|
Zoroastrian Wedding
Zoroastrian weddings are a religious ceremony in Zoroastrianism in which two individuals, a man and a woman are united. In Zoroastrianism, marriage within the community is encouraged, and is greatly favored in religious texts. The following information will detail ceremony procedures and traditional processes for a Zoroastrian wedding. Prior to ceremony Age In the Avesta, manhood and womanhood are gained at the age of 15, when they would be ready for marriage. However, in India, the threshold for marriage is set by the Parsi Marriage and Divorce Act, 1936 which states the threshold at 21 for males and 18 for females. If either of the marrying parties are below the age given in the act, the parents of the underage marrying party must sign on the marriage certificate to signify their approval. Arranged marriages Traditionally marriages are arranged by the parents with the consent of the children. In recent times however, it is not uncommon for this system to be reversed, with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religions, Iranian religion and one of the world's History of religion, oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian peoples, Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a Dualism in cosmology, dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a Monotheism, monotheistic ontology and an eschatology which predicts the ultimate conquest of evil by good. Zoroastrianism exalts an uncreated and benevolent deity of wisdom known as ''Ahura Mazda'' () as its supreme being. Historically, the unique features of Zoroastrianism, such as its monotheism, messianism, belief in Free will in theology, free will and Judgement (afterlife), judgement after death, conception of heaven, hell, Angel, angels, and Demon, demons, among other concepts, may have influenced other religious and philosophical systems, including the Abrahamic religions and Gnosticism, Southern, Eastern and Northern Buddhism, Northern Buddhism, and Ancient Greek philosoph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woman
A woman is an adult female human. Prior to adulthood, a female human is referred to as a girl (a female child or adolescent). The plural ''women'' is sometimes used in certain phrases such as "women's rights" to denote female humans regardless of age. Typically, women inherit a pair of X chromosomes, one from each parent, and are capable of pregnancy and giving birth from puberty until menopause. More generally, sex differentiation of the female fetus is governed by the lack of a present, or functioning, SRY-gene on either one of the respective sex chromosomes. Female anatomy is distinguished from male anatomy by the female reproductive system, which includes the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, and vulva. A fully developed woman generally has a wider pelvis, broader hips, and larger breasts than an adult man. Women have significantly less facial and other body hair, have a higher body fat composition, and are on average shorter and less muscular than men. Throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avesta
The Avesta () is the primary collection of religious texts of Zoroastrianism, composed in the Avestan language. The Avesta texts fall into several different categories, arranged either by dialect, or by usage. The principal text in the liturgical group is the ''Yasna'', which takes its name from the Yasna ceremony, Zoroastrianism's primary act of worship, and at which the ''Yasna'' text is recited. The most important portion of the ''Yasna'' texts are the five Gathas, consisting of seventeen hymns attributed to Zoroaster himself. These hymns, together with five other short Old Avestan texts that are also part of the ''Yasna'', are in the Old (or 'Gathic') Avestan language. The remainder of the ''Yasna'''s texts are in Younger Avestan, which is not only from a later stage of the language, but also from a different geographic region. Extensions to the Yasna ceremony include the texts of the ''Vendidad'' and the ''Visperad''. The ''Visperad'' extensions consist mainly of addit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
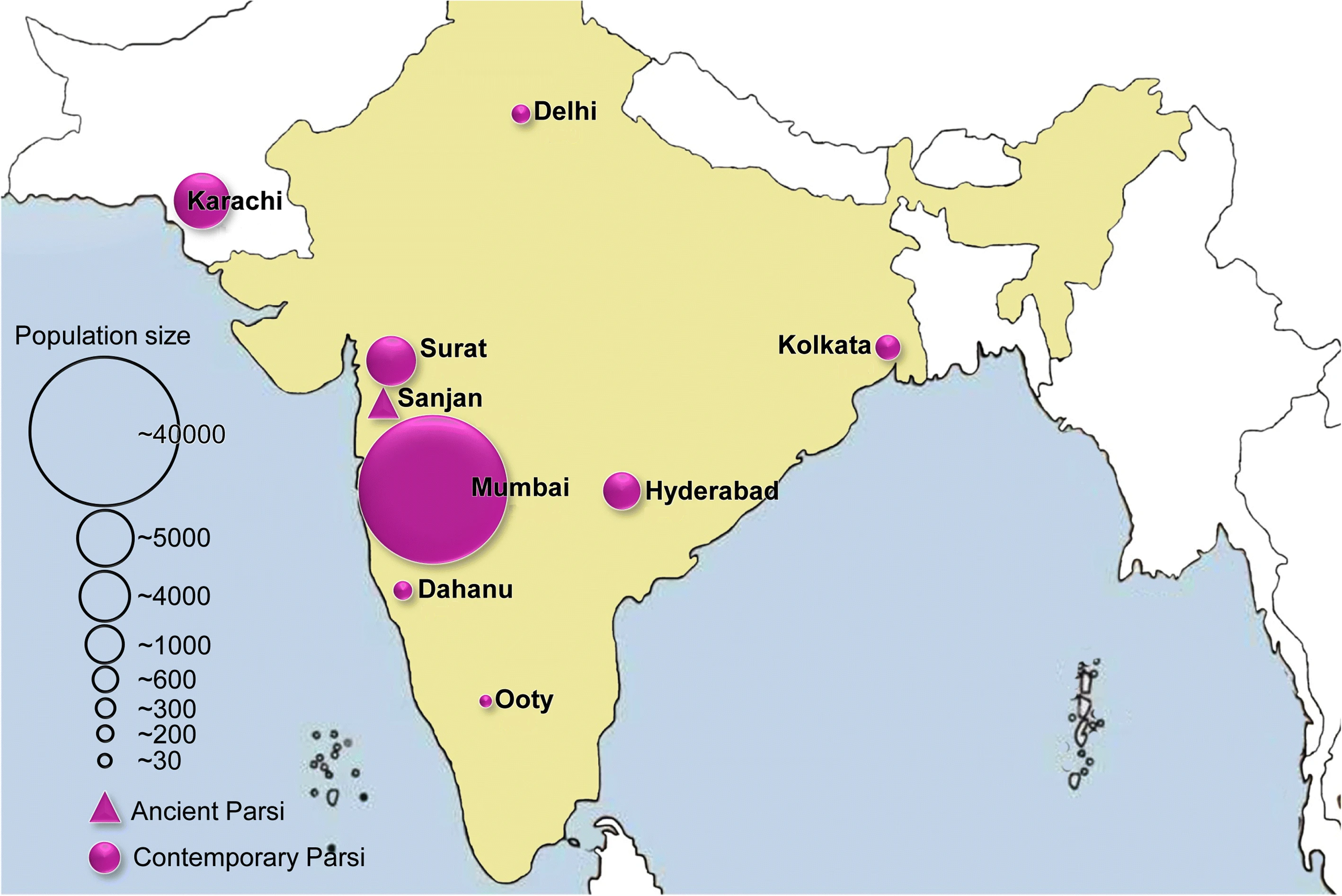
Parsi Marriage And Divorce Act, 1936
Parsis () or Parsees are an ethnoreligious group of the Indian subcontinent adhering to Zoroastrianism. They are descended from Persians who migrated to Medieval India during and after the Arab conquest of Iran (part of the early Muslim conquests) in order to preserve their Zoroastrian identity. The Parsi people comprise the older of the Indian subcontinent's two Zoroastrian communities vis-à-vis the Iranis, whose ancestors migrated to British-ruled India from Qajar-era Iran. According to a 16th-century Parsi epic, ''Qissa-i Sanjan'', Zoroastrian Persians continued to migrate to the Indian subcontinent from Greater Iran in between the 8th and 10th centuries, and ultimately settled in present-day Gujarat after being granted refuge by a local Hindu king. Prior to the 7th-century fall of the Sassanid Empire to the Rashidun Caliphate, the Iranian mainland (historically known as 'Persia') had a Zoroastrian majority, and Zoroastrianism had served as the Iranian state religion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arranged Marriage
Arranged marriage is a type of marital union where the bride and groom are primarily selected by individuals other than the couple themselves, particularly by family members such as the parents. In some cultures a professional matchmaker may be used to find a spouse for a young person. Arranged marriages have historically been prominent in many cultures. The practice remains common in many regions, notably South Asia, the Middle East, North Africa, and the Caucasus. In many other parts of the world, the practice has declined substantially during the 19th and 20th centuries. Forced marriages, practiced in some families, are condemned by the United Nations. The specific sub-category of forced child marriage is especially condemned. In other cultures, people mostly choose their own partner. History Arranged marriages were very common throughout the world until the 18th century. Typically, marriages were arranged by parents, grandparents or other close relatives and trusted friends. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Betrothal
An engagement or betrothal is the period of time between the declaration of acceptance of a marriage proposal and the marriage itself (which is typically but not always commenced with a wedding). During this period, a couple is said to be ''fiancés'' (from the French), ''betrothed,'' ''intended'', ''affianced'', ''engaged to be married,'' or simply ''engaged''. Future brides and grooms may be called ''fiancée'' (feminine) or ''fiancé'' (masculine), ''the betrothed'', a ''wife-to-be'' or ''husband-to-be'', respectively. The duration of the courtship varies vastly, and is largely dependent on cultural norms or upon the agreement of the parties involved. Long engagements were once common in formal arranged marriages, and it was not uncommon for parents betrothing children to arrange marriages many years before the engaged couple were old enough. This is still done in some countries. Many traditional Christian denominations have optional rites for Christian betrothal (also k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
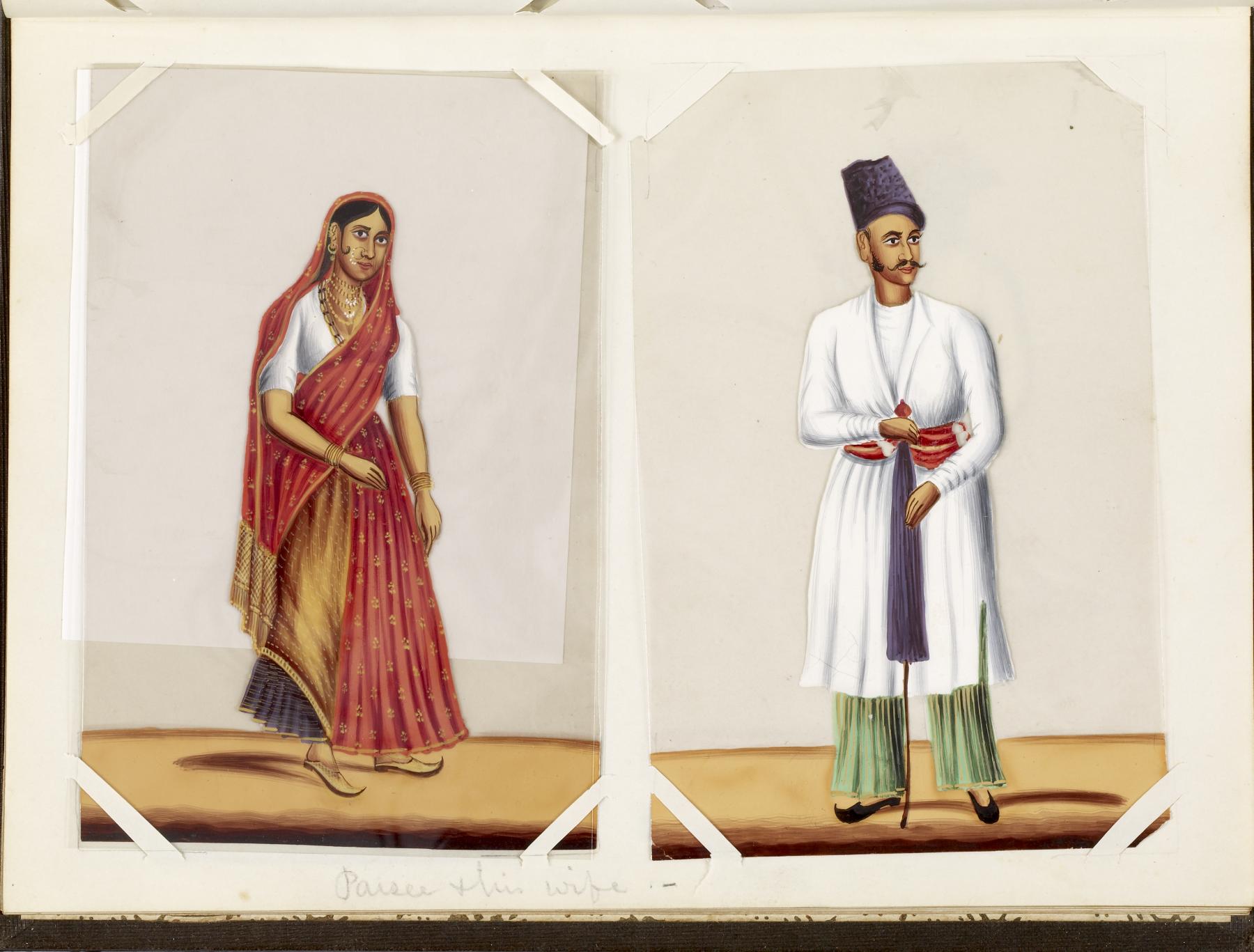
Parsi Groom
Parsis () or Parsees are an ethnoreligious group of the Indian subcontinent adhering to Zoroastrianism. They are descended from Persians who migrated to Medieval India during and after the Arab conquest of Iran (part of the early Muslim conquests) in order to preserve their Zoroastrian identity. The Parsi people comprise the older of the Indian subcontinent's two Zoroastrian communities vis-à-vis the Iranis, whose ancestors migrated to British-ruled India from Qajar-era Iran. According to a 16th-century Parsi epic, ''Qissa-i Sanjan'', Zoroastrian Persians continued to migrate to the Indian subcontinent from Greater Iran in between the 8th and 10th centuries, and ultimately settled in present-day Gujarat after being granted refuge by a local Hindu king. Prior to the 7th-century fall of the Sassanid Empire to the Rashidun Caliphate, the Iranian mainland (historically known as 'Persia') had a Zoroastrian majority, and Zoroastrianism had served as the Iranian state religion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luck
Luck is the phenomenon and belief that defines the experience of improbable events, especially improbably positive or negative ones. The naturalistic interpretation is that positive and negative events may happen at any time, both due to random and non-random natural and artificial processes, and that even improbable events can happen by random chance. In this view, the epithet "lucky" or "unlucky" is a descriptive label that refers to an event's positivity, negativity, or improbability. Supernatural interpretations of luck consider it to be an attribute of a person or object, or the result of a favorable or unfavorable view of a deity upon a person. These interpretations often ''prescribe'' how luckiness or unluckiness can be obtained, such as by carrying a lucky charm or offering sacrifices or prayers to a deity. Saying someone is "born lucky" may hold different meanings, depending on the interpretation: it could simply mean that they have been born into a good family or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family ( Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, the seed, or the fruit, which botanically is a drupe, not a nut. The name comes from the old Portuguese word '' coco'', meaning "head" or "skull", after the three indentations on the coconut shell that resemble facial features. They are ubiquitous in coastal tropical regions and are a cultural icon of the tropics. The coconut tree provides food, fuel, cosmetics, folk medicine and building materials, among many other uses. The inner flesh of the mature seed, as well as the coconut milk extracted from it, form a regular part of the diets of many people in the tropics and subtropics. Coconuts are distinct from other fruits because their endosperm contains a large quantity of clear liquid, called ''coconut water'' or ''coconut juice''. Mature, ripe coconut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toast (honor)
A toast is a ritual during which a drink is taken as an expression of honor or goodwill. The term may be applied to the person or thing so honored, the drink taken, or the verbal expression accompanying the drink. Thus, a person could be "the toast of the evening", for whom someone "proposes a toast" to congratulate and for whom a third person "toasts" in agreement. The ritual forms the basis of the literary and performance genre, of which Mark Twain's "To the Babies" is a well-known example. The toast as described in this article is rooted in Western culture, but certain cultures outside that sphere have their own traditions in which consuming a drink is connected with ideas of celebration and honor. While the physical and verbal ritual of the toast may be elaborate and formal, merely raising one's glass towards someone or something and then drinking is essentially a toast as well, the message being one of goodwill towards the person or thing indicated. History According to var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_p012_BAKU%2C_FIRE_TEMPLE_(cropped).jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)