'' ("Dawn") was given to the FGB because it signified the dawn of a new era of international cooperation in space. Although it was built by a Russian company, it is owned by the United States. Construct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA (Japan), ESA (Europe), and CSA (Canada). The ownership and use of the space station is established by intergovernmental treaties and agreements. The station serves as a microgravity and space environment research laboratory in which scientific research is conducted in astrobiology, astronomy, meteorology, physics, and other fields. The ISS is suited for testing the spacecraft systems and equipment required for possible future long-duration missions to the Moon and Mars. The ISS programme evolved from the Space Station ''Freedom'', a 1984 American proposal to construct a permanently crewed Earth-orbiting station, and the contemporaneous Soviet/Russian '' Mir-2'' proposal from 1976 with similar aims. The ISS is the ninth space station to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zenit (rocket Family)
Zenit ( uk, Зеніт, russian: Зени́т; meaning ''Zenith'') is a family of space launch vehicles designed by the Yuzhnoye Design Bureau in Dnipro, Ukraine, which was then part of the Soviet Union. Zenit was originally built in the 1980s for two purposes: as a liquid rocket booster for the Energia rocket and, equipped with a second stage, as a stand-alone middle-weight launcher with a payload greater than the 7 tonnes of the Soyuz but smaller than the 20 tonnes payload of the Proton. The last rocket family developed in the USSR, the Zenit was intended as an eventual replacement for the dated Soyuz and Proton families, and it would employ propellants which were safer and less toxic than the Proton's nitrogen tetroxide/UDMH mix. Zenit was planned to take over crewed spaceship launches from Soyuz, but these plans were abandoned after the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. Zenit-3SL was launched by the Sea Launch consortium's floating launch platform in the Pacific Ocea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


.jpg)

