|
Zwanzig Ab
Zwanzig ab, 20 ab or simply Zwanzig is card game for four players. It is a member of the Rams family in which the key feature is that players may choose to drop out of the game if they believe their hand is not strong enough to take a minimum number of tricks. It appears to be a recent, internet-propagated variant of Schnalzen or Bohemian Watten. However, the latter has a natural card ranking, is played with double German cards and a Weli, has no exchanging and has a different scoring system. It is suitable for children from 8 upwards. It may be related from Fünf dazu! which is a simpler game described by Gööck in 1967 that has neither trumps nor the option to drop out. Aim Each player begins with twenty points and the aim is to be the first to zero, hence the name; ''zwanzig ab'' means "twenty down" in German. Cards Zwanzig ab! is played with a 32-card Skat pack which may be either French- or German-suited. Card ranking follows the Skat schedule used in ace–ten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plain-trick
A trick-taking game is a card or tile-based game in which play of a ''hand'' centers on a series of finite rounds or units of play, called ''tricks'', which are each evaluated to determine a winner or ''taker'' of that trick. The object of such games then may be closely tied to the number of tricks taken, as in plain-trick games such as contract bridge, whist, and spades, or to the value of the cards contained in taken tricks, as in point-trick games such as pinochle, the tarot family, briscola, and most evasion games like hearts. Trick-and-draw games are trick-taking games in which the players can fill up their hands after each trick. In most variants, players are free to play any card into a trick in the first phase of the game, but must ''follow suit'' as soon as the stock is depleted. Trick-avoidance games like reversis or polignac are those in which the aim is to avoid taking some or all tricks. The domino game Texas 42 is an example of a trick-taking game that is not a ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ace–ten Games
An Ace-Ten game is a type of card game, highly popular in Europe, in which the Aces and Tens are of particularly high value. Description Many of Europe's most popular card games feature the Ace-Ten scoring system, where the cards count as Ace = 11, Ten = 10, King = 4, Queen or Ober = 3, Jack or Unter = 2. Pip cards below the Ten generally have no card point value and the pack is often shortened by removing the lower pip cards or 'non-counters'. This means that, in a typical shortened pack of between 20 and 36 cards, there are 120 card points and thus a winning total is typically 61 points. Wins are doubled for scoring three-quarters of the total points and trebled for winning every trick, a scoring system known as the Skat schedule after its "most illustrious" example, the German national game of Skat. There are 3 branches of the Ace-Ten family: * Schafkopf group. The trump suit is bolstered by the promotion of all Unters (Jacks) or all Obers (Queens) or both to be permanen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forehand (card Player)
Card players are those participating in a card game. Various names are given to card players based on their role or position. Position Games of Anglo-American origin In games of Anglo-American origin played in English-speaking countries, age refers to the order of priority in which players make the first lead, bid or bet, based on their position at the table.''The Language of Cards'' at www.parlettgames.uk. Retrieved 4 August 2018 This changes constantly as the dealer rotates either clockwise or anticlockwise around the table. They are traditionally referred to as follows: ; Eldest hand (or elder hand): the player who enjoys greatest priority and e.g. is the first to receive cards in the deal. Elder is the non-dealer in two-hand games. ; Youngest hand (or younger hand): the player who has the lowest p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
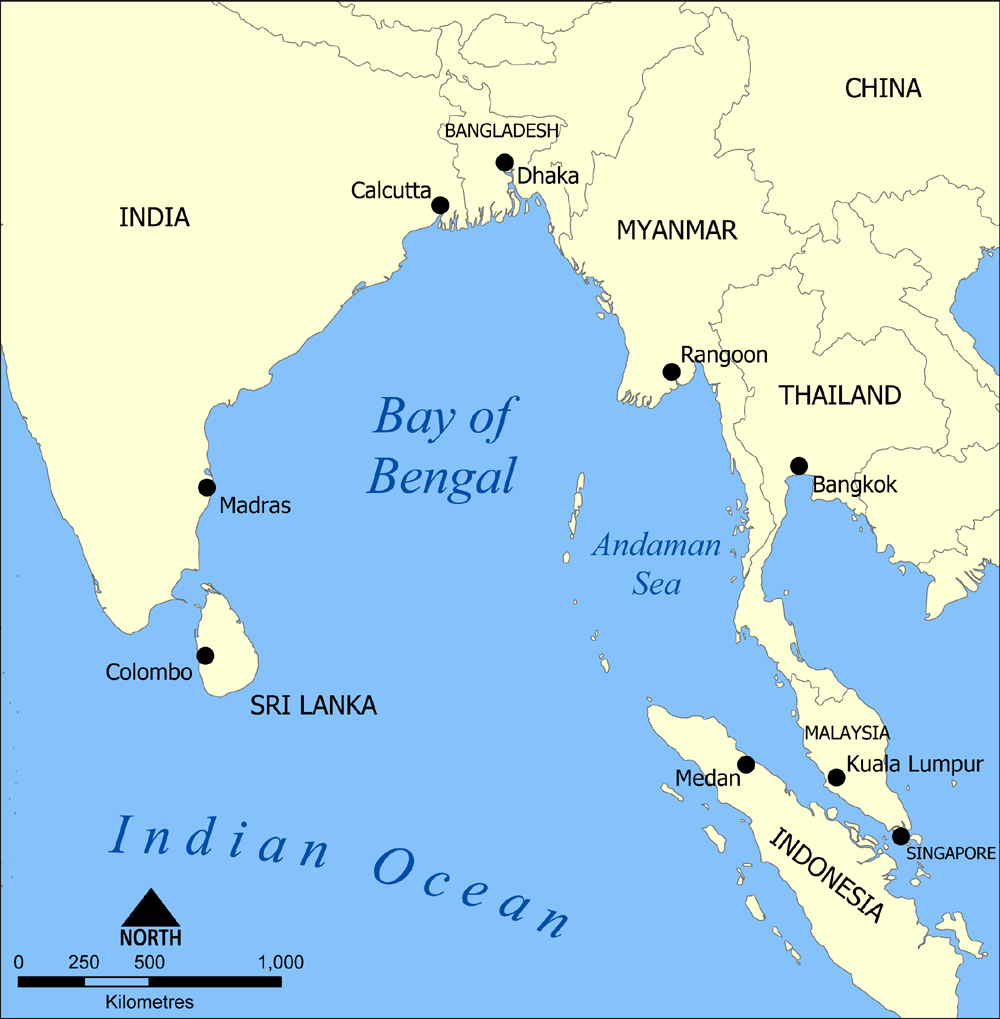
Bay Schellen
A bay is a recessed, coastal body of water that directly connects to a larger main body of water, such as an ocean, a lake, or another bay. A large bay is usually called a gulf, sea, sound, or bight. A cove is a small, circular bay with a narrow entrance. A fjord is an elongated bay formed by glacial action. A bay can be the estuary of a river, such as the Chesapeake Bay, an estuary of the Susquehanna River. Bays may also be nested within each other; for example, James Bay is an arm of Hudson Bay in northeastern Canada. Some large bays, such as the Bay of Bengal and Hudson Bay, have varied marine geology. The land surrounding a bay often reduces the strength of winds and blocks waves. Bays may have as wide a variety of shoreline characteristics as other shorelines. In some cases, bays have beaches, which "are usually characterized by a steep upper foreshore with a broad, flat fronting terrace".Maurice Schwartz, ''Encyclopedia of Coastal Science'' (2006), p. 129. Bays were sig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay Herz
A bay is a recessed, coastal body of water that directly connects to a larger main body of water, such as an ocean, a lake, or another bay. A large bay is usually called a gulf, sea, sound, or bight. A cove is a small, circular bay with a narrow entrance. A fjord is an elongated bay formed by glacial action. A bay can be the estuary of a river, such as the Chesapeake Bay, an estuary of the Susquehanna River. Bays may also be nested within each other; for example, James Bay is an arm of Hudson Bay in northeastern Canada. Some large bays, such as the Bay of Bengal and Hudson Bay, have varied marine geology. The land surrounding a bay often reduces the strength of winds and blocks waves. Bays may have as wide a variety of shoreline characteristics as other shorelines. In some cases, bays have beaches, which "are usually characterized by a steep upper foreshore with a broad, flat fronting terrace".Maurice Schwartz, ''Encyclopedia of Coastal Science'' (2006), p. 129. Bays were sig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay Gras
A bay is a recessed, coastal body of water that directly connects to a larger main body of water, such as an ocean, a lake, or another bay. A large bay is usually called a gulf, sea, sound, or bight. A cove is a small, circular bay with a narrow entrance. A fjord is an elongated bay formed by glacial action. A bay can be the estuary of a river, such as the Chesapeake Bay, an estuary of the Susquehanna River. Bays may also be nested within each other; for example, James Bay is an arm of Hudson Bay in northeastern Canada. Some large bays, such as the Bay of Bengal and Hudson Bay, have varied marine geology. The land surrounding a bay often reduces the strength of winds and blocks waves. Bays may have as wide a variety of shoreline characteristics as other shorelines. In some cases, bays have beaches, which "are usually characterized by a steep upper foreshore with a broad, flat fronting terrace".Maurice Schwartz, ''Encyclopedia of Coastal Science'' (2006), p. 129. Bays were sig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay Eichel
A bay is a recessed, coastal body of water that directly connects to a larger main body of water, such as an ocean, a lake, or another bay. A large bay is usually called a gulf, sea, sound, or bight. A cove is a small, circular bay with a narrow entrance. A fjord is an elongated bay formed by glacial action. A bay can be the estuary of a river, such as the Chesapeake Bay, an estuary of the Susquehanna River. Bays may also be nested within each other; for example, James Bay is an arm of Hudson Bay in northeastern Canada. Some large bays, such as the Bay of Bengal and Hudson Bay, have varied marine geology. The land surrounding a bay often reduces the strength of winds and blocks waves. Bays may have as wide a variety of shoreline characteristics as other shorelines. In some cases, bays have beaches, which "are usually characterized by a steep upper foreshore with a broad, flat fronting terrace".Maurice Schwartz, ''Encyclopedia of Coastal Science'' (2006), p. 129. Bays were sig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bells (card Suit)
Bells are a suit in playing cards of the Swiss-suited and German-suited cards. Unlike the other German suits, this suit was not adapted by French card makers. In its place, there was initially a suit of red crescents until the suit of Diamonds was added to the French pack (known as tiles in France). The suit is usually known in German as ''Schellen'', but is sometimes abbreviated to ''Schell''. Cards are referred to as in a French deck e.g. the "9 of Bells", but in German as ''"Schellen 9"'', or the "Unter of Bells" (''Schellunter'' or ''Schell-Unter''). Bells are the lowest suit in Skat, Schafkopf and Doppelkopf, but the second highest in Préférence. The 7 of Bells (''Schellen 7'') or, in South Tyrol the 6 of Bells (''Belle, Weli'') is the second highest trump card in the game of Watten. The gallery below shows a suit of Bells from a German suited pack of 32 cards, plus the ''Weli'' or 6 of Bells which is used in some games as an 'honour' card. The main pack is of the Saxon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hearts (card Suit)
Hearts (french: Cœur, german: Herz) is one of the four suits in playing cards of both the French deck and the German deck. However, the symbol is slightly different: in a French deck and in a German-suited deck. In Bridge, for which in Germany the French deck is common, it is called by its French name, ''Cœur''. In games using German-suited cards the suit of Hearts is often called "Red" (''Rot''). In the game of Watten, the King of Hearts is the highest Trump. This suit was invented in 15th century Germany and is a survivor from a large pool of experimental suit signs created to replace the Latin suits. Name The origin of the term "heart" to describe the symbol, which only very marginally resembles a true heart, is not known. In general, equivalents in other languages also mean "heart". File:Bay herz.svg, The heart in German suited cards File:Naipe copas.png, The heart in French suited cards Characteristics The heart typically has a form of cardioid, the lower par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leaves (card Suit)
Leaves are one of the four suits in German-suited packs of playing cards. This suit was invented in 15th century Germany and is a survivor from a large pool of experimental suit signs created to replace the Latin suits. Around 1480, French card makers adapted this sign into Spades in the French pack (known as pikes in France). As its name suggests, the leaf is represented by a stylized green leaf. The left half is lighter than the right half; it can sometimes be yellow. Veins are visible and there is usually a petiole. There may also be smaller leaves. They are usually known in German as ''Laub'' ("foliage"), but also as ''Gras'' ("grass"), ''Blatt'' ("leaf") or ''Grün'' ("green"). Cards are referred to as in a French pack e.g. the "King of Leaves", but in German as ''"Laub-König"'' or ''"Grün-König"'' i.e. "Leaf King". It is the second-highest suit in the games of Skat, Schafkopf and Doppelkopf, and the second lowest in Préférence. The gallery below shows a suit of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acorns (card Suit)
Acorns (German: ''Eichel'', or more unusually ''Hackl'' or ''Ecker'') is a suit in a deck of German playing cards or Swiss playing cards. This suit was invented in 15th-century German-speaking lands and is a survivor from a large pool of experimental suit signs created to replace the Latin suits. Around 1480, French card makers adapted this sign into clubs in a French deck (known as clovers in France). In English, cards are referred to as in a French deck (e.g. the "10 of Acorns"), but in German as ''Eichel-Zehn''. Acorns are the highest suit in the games of Skat, Schafkopf and Doppelkopf, but the lowest in Préférence. In Watten, the 7 of Acorns (the ''Spitz'' or ''Soach'') is the third highest trump card. The gallery below shows a suit of Acorns from a German-suited deck of 32 cards. The pack is of the Saxonian pattern: File:Saxonian Deck - Acorns - 07.jpg , 7 File:Saxonian Deck - Acorns - 08.jpg , 8 File:Saxonian Deck - Acorns - 09.jpg , 9 File:Saxonian Deck - Acorns - 10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |