|
ZDFinfo
ZDFinfo is a German free-to-air documentary television channel owned by ZDF. It was launched on 27 August 1997 as ZDFinfokanal, and later rebranded as ZDFinfo on 5 September 2011. On 1 May 2012, a high-definition simulcast the channel was launched. ZDF offered another documentary channel, ZDFdokukanal ZDFdokukanal was a TV station between 1 April 2000 and 31 October 2009 and part of the digital TV package offered by ZDF. Distribution The program was broadcast nationwide via the TV cable networks (DVB-C) and the satellite Astra 19.2°E (DVB- ..., between 2000 and 2009. References External links * Publicly funded broadcasters German-language television networks Television stations in Germany Television channels and stations established in 1997 Mass media in Mainz ZDF {{Germany-tv-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ZDFdokukanal
ZDFdokukanal was a TV station between 1 April 2000 and 31 October 2009 and part of the digital TV package offered by ZDF. Distribution The program was broadcast nationwide via the TV cable networks (DVB-C) and the satellite Astra 19.2°E (DVB-S). In the regions where DVB-T was available, ZDFdokukanal could be also received via antenna between 9 pm and 6 am, alternating with KiKa. It was also included in the IPTV offer of some DSL providers. Programming The station provided background information on nature, science, history and society. Since May 2009, the station has been transformed into a youth and family station in which the proportion of the documentaries has gradually been reduced and the number of entertainment programming has been increased. On 19 August 2009, ZDF announced that the station would cease broadcasting as of 31 October 2009. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free-to-air
Free-to-air (FTA) services are television (TV) and radio services broadcast in unencrypted form, allowing any person with the FTA Receiver, appropriate receiving equipment to receive the signal and view or listen to the content without requiring a Pay television, subscription, other ongoing cost, or one-off fee (e.g., pay-per-view). In the traditional sense, this is carried on Radio, terrestrial radio signals and received with an antenna. FTA also refers to channels and broadcasters providing content for which no subscription is expected, even though they may be delivered to the viewer/listener by another carrier for which a subscription is required, e.g., cable television, the Internet, or satellite television, satellite. These carriers may be mandated (or OPT) in some geographies to deliver FTA channels even if a premium subscription is not present (providing the necessary equipment is still available), especially where FTA channels are expected to be used for emergency broadcas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ZDFneo
ZDFneo is a German free-to-air television channel, programmed for an audience aged 25 to 49 to counter the primarily older-skewing main channels of public broadcasters ZDF and ARD. It replaced ZDF's documentary channel ZDFdokukanal on 1 November 2009. History On 1 October 2017, the station was to receive a new on-air design and a new broadcasting logo; this was brought forward to 26 September 2017. Distribution ZDFneo is broadcast (along with the rest of ZDFvision) via DVB-T digital terrestrial television, receivable in most areas of Germany. It is also transmitted in DVB-C through German cable networks, and in DVB-S from the Astra 1H satellite. Since 30 April 2012, ZDFneo has been broadcast in HD (720p). The program was initially only scaled up by 576i, since ZDFneo had no HD-capable playout at this time. Since mid-May 2015, the program is broadcast in native HD quality. Programmes ZDFneo's broadcasts mostly consists of comedy and drama series produced in-house. Shows ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Television Channel
A television channel is a terrestrial frequency or virtual number over which a television station or television network is distributed. For example, in North America, "channel 2" refers to the terrestrial or cable band of 54 to 60 MHz, with carrier frequencies of 55.25 MHz for NTSC analog video (VSB) and 59.75 MHz for analog audio ( FM), or 55.31 MHz for digital ATSC (8VSB). Channels may be shared by many different television stations or cable-distributed channels depending on the location and service provider Depending on the multinational bandplan for a given regional n, analog television channels are typically 6, 7, or 8 MHz in bandwidth, and therefore television channel frequencies vary as well. Channel numbering is also different. Digital terrestrial television channels are the same as their analog predecessors for legacy reasons, however through multiplexing, each physical radio frequency (RF) channel can carry several digital subchannels. On sat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Television Channels And Stations Established In 1997
Television, sometimes shortened to TV, is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. The term can refer to a television set, or the medium of television transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, entertainment, news, and sports. Television became available in crude experimental forms in the late 1920s, but only after several years of further development was the new technology marketed to consumers. After World War II, an improved form of black-and-white television broadcasting became popular in the United Kingdom and the United States, and television sets became commonplace in homes, businesses, and institutions. During the 1950s, television was the primary medium for influencing public opinion.Diggs-Brown, Barbara (2011''Strategic Public Relations: Audience Focused Practice''p. 48 In the mid-1960s, color broadcasting was introduced in the U.S. and most other developed countries. The availability of various types of archival sto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Television Stations In Germany
Television, sometimes shortened to TV, is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. The term can refer to a television set, or the medium of television transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, entertainment, news, and sports. Television became available in crude experimental forms in the late 1920s, but only after several years of further development was the new technology marketed to consumers. After World War II, an improved form of black-and-white television broadcasting became popular in the United Kingdom and the United States, and television sets became commonplace in homes, businesses, and institutions. During the 1950s, television was the primary medium for influencing public opinion.Diggs-Brown, Barbara (2011''Strategic Public Relations: Audience Focused Practice''p. 48 In the mid-1960s, color broadcasting was introduced in the U.S. and most other developed countries. The availability of various types of archival stor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German-language Television Networks
German ( ) is a West Germanic language mainly spoken in Central Europe. It is the most widely spoken and official or co-official language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, and the Italian province of South Tyrol. It is also a co-official language of Luxembourg and Belgium, as well as a national language in Namibia. Outside Germany, it is also spoken by German communities in France (Bas-Rhin), Czech Republic ( North Bohemia), Poland (Upper Silesia), Slovakia (Bratislava Region), and Hungary (Sopron). German is most similar to other languages within the West Germanic language branch, including Afrikaans, Dutch, English, the Frisian languages, Low German, Luxembourgish, Scots, and Yiddish. It also contains close similarities in vocabulary to some languages in the North Germanic group, such as Danish, Norwegian, and Swedish. German is the second most widely spoken Germanic language after English, which is also a West Germanic language. German is one of the maj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Publicly Funded Broadcasters
In public relations and communication science, publics are groups of individual people, and the public (a.k.a. the general public) is the totality of such groupings. This is a different concept to the sociological concept of the ''Öffentlichkeit'' or public sphere. The concept of a public has also been defined in political science, psychology, marketing, and advertising. In public relations and communication science, it is one of the more ambiguous concepts in the field. Although it has definitions in the theory of the field that have been formulated from the early 20th century onwards, and suffered more recent years from being blurred, as a result of conflation of the idea of a public with the notions of audience, market segment, community, constituency, and stakeholder. Etymology and definitions The name "public" originates with the Latin '' publicus'' (also '' poplicus''), from ''populus'', to the English word 'populace', and in general denotes some mass population ("the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simulcast
Simulcast (a portmanteau of simultaneous broadcast) is the broadcasting of programmes/programs or events across more than one resolution, bitrate or medium, or more than one service on the same medium, at exactly the same time (that is, simultaneously). For example, Absolute Radio is simulcast on both AM and on satellite radio. Likewise, the BBC's Prom concerts were formerly simulcast on both BBC Radio 3 and BBC Television. Another application is the transmission of the original-language soundtrack of movies or TV series over local or Internet radio, with the television broadcast having been dubbed into a local language. Early radio simulcasts Before launching stereo radio, experiments were conducted by transmitting left and right channels on different radio channels. The earliest record found was a broadcast by the BBC in 1926 of a Halle Orchestra concert from Manchester, using the wavelengths of the regional stations and Daventry. In its earliest days the BBC often transmit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
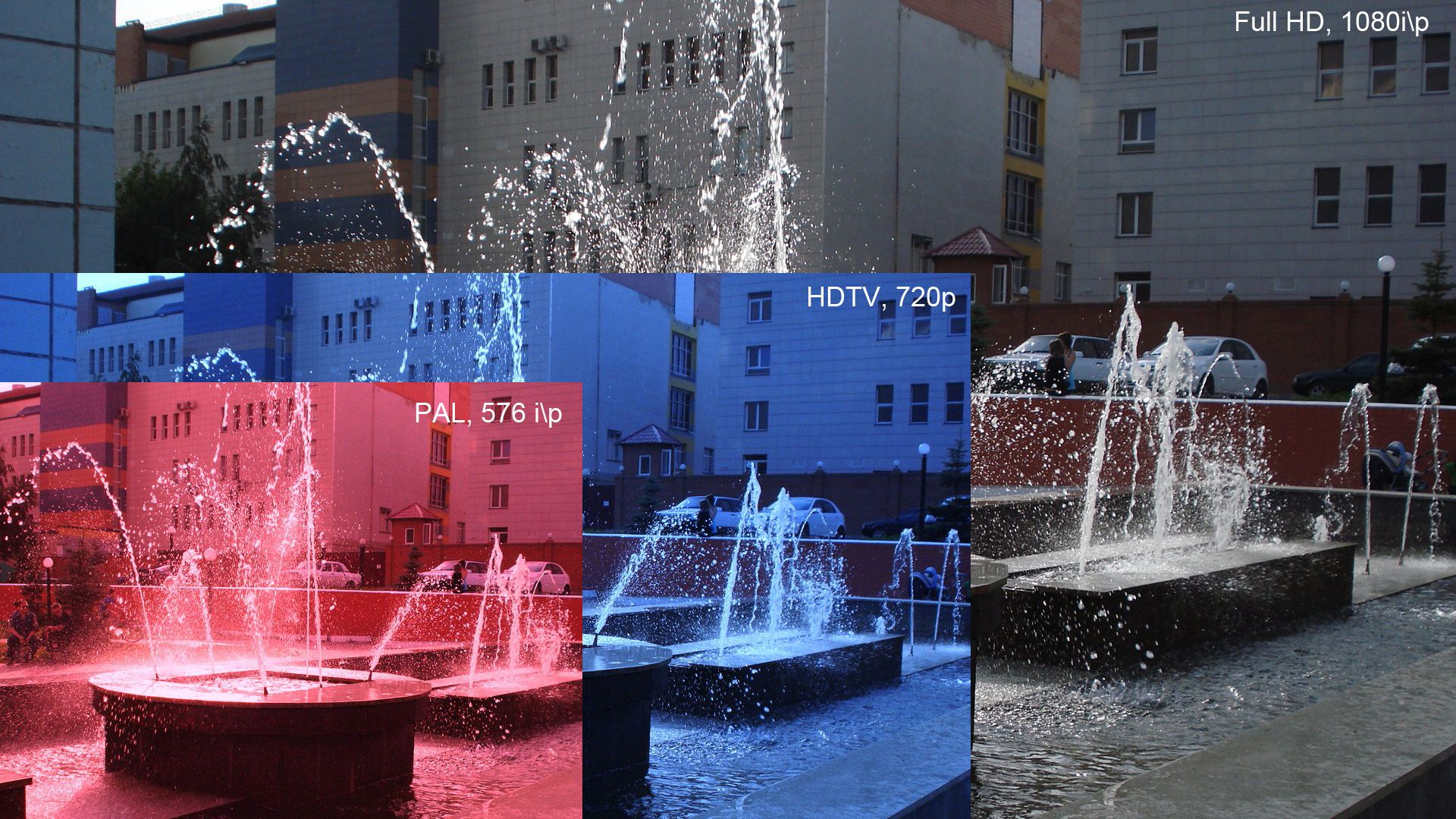
1080p
1080p (1920×1080 progressively displayed pixels; also known as Full HD or FHD, and BT.709) is a set of HDTV high-definition video modes characterized by 1,920 pixels displayed across the screen horizontally and 1,080 pixels down the screen vertically; the ''p'' stands for progressive scan, ''i.e.'' non-interlaced. The term usually assumes a widescreen aspect ratio of 16:9, implying a resolution of 2.1 megapixels. It is often marketed as Full HD or FHD, to contrast 1080p with 720p resolution screens. Although 1080p is sometimes informally referred to as 2K, these terms reflect two distinct technical standards, with differences including resolution and aspect ratio. 1080p video signals are supported by ATSC standards in the United States and DVB standards in Europe. Applications of the 1080p standard include television broadcasts, Blu-ray Discs, smartphones, Internet content such as YouTube videos and Netflix TV shows and movies, consumer-grade televisions and projector ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HDTV
High-definition television (HD or HDTV) describes a television system which provides a substantially higher image resolution than the previous generation of technologies. The term has been used since 1936; in more recent times, it refers to the generation following standard-definition television (SDTV), often abbreviated to HDTV or HD-TV. It is the current de facto standard video format used in most broadcasts: terrestrial broadcast television, cable television, satellite television and Blu-ray Discs. Formats HDTV may be transmitted in various formats: * 720p (1280 horizontal pixels × 720 lines): 921,600 pixels * 1080i (1920×1080) interlaced scan: 1,036,800 pixels (~1.04 MP). * 1080p (1920×1080) progressive scan: 2,073,600 pixels (~2.07 MP). ** Some countries also use a non-standard CEA resolution, such as 1440×1080i: 777,600 pixels (~0.78 MP) per field or 1,555,200 pixels (~1.56 MP) per frame When transmitted at two megapixels per frame, HDTV provides about five times a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Terrestrial Television
Digital terrestrial television (DTTV or DTT, or DTTB with "broadcasting") is a technology for terrestrial television in which land-based (terrestrial) television stations broadcast television content by radio waves to televisions in consumers' residences in a digital format. DTTV is a major technological advance over the previous analog television, and has largely replaced analog which had been in common use since the middle of the 20th century. Test broadcasts began in 1998 with the changeover to DTTV (aka Analog Switchoff (ASO), or Digital Switchover (DSO)) beginning in 2006 and is now complete in many countries. The advantages of ''digital'' terrestrial television are similar to those obtained by digitising platforms such as cable TV, satellite, and telecommunications: more efficient use of limited radio spectrum bandwidth, provision of more television channels than analog, better quality images, and potentially lower operating costs for broadcasters (after the initial up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |