|
Zenneck Wave
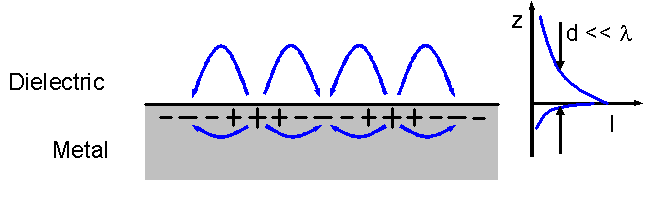
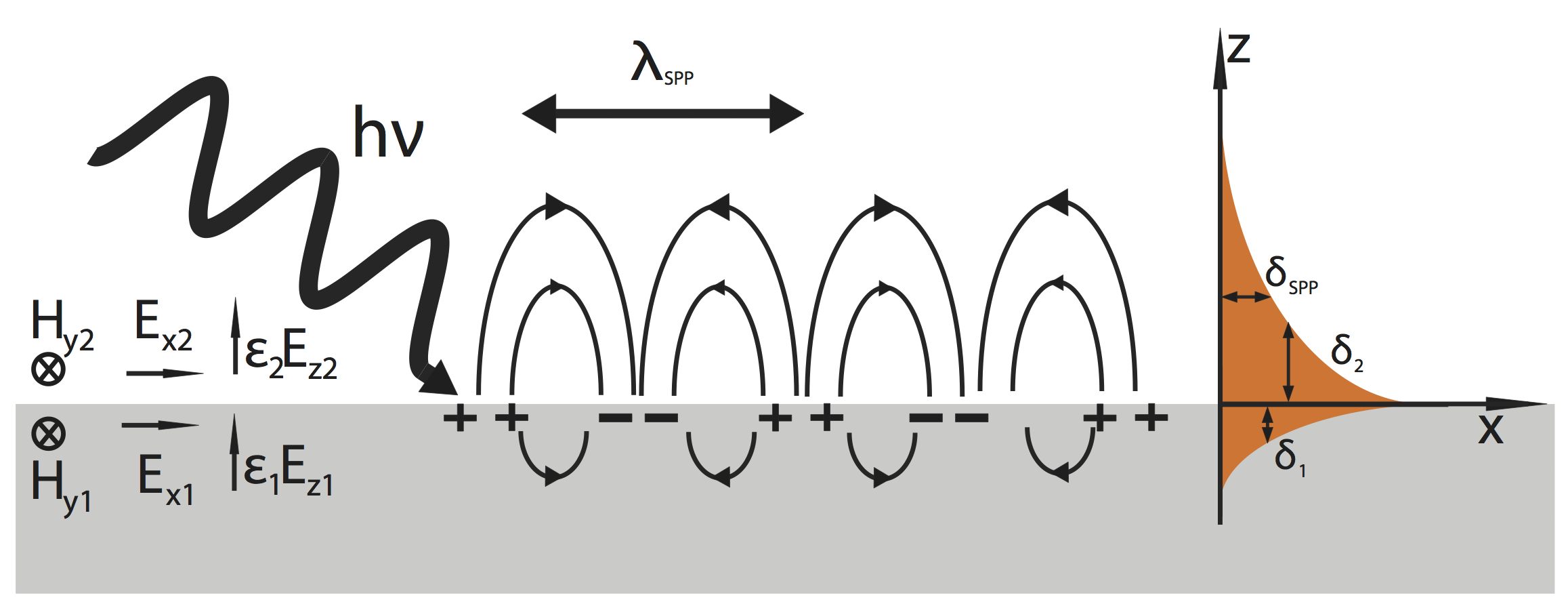
The Zenneck wave, Zenneck surface wave or Sommerfeld-Zenneck surface wave is a longitudinal, inhomogeneous or non-uniform electromagnetic plane wave incident at the complex Brewster's angle onto a planar or spherical boundary interface between two homogeneous media having different dielectric constants.Corum, K.L. and J.F. Corum, “Bell Labs and the ‘Crucial’ 1936 Seneca Lake Experiment.” Republished as: The Zenneck wave propagates parallel to the interface and decays exponentially vertical to it, a property known as evanescence. It exists under the condition that the permittivity of one of the materials forming the interface is negative, while the other one is positive, as for example the interface between air and a lossy conducting medium such as the terrestrial transmission line, below the plasma frequency. Arising from original analysis by Arnold Sommerfeld and Jonathan Zenneck of the problem of wave propagation over a lossy earth, it exists as an exact solution to Max ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plane Wave
In physics, a plane wave is a special case of wave or field: a physical quantity whose value, at any moment, is constant through any plane that is perpendicular to a fixed direction in space. For any position \vec x in space and any time t, the value of such a field can be written as :F(\vec x,t) = G(\vec x \cdot \vec n, t), where \vec n is a unit-length vector, and G(d,t) is a function that gives the field's value as dependent on only two real parameters: the time t, and the scalar-valued displacement d = \vec x \cdot \vec n of the point \vec x along the direction \vec n. The displacement is constant over each plane perpendicular to \vec n. The values of the field F may be scalars, vectors, or any other physical or mathematical quantity. They can be complex numbers, as in a complex exponential plane wave. When the values of F are vectors, the wave is said to be a longitudinal wave if the vectors are always collinear with the vector \vec n, and a transverse wave if they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brewster's Angle
Brewster's angle (also known as the polarization angle) is an angle of incidence at which light with a particular polarization is perfectly transmitted through a transparent dielectric surface, with ''no reflection''. When ''unpolarized'' light is incident at this angle, the light that is reflected from the surface is therefore perfectly polarized. This special angle of incidence is named after the Scottish physicist Sir David Brewster (1781–1868). Explanation When light encounters a boundary between two media with different refractive indices, some of it is usually reflected as shown in the figure above. The fraction that is reflected is described by the Fresnel equations, and depends on the incoming light's polarization and angle of incidence. The Fresnel equations predict that light with the ''p'' polarization (electric field polarized in the same plane as the incident ray and the surface normal at the point of incidence) will not be reflected if the angle of incidence is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evanescent Field
In electromagnetics, an evanescent field, or evanescent wave, is an oscillating electric and/or magnetic field that does not propagate as an electromagnetic wave but whose energy is spatially concentrated in the vicinity of the source (oscillating charges and currents). Even when there is a propagating electromagnetic wave produced (e.g., by a transmitting antenna), one can still identify as an evanescent field the component of the electric or magnetic field that cannot be attributed to the propagating wave observed at a distance of many wavelengths (such as the far field of a transmitting antenna). A hallmark of an evanescent field is that there is no net energy flow in that region. Since the net flow of electromagnetic energy is given by the average Poynting vector, this means that the Poynting vector in these regions, as averaged over a complete oscillation cycle, is zero. Use of the term In many cases one cannot simply say that a field is or is not "evanescent": Having Po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permittivity
In electromagnetism, the absolute permittivity, often simply called permittivity and denoted by the Greek letter ''ε'' ( epsilon), is a measure of the electric polarizability of a dielectric. A material with high permittivity polarizes more in response to an applied electric field than a material with low permittivity, thereby storing more energy in the material. In electrostatics, the permittivity plays an important role in determining the capacitance of a capacitor. In the simplest case, the electric displacement field D resulting from an applied electric field E is :\mathbf = \varepsilon \mathbf. More generally, the permittivity is a thermodynamic function of state. It can depend on the frequency, magnitude, and direction of the applied field. The SI unit for permittivity is farad per meter (F/m). The permittivity is often represented by the relative permittivity ''ε''r which is the ratio of the absolute permittivity ''ε'' and the vacuum permittivity ''ε''0 :\kappa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma Frequency
Plasma oscillations, also known as Langmuir waves (after Irving Langmuir), are rapid oscillations of the electron density in conducting media such as plasmas or metals in the ultraviolet region. The oscillations can be described as an instability in the dielectric function of a free electron gas. The frequency only depends weakly on the wavelength of the oscillation. The quasiparticle resulting from the quantization of these oscillations is the plasmon. Langmuir waves were discovered by American physicists Irving Langmuir and Lewi Tonks in the 1920s. They are parallel in form to Jeans instability waves, which are caused by gravitational instabilities in a static medium. Mechanism Consider an electrically neutral plasma in equilibrium, consisting of a gas of positively charged ions and negatively charged electrons. If one displaces by a tiny amount an electron or a group of electrons with respect to the ions, the Coulomb force pulls the electrons back, acting as a restoring fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arnold Sommerfeld
Arnold Johannes Wilhelm Sommerfeld, (; 5 December 1868 – 26 April 1951) was a German theoretical physicist who pioneered developments in atomic and quantum physics, and also educated and mentored many students for the new era of theoretical physics. He served as doctoral supervisor for many Nobel Prize winners in physics and chemistry (only J. J. Thomson's record of mentorship is comparable to his). He introduced the second quantum number (azimuthal quantum number) and the third quantum number (magnetic quantum number). He also introduced the fine-structure constant and pioneered X-ray wave theory. Early life and education Sommerfeld was born in 1868 to a family with deep ancestral roots in Prussia. His mother Cäcilie Matthias (1839–1902) was the daughter of a Potsdam builder. His father Franz Sommerfeld (1820–1906) was a physician from a leading family in Königsberg, where Arnold's grandfather had resettled from the hinterland in 1822 for a career as Court Postal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jonathan Zenneck
Jonathan Adolf Wilhelm Zenneck (15 April 1871 – 8 April 1959) was a German physicist and electrical engineer who contributed to researches in radio circuit performance and to the scientific and educational contributions to the literature of the pioneer radio art. Zenneck improved the Braun cathode ray tube by adding a second deflection structure at right angles to the first, which allowed two-dimensional viewing of a waveform. This two-dimensional display is fundamental to the oscilloscope. Early years Zenneck was born in Ruppertshofen, Württemberg. In 1885, Zenneck entered the Evangelical-Theological Seminary in Maulbronn. In 1887, while in a Blaubeuren seminary, Zenneck learned Latin, Greek, French, and Hebrew. In 1889, Zenneck enrolled in the University of Tübingen. At the Tübingen Seminary, he studied mathematics and natural sciences. In 1894, Zenneck took the state examination in mathematics and natural sciences and the examination for his doctor's degree. His dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxwell's Equations
Maxwell's equations, or Maxwell–Heaviside equations, are a set of coupled partial differential equations that, together with the Lorentz force law, form the foundation of classical electromagnetism, classical optics, and electric circuits. The equations provide a mathematical model for electric, optical, and radio technologies, such as power generation, electric motors, wireless communication, lenses, radar etc. They describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated by charges, currents, and changes of the fields.''Electric'' and ''magnetic'' fields, according to the theory of relativity, are the components of a single electromagnetic field. The equations are named after the physicist and mathematician James Clerk Maxwell, who, in 1861 and 1862, published an early form of the equations that included the Lorentz force law. Maxwell first used the equations to propose that light is an electromagnetic phenomenon. The modern form of the equations in their most common formul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longitudinal Wave
Longitudinal waves are waves in which the vibration of the medium is parallel ("along") to the direction the wave travels and displacement of the medium is in the same (or opposite) direction of the wave propagation. Mechanical longitudinal waves are also called ''compressional'' or compression waves, because they produce compression and rarefaction when traveling through a medium, and pressure waves, because they produce increases and decreases in pressure. A wave along the length of a stretched Slinky toy, where the distance between coils increases and decreases, is a good visualization. Real-world examples include sound waves (vibrations in pressure, a particle of displacement, and particle velocity propagated in an elastic medium) and seismic P-waves (created by earthquakes and explosions). The other main type of wave is the transverse wave, in which the displacements of the medium are at right angles to the direction of propagation. Transverse waves, for instance, describe ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body-centric Wireless Network
On-body wireless or body-centric wireless is the interconnection and networking of wearable computer system components and sensors through a system of transceivers, space wave antennas, and surface guided wave antennas for telemetry and telecommunications. The technique uses the surface of the human body as a transmission medium or path for electromagnetic waves. The topic of body-centric wireless networks (BCWN) can be divided into three main domains based on wireless sensor nodes placement, i.e., communication between the nodes that are on the body surface; communication from the body-surface to nearby base station; and at least one node may be implanted within the body. These three domains have been called on-body, off-body and in-body, respectively.Qammer H. Abbasi, Masood Ur Rehman, Khalid Qaraqe and Akram Alomainy, "Advances in Body-Centric Wireless Communications: Applications and Stateof- the-art", The Institution of Engineering and Technology (IET) Publication, July, 2016 Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Plasmon
Surface plasmons (SPs) are coherent delocalized electron oscillations that exist at the interface between any two materials where the real part of the dielectric function changes sign across the interface (e.g. a metal-dielectric interface, such as a metal sheet in air). SPs have lower energy than bulk (or volume) plasmons which quantise the longitudinal electron oscillations about positive ion cores within the bulk of an electron gas (or plasma). The charge motion in a surface plasmon always creates electromagnetic fields outside (as well as inside) the metal. The ''total'' excitation, including both the charge motion and associated electromagnetic field, is called either a surface plasmon polariton at a planar interface, or a localized surface plasmon for the closed surface of a small particle. The existence of surface plasmons was first predicted in 1957 by Rufus Ritchie. In the following two decades, surface plasmons were extensively studied by many scientists, the foremost o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |