|
Zipporah At The Inn
Zipporah at the inn is the name given to an episode alluded to in three verses of the Book of Exodus. This much-debated passage is one of the more perplexing conundrums of the Torah. Passage The verses in question are Exodus 4:24–26, the context is Moses, his wife Zipporah and their son Gershom reaching an inn on their way from Midian to Egypt to announce the plagues to the Pharaoh: Leningrad Codex text: :24. :25. :26. King James Version translation: :24. And it came to pass by the way in the inn, that the Lᴏʀᴅ met him, and sought to kill him. :25. Then Zipporah took a sharp stone, and cut off the foreskin of her son, and cast it at his feet, and said, "Surely a bloody husband art thou to me." :26. So he let him go: then she said, A bloody husband thou art, because of the circumcision. New Revised Standard Version translation: :On the way, at a place where they spent the night, the Lᴏʀᴅ met him and tried to kill him. But Zipporah took a flint and cut off he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weenix Circumcision Of Son Of Moses
Weenix, Wenix, Weeninx is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: *Jan Baptist Weenix (1621–1660), Dutch painter *Jan Weenix (1640–1719), Dutch painter, son of Jan Baptist *Maria Weenix (1697–1774), Dutch painter, daughter of Jan {{surname Dutch-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
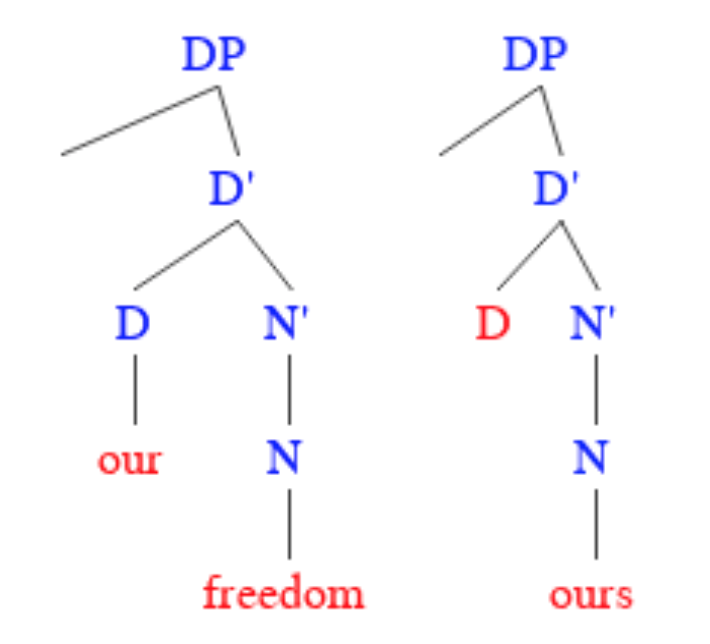
Pronoun
In linguistics and grammar, a pronoun (abbreviated ) is a word or a group of words that one may substitute for a noun or noun phrase. Pronouns have traditionally been regarded as one of the parts of speech, but some modern theorists would not consider them to form a single class, in view of the variety of functions they perform cross-linguistically. An example of a pronoun is "you", which can be either singular or plural. Subtypes include personal and possessive pronouns, reflexive and reciprocal pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, relative and interrogative pronouns, and indefinite pronouns. The use of pronouns often involves anaphora, where the meaning of the pronoun is dependent on an antecedent. For example, in the sentence ''That poor man looks as if he needs a new coat'', the meaning of the pronoun ''he'' is dependent on its antecedent, ''that poor man''. The name of the adjective that belongs with a "pronoun" is called a "pronominal". A pronominal is also a word or ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Kugel
James L. Kugel (Hebrew: Yaakov Kaduri, יעקב כדורי; born August 22, 1945) is Professor Emeritus in the Bible Department at Bar Ilan University in Israel and the Harry M. Starr Professor Emeritus of Classical and Modern Hebrew Literature at Harvard University. James Kugel is the author and editor of 16 books and numerous articles on the Bible and its early commentators, focusing on the Second Temple period. He identifies as an Orthodox Jew. ''Moment Magazine'' published a long-form profile called, "Professor of Disbelief," on James Kugel in their MARCH/APRIL 2014 issue. In 2001, his book, the ''Bible As It Was'' won the University of Louisville and the Louisville Presbyterian Theological Seminary Grawemeyer Award in religion. The prize "recognizes outstanding and creative works that promote understanding of the relationship between human beings and the divine." ''The Bible As It Was'' was published in 1997 by Harvard University. It is the annotated version of a lengthier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samaritan Alphabet
The Samaritan script is used by the Samaritans for religious writings, including the Samaritan Pentateuch, writings in Samaritan Hebrew, and for commentaries and translations in Samaritan Aramaic and occasionally Arabic. Samaritan is a direct descendant of the Paleo-Hebrew alphabet, which was a variety of the Phoenician alphabet. Paleo-Hebrew is the alphabet in which large parts of the Hebrew Bible were originally penned according to the consensus of most scholars, who also believe that these scripts are descendants of the Proto-Sinaitic script. Paleo-Hebrew script was used by the ancient Israelites, both Jews and Samaritans. The better-known "square script" Hebrew alphabet which has been traditionally used by Jews since the Babylonian exile is a stylized version of the Aramaic alphabet called Ashurit (כתב אשורי), though religious literalist interpretations of assume that the text asserts that it was received on Sinai from the Finger of God and that it has been in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masoretic Text
The Masoretic Text (MT or 𝕸; he, נֻסָּח הַמָּסוֹרָה, Nūssāḥ Hammāsōrā, lit. 'Text of the Tradition') is the authoritative Hebrew and Aramaic text of the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible (Tanakh) in Rabbinic Judaism. The Masoretic Text defines the Jewish canon and its precise letter-text, with its vocalization and accentuation known as the ''mas'sora''. Referring to the Masoretic Text, ''mesorah'' specifically means the diacritic markings of the text of the Hebrew scriptures and the concise marginal notes in manuscripts (and later printings) of the Tanakh which note textual details, usually about the precise spelling of words. It was primarily copied, edited and distributed by a group of Jews known as the Masoretes between the 7th and 10th centuries of the Common Era (CE). The oldest known complete copy, the Leningrad Codex, dates from the early 11th century CE. The differences attested to in the Dead Sea Scrolls indicate that multiple versions of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samaritan Pentateuch
The Samaritan Torah ( Samaritan Hebrew: , ''Tōrāʾ''), also called the Samaritan Pentateuch, is a text of the Torah written in the Samaritan script and used as sacred scripture by the Samaritans. It dates back to one of the ancient versions of the Hebrew Bible that existed during the Second Temple period, and constitutes the entire biblical canon in Samaritanism. Some six thousand differences exist between the Samaritan and the Jewish Masoretic Text. Most are minor variations in the spelling of words or grammatical constructions, but others involve significant semantic changes, such as the uniquely Samaritan commandment to construct an altar on Mount Gerizim. Nearly two thousand of these textual variations agree with the Koine Greek Septuagint and some are shared with the Latin Vulgate. Throughout their history, Samaritans have made use of translations of the Samaritan Pentateuch into Aramaic, Greek, and Arabic, as well as liturgical and exegetical works based upon it. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eleazar Of Modi'im
Eleazar of Modi'im ( he, אלעזר המודעי) was a Jewish scholar of the second tannaitic generation (1st and 2nd centuries), disciple of Johanan ben Zakkai, and contemporary of Joshua ben Hananiah and Eliezer ben Hyrcanus. Rabbinic career Eleazar of Modi'im was an expert aggadist and frequently discussed exegetical topics with his distinguished contemporaries. Gamaliel II often deferred to Eleazar's interpretations, admitting, "The Moda'i's views are still indispensable". Few of his teachings are preserved in ''halakha'' and most of what is known about him comes from hearsay.As he lived through the Hadrianic persecutions and the Bar Kokba insurrection, many of his homilies refer, explicitly or implicitly, to existence under such conditions. Eleazar expressed his confidence in Providence in this comment on the biblical statement (Exodus 16:4), "the people shall go out, and gather a certain rate every day" (lit. "the portion of the day on its day," דבר יום ביומו ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Destroying Angel (Bible)
In the Hebrew Bible, the destroying angel (, ''malʾāḵ hamašḥīṯ''), also known as mashḥit ( ''mašḥīṯ'', 'destroyer'; plural: , ''mašḥīṯīm'', 'spoilers, ravagers'), is an entity sent out by YHWH on several occasions to kill the enemies of the Hebrews. These angels (''mal'akh'') are also variously referred to as ''memitim'' (, 'executioners, slayers'), or Angel of the Lord. The latter is found in Job 33:22, as well as in Proverbs 16:14 in the plural, "messengers of death". ''Mashchith'' was also used as an alternate name for one of the seven compartments of Gehenna. In 2 Samuel 24:15-16, the destroying angel kills the inhabitants of Jerusalem. In I Chronicles 21:15, the same "Angel of the Lord" is seen by David to stand "between the earth and the heaven, with a drawn sword in his hand stretched out against Hebrews's enemies". Later, in II Kings 19:35, the angel kills 185,000 Assyrian soldiers. In the Book of Enoch, angels of punishment and destruction b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Targum
A targum ( arc, תרגום 'interpretation, translation, version') was an originally spoken translation of the Hebrew Bible (also called the ''Tanakh'') that a professional translator ( ''mǝturgǝmān'') would give in the common language of the listeners when that was not Hebrew. This had become necessary near the end of the first century BC, as the common language was Aramaic and Hebrew was used for little more than schooling and worship. The translator frequently expanded his translation with paraphrases, explanations and examples, so it became a kind of sermon. Writing down the targum was initially prohibited; nevertheless, some targumitic writings appeared as early as the middle of the first century AD. They were not then recognized as authoritative by the religious leaders. Some subsequent Jewish traditions (beginning with the Babylonian Jews) accepted the written targumim as authoritative translations of the Hebrew scriptures into Aramaic. Today, the common meaning of '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midrash
''Midrash'' (;"midrash" ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. he, מִדְרָשׁ; or מִדְרָשׁוֹת ''midrashot'') is expansive using a rabbinic mode of interpretation prominent in the . The word itself means "textual interpretation", "study", or " |
Targum Neophyti
Targum Neofiti (or Targum Neophyti) is the largest of the Western Targumim on the Torah, or Palestinian Targumim. The extant copy consists of 450 folios covering all books of the Torah, with only a few damaged verses. More than a mere Aramaic translation of the Hebrew text, Neofiti offers lengthy expansions on the biblical text at several places. It is often more expansive than Targum Onkelos, but less so than Targum Pseudo-Jonathan. History In 1587, Andrea de Monte gave the Targum Neofiti to his friend Ugo Boncompagni, who, like him, was a convert from Judaism. De Monte had censored it by deleting most references to idolatry while he owned the manuscript. In 1602 Boncampagni gave what was at that time labeled "Item 1" along with a fragmentary targum to the College of the Neophytes, the document's namesake, who preserved it until 1886, when the Vatican bought it along with other manuscripts when the Collegium closed. At that time Targum Neofiti was titled incorrectly as a ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eliezer
Eliezer (, "Help/Court of El") was the name of at least three different individuals in the Bible. Eliezer of Damascus Eliezer of Damascus () was, according to the Targums, the son of Nimrod. Eliezer was head of the patriarch Abraham's household, as mentioned in the Book of Genesis (15:2). Medieval biblical exegetes have explained the noun ''ben mešeq'' as meaning "butler; steward; overseer", while the name ''Damméseq Eliʿézer'' is explained by Targum Onkelos as meaning "Eliezer the Damascene." Others say that he was given the name "Damascus" by Abraham who purchased Eliezer from Nimrod, and had passed through the city of Damascus while returning with his servant from Babylonia. Other translations of Genesis describe Eliezer as Abraham's heir. There is an interpretation in Bereshit Rabbah (43:2), cited by Rashi, that Eliezer went alone with Abraham to rescue Lot, with the reference to "his initiates" stated to be 318 in number () being the numerical value of Eliezer's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |