|
Zinc Methyl
Dimethylzinc, also known as Zinc methyl, DMZ, or DMZn is a colorless volatile liquid Zn(CH3)2, formed by the action of methyl iodide on zinc at elevated temperature or on zinc sodium alloy. :2Zn + 2CH3I → Zn(CH3)2 + ZnI2 The sodium assists the reaction of the zinc with the methyl iodide. Zinc iodide is formed as a byproduct. It has a disagreeable odor, and is pyrophoric. It has been of great importance in the synthesis of organic compounds. It is soluble in alkanes and often sold as a solution in hexanes. It belongs to the large series of similar compounds such as diethylzinc. History This substance was first prepared by Edward Frankland during his work with Robert Bunsen in 1849 at the University of Marburg. After heating a mixture of zinc and methyl iodide in an airtight vessel, a flame burst out when the seal was broken. In the laboratory, this synthesis method remains unchanged today, except that copper or copper compounds are used to activate the zinc. Uses Dimeth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethylcadmium
Dimethylcadmium is the organocadmium compound with the formula Cd(CH3)2. It is a colorless highly toxic liquid that fumes in air. It is a linear molecule with C-Cd bond lengths of 213 pm. The compound finds limited use as a reagent in organic synthesis and in metalorganic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD). It has also been used in the synthesis of cadmium selenide nanoparticles, although efforts have been made to replace it in this capacity due to its toxicity. Dimethylcadmium is prepared by treating cadmium dihalides with methyl Grignard reagents or methyllithium. :CdBr2 + 2 CH3MgBr → Cd(CH3)2 + 2 MgBr2 The same method was used in the first preparation of this compound. Dimethylcadmium is a weak Lewis acid, forming a labile adduct with diethyl ether Diethyl ether, or simply ether, is an organic compound in the ether class with the formula , sometimes abbreviated as (see Pseudoelement symbols). It is a colourless, highly volatile, sweet-smelling ("ethereal odour"), ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MOCVD
Metalorganic vapour-phase epitaxy (MOVPE), also known as organometallic vapour-phase epitaxy (OMVPE) or metalorganic chemical vapour deposition (MOCVD), is a chemical vapour deposition method used to produce single- or polycrystalline thin films. It is a process for growing crystalline layers to create complex semiconductor multilayer structures. In contrast to molecular-beam epitaxy (MBE), the growth of crystals is by chemical reaction and not physical deposition. This takes place not in vacuum, but from the gas phase at moderate pressures (10 to 760 Torr). As such, this technique is preferred for the formation of devices incorporating thermodynamically metastable alloys, and it has become a major process in the manufacture of optoelectronics, such as Light-emitting diodes. It was invented in 1968 at North American Aviation (later Rockwell International) Science Center by Harold M. Manasevit. Basic principles In MOCVD ultrapure precursor gases are injected into a reactor, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetragonal
In crystallography, the tetragonal crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. Tetragonal crystal lattices result from stretching a cubic lattice along one of its lattice vectors, so that the cube becomes a rectangular prism with a square base (''a'' by ''a'') and height (''c'', which is different from ''a''). Bravais lattices There are two tetragonal Bravais lattices: the primitive tetragonal and the body-centered tetragonal. The base-centered tetragonal lattice is equivalent to the primitive tetragonal lattice with a smaller unit cell, while the face-centered tetragonal lattice is equivalent to the body-centered tetragonal lattice with a smaller unit cell. Crystal classes The point groups that fall under this crystal system are listed below, followed by their representations in international notation, Schoenflies notation, orbifold notation, Coxeter notation and mineral examples.Hurlbut, Cornelius S.; Klein, Cornelis, 1985, ''Manual of Mineralogy'', 20th ed., p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid
Solid is one of the State of matter#Four fundamental states, four fundamental states of matter (the others being liquid, gas, and Plasma (physics), plasma). The molecules in a solid are closely packed together and contain the least amount of kinetic energy. A solid is characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to a force applied to the surface. Unlike a liquid, a solid object does not flow to take on the shape of its container, nor does it expand to fill the entire available volume like a gas. The atoms in a solid are bound to each other, either in a regular geometric lattice (crystal, crystalline solids, which include metals and ordinary ice), or irregularly (an amorphous solid such as common window glass). Solids cannot be compressed with little pressure whereas gases can be compressed with little pressure because the molecules in a gas are loosely packed. The branch of physics that deals with solids is called solid-state physics, and is the main branch of condens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Journal Of Chemistry
The ''New Journal of Chemistry'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal publishing research and review articles on all aspects of chemistry. It is published by the Royal Society of Chemistry on behalf of the French National Centre for Scientific Research (CNRS). It was established as ''Nouveau Journal de Chimie'' in 1977, acquiring its current title in 1999. The editors-in-chief are Denise Parent (CNRS) and Sarah Ruthven (RSC). According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 3.591. Article types * Research papers: which contain original scientific work that has not been published previously * Letters: original scientific work that is of an urgent nature and that has not been published previously * Perspectives: invited from younger prize-winning scientists who present their work and ideas, setting these in the context of the work of others * Interfaces: written by pairs of collaborating scientists from different disciplines on their co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photonic
Photonics is a branch of optics that involves the application of generation, detection, and manipulation of light in form of photons through emission, transmission, modulation, signal processing, switching, amplification, and sensing. Though covering all light's technical applications over the whole spectrum, most photonic applications are in the range of visible and near-infrared light. The term photonics developed as an outgrowth of the first practical semiconductor light emitters invented in the early 1960s and optical fibers developed in the 1970s. History The word 'Photonics' is derived from the Greek word "phos" meaning light (which has genitive case "photos" and in compound words the root "photo-" is used); it appeared in the late 1960s to describe a research field whose goal was to use light to perform functions that traditionally fell within the typical domain of electronics, such as telecommunications, information processing, etc. Photonics as a field began with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronics
The field of electronics is a branch of physics and electrical engineering that deals with the emission, behaviour and effects of electrons using electronic devices. Electronics uses active devices to control electron flow by amplification and rectification, which distinguishes it from classical electrical engineering, which only uses passive effects such as resistance, capacitance and inductance to control electric current flow. Electronics has hugely influenced the development of modern society. The central driving force behind the entire electronics industry is the semiconductor industry sector, which has annual sales of over $481 billion as of 2018. The largest industry sector is e-commerce, which generated over $29 trillion in 2017. History and development Electronics has hugely influenced the development of modern society. The identification of the electron in 1897, along with the subsequent invention of the vacuum tube which could amplify and rectify small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminium Gallium Arsenide
Aluminium gallium arsenide (also gallium aluminium arsenide) ( Alx Ga1−x As) is a semiconductor material with very nearly the same lattice constant as GaAs, but a larger bandgap. The ''x'' in the formula above is a number between 0 and 1 - this indicates an arbitrary alloy between GaAs and AlAs. The chemical formula ''AlGaAs'' should be considered an abbreviated form of the above, rather than any particular ratio. The bandgap varies between 1.42 eV (GaAs) and 2.16 eV (AlAs). For x < 0.4, the bandgap is direct. The is related with the bandgap via the and varies between 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GaAs
Gallium arsenide (GaAs) is a III-V direct band gap semiconductor with a zinc blende crystal structure. Gallium arsenide is used in the manufacture of devices such as microwave frequency integrated circuits, monolithic microwave integrated circuits, infrared light-emitting diodes, laser diodes, solar cells and optical windows. GaAs is often used as a substrate material for the epitaxial growth of other III-V semiconductors, including indium gallium arsenide, aluminum gallium arsenide and others. Preparation and chemistry In the compound, gallium has a +3 oxidation state. Gallium arsenide single crystals can be prepared by three industrial processes: * The vertical gradient freeze (VGF) process. * Crystal growth using a horizontal zone furnace in the Bridgman-Stockbarger technique, in which gallium and arsenic vapors react, and free molecules deposit on a seed crystal at the cooler end of the furnace. * Liquid encapsulated Czochralski (LEC) growth is used for producing high-puri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductors
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical resistivity and conductivity, electrical conductivity value falling between that of a electrical conductor, conductor, such as copper, and an insulator (electricity), insulator, such as glass. Its electrical resistivity and conductivity, resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way. Its conducting properties may be altered in useful ways by introducing impurities ("doping (semiconductor), doping") into the crystal structure. When two differently doped regions exist in the same crystal, a semiconductor junction is created. The behavior of charge carriers, which include electrons, ions, and electron holes, at these junctions is the basis of diodes, transistors, and most modern electronics. Some examples of semiconductors are silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, and elements near the so-called "metalloid staircase" on the periodic table. After silicon, gallium arsenide is the second-most common s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dopant
A dopant, also called a doping agent, is a trace of impurity element that is introduced into a chemical material to alter its original electrical or optical properties. The amount of dopant necessary to cause changes is typically very low. When doped into crystalline substances, the dopant's atoms get incorporated into its crystal lattice. The crystalline materials are frequently either crystals of a semiconductor such as silicon and germanium for use in solid-state electronics, or transparent crystals for use in the production of various laser types; however, in some cases of the latter, noncrystalline substances such as glass can also be doped with impurities. In solid-state electronics using the proper types and amounts of dopants in semiconductors is what produces the p-type semiconductors and n-type semiconductors that are essential for making transistors and diodes. Transparent crystals Lasing media The procedure of doping tiny amounts of the metals chromium (Cr), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
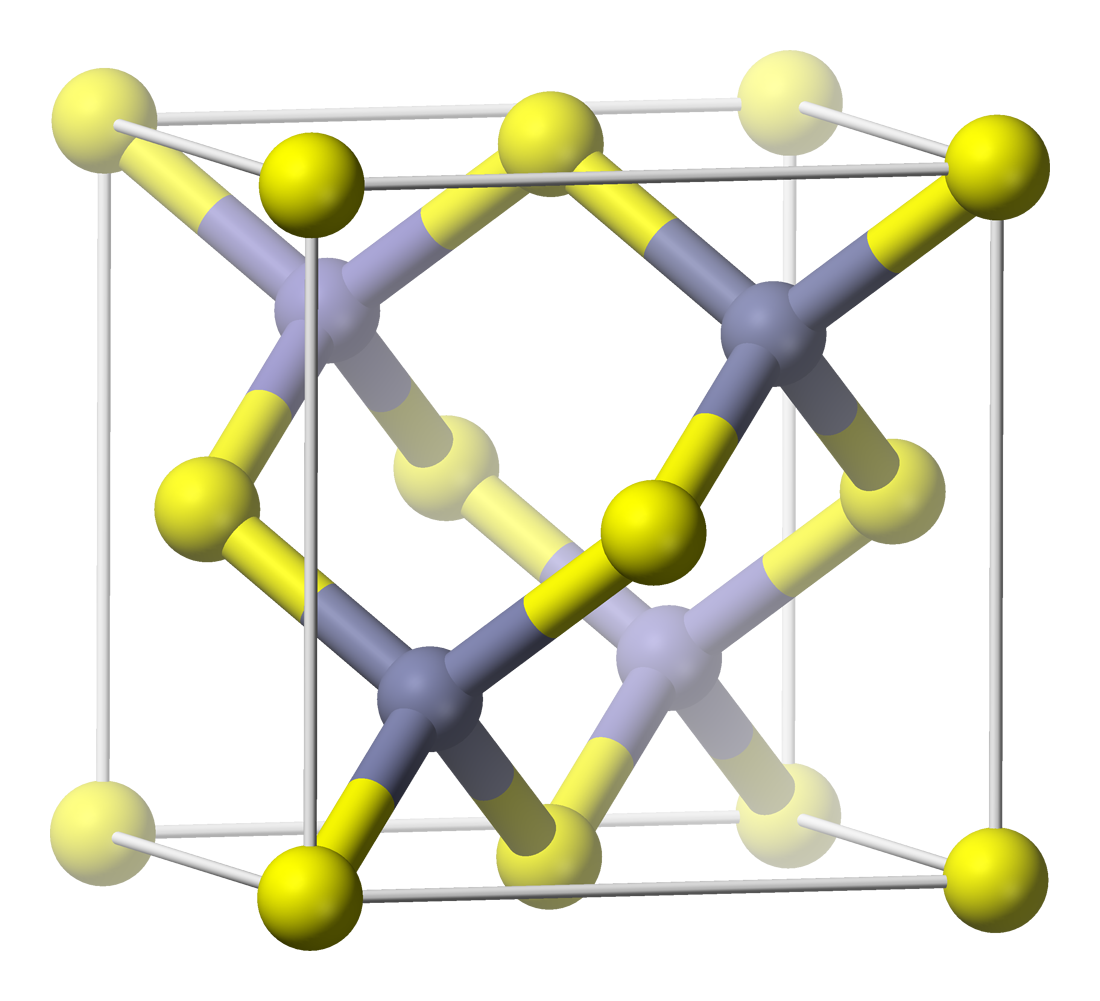
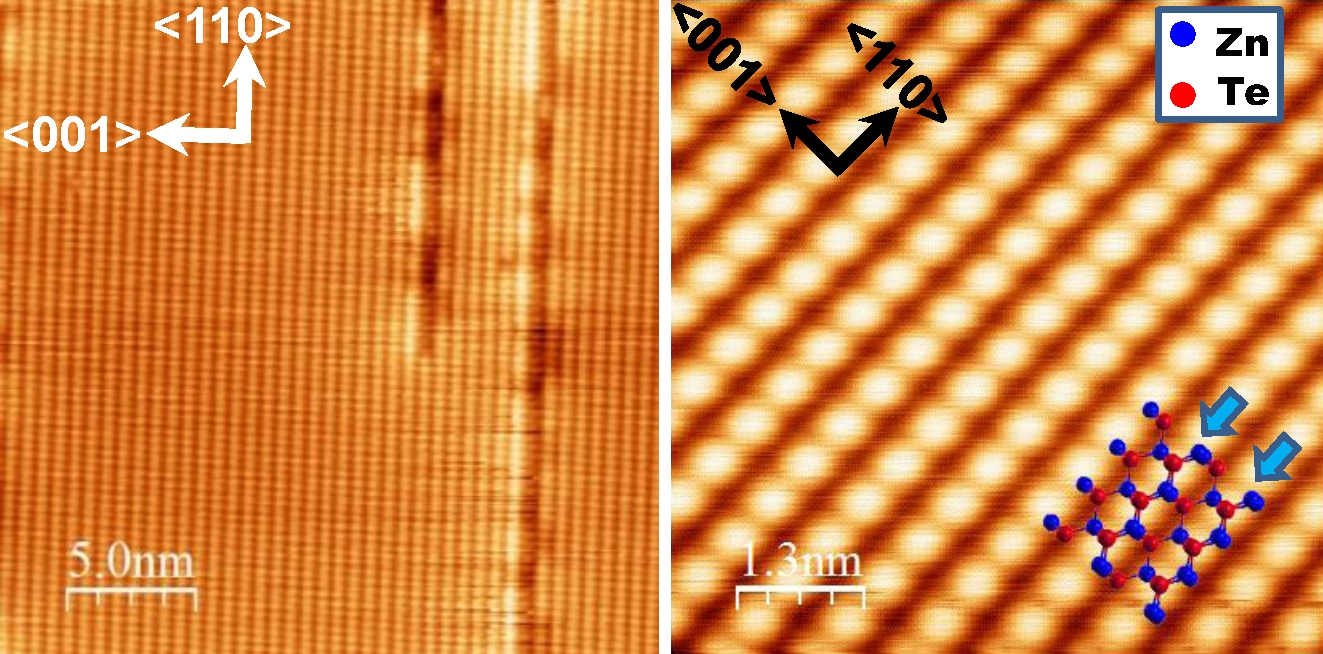
ZnTe
Zinc telluride is a binary chemical compound with the formula ZnTe. This solid is a semiconductor material with a direct band gap of 2.26 eV. It is usually a p-type semiconductor. Its crystal structure is cubic, like that for sphalerite and diamond. Properties ZnTe has the appearance of grey or brownish-red powder, or ruby-red crystals when refined by sublimation. Zinc telluride typically had a cubic (sphalerite, or "zincblende") crystal structure, but can be also prepared as rocksalt crystals or in hexagonal crystals (wurtzite structure). Irradiated by a strong optical beam burns in presence of oxygen. Its lattice constant is 0.6101 nm, allowing it to be grown with or on aluminium antimonide, gallium antimonide, indium arsenide, and lead selenide. With some lattice mismatch, it can also be grown on other substrates such as GaAs, and it can be grown in thin-film polycrystalline (or nanocrystalline) form on substrates such as glass, for example, in the manufacture of thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |