|
Zawiya Of Sidi Muhammad Ben Sliman Al-Jazuli
The Zawiya of Sidi Muhammad Ben Sliman al-Jazuli (also Zaouia of Sidi Ben Slimane al-Jazouli or Zawiya al-Jazuliya, among other variations) is an Islamic religious complex ( zawiya) in Marrakesh, Morocco. It is centered around the tomb of the 15th-century Muslim scholar and Sufi saint Muhammad al-Jazuli (also known as Imam al-Jazuli, full name: ''Abū 'Abdullah Muḥammad ibn Sulaymān ibn Abū Bakr al-Jazūli al-Simlālī''), who is one of the Seven Saints of Marrakesh. Historical background Al-Jazuli was a major figure in the history of Moroccan Sufism. He lived at a time when local Sufi movements were also filling a void of political leadership against the encroachment of Portuguese and Spanish forces into the country. Originating from the Sous region in southern Morocco, he spent much time in Fes where he wrote his most famous work, the Dala'il al-Khayrat, and gained enormous influence over zawiyas and followers across the country. He subsequently moved around the coast of M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ''Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the Muhammad in Islam, main and final Islamic prophet.Peters, F. E. 2009. "Allāh." In , edited by J. L. Esposito. Oxford: Oxford University Press. . (See alsoquick reference) "[T]he Muslims' understanding of Allāh is based...on the Qurʿān's public witness. Allāh is Unique, the Creator, Sovereign, and Judge of mankind. It is Allāh who directs the universe through his direct action on nature and who has guided human history through his prophets, Abraham, with whom he made his covenant, Moses/Moosa, Jesus/Eesa, and Muḥammad, through all of whom he founded his chosen communities, the 'Peoples of the Book.'" It is the Major religious groups, world's second-largest religion behind Christianity, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dala'il Al-Khayrat
''Dalāil al-khayrāt wa-shawāriq al-anwār fī dhikr al-ṣalāt alá al-Nabī al-mukhtār'' ( ar, دلائل الخيرات وشوارق الأنوار في ذكر الصلاة على النبي المختار, translation=Waymarks of Benefits and the Brilliant Burst of Lights in the Remembrance of Blessings on the Chosen Prophet), usually shortened to ''Dala'il al-Khayrat'', is a famous collection of prayers for the Islamic prophet Muhammad, which was written by the Moroccan Shadhili scholar Muhammad al-Jazuli (died 1465 AD). It is popular in parts of the Islamic world amongst traditional Muslims—specifically North Africa, the Levant, Turkey, the Caucasus and South Asia—and is divided into sections for daily recitation. Background Moroccan ''hadith'' scholar Abdullah al-Talidi wrote of the ''Dala'il al-Khayrat'': "Millions of Muslims from East to West tried it and found its good, its blessing, and its benefit for centuries and over generations, and witnessed its unbeliev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
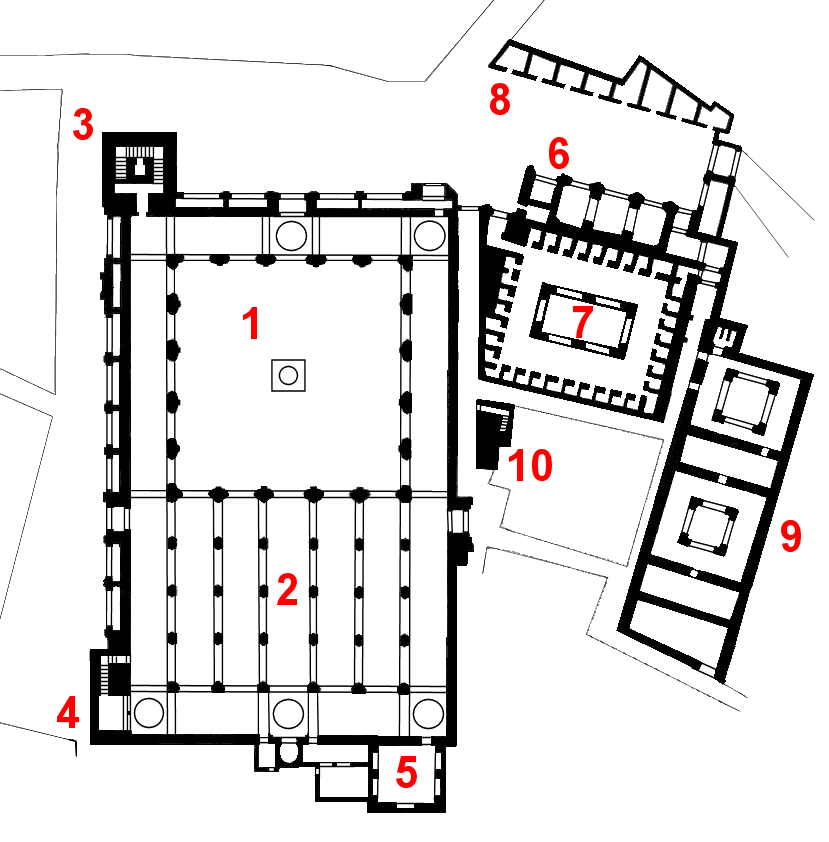
Zawiya Of Sidi Bel Abbes
The Zawiya of Sidi Bel Abbes or Zaouia of Sidi Bel-Abbès (, Berber: ⵣⴰⵡⵉⵢⴰ ⵙⵉⴷⵉ ⴱⵍⵄⴻⴱⴰⵙ) is an Islamic religious complex ( zawiya) in Marrakesh, Morocco. The complex is centered around the mausoleum of Abu al-Abbas as-Sabti (or Sidi Bel Abbes), a Sufi teacher who died in 1204. He is the most venerated of the Seven Saints of Marrakesh, generally considered the "patron saint" of the city. The zawiya's architecture dates in part to the late Saadian period (early 17th century) but has been modified and restored multiple times since then. History Abu al-Abbas al-Sabti (full name: ''Sidi Ahmed ibn Dja'far al-Khazraji Abu al-Abbas as-Sabti'') was born in Ceuta in 1129 or 1130. He studied under Abu Abd Allah al-Fakhkhar, who was in turn a student of Qadi Ayyad (another of the seven saints buried in Marrakesh). In 1146 he moved to Marrakesh during the final weeks of the Almohad siege of the city and established himself there after its capture, mainly st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bab Doukkala Mosque
The Bab Doukkala Mosque (or Mosque of Bab Doukkala) is a major neighbourhood mosque (a Friday mosque) in Marrakesh, Morocco, dating from the 16th century. It is named after the nearby city gate, Bab Doukkala, in the western city walls. It is also known as the al-Hurra Mosque (or Mosque of the Free One, in reference to its founder, Massa'uda al-Wizkitiya). Historical background It was commissioned by Lalla Mas'uda bint Ahmad, a daughter of Muhammad al-Sheikh (the founder of the Saadian Dynasty) and mother of Sultan Ahmad al-Mansur, during the Saadian Dynasty. Construction of the mosque began in 1557-58 CE (965 AH) and probably finished around 1570-71 CE (979 AH), which would have been under the reign of Moulay Abdallah al-Ghalib. Lalla Ma'suda's status as a powerful and "free" or independent woman may have given the mosque its alternate name of ''Jami' al-Hurra'' ("Mosque of Freedom"). In 1557-58 CE the sultan had ordered that the Jewish population of the city relocate t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mouassine Mosque
The Mouassine Mosque or al-Muwassin Mosque () is a major neighbourhood mosque (a Friday mosque) in Marrakech, Morocco, dating from the 16th century during the Saadian Dynasty. It shares its name with the Mouassine neighbourhood. History Background The mosque was commissioned by the Saadian sultan Moulay Abdallah al-Ghalib. Construction took place between 1562-63 CE (970 AH) and 1572-73 CE (980 AH). In 1557-58 CE the sultan had ordered that the Jewish population of the city relocate to an area closer to the Kasbah (royal citadel), resulting in the creation of a new Jewish ''mellah'' which continued to exist into modern times. Construction of the mellah was probably finished around 1562-63. Meanwhile, the emptying of the old Jewish neighbourhoods had liberated a large amount of space within the city which was open to redevelopment. The Mouassine Mosque, along with the Bab Doukkala Mosque whose construction began slightly earlier, appears to have been part of a larger plan t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zawiya Al-jazuli DSCF1477
Zawiya (institution) is an Islamic religious school or monastery. Zawiya, Zawiyah, Zawia, Zaouia, Zaouiet and similar terms may also refer to: Places Algeria * Aïn Zaouia, an Algerian town * Mazer Zaouia, an Algerian village * Zaouia El Abidia, an Algerian town * Zaouia el Kbira, an Algerian village * Zaouia Foukania, an Algerian village * Zaouia Sidi Moussa, an Algerian village * Zaouiet Kounta, an Algerian town * Zaouiet Kounta District, an Algerian district * Zawiya Thaalibia, an Algerian zawiya in the Casbah of Algiers * Zawiya Thaalibia, an Algerian zawiya in the Issers * Zawiyas in Algeria, an Algerian Islamic topic * Zawiyet El Hamel, a Sufi zawiya in Algeria * Zawiyet Sidi Amar Cherif, a Sufi zawiya in Algeria * Zawiyet Sidi Boumerdassi, a Sufi zawiya in Algeria * Zawiyet Sidi Boushaki, a Sufi zawiya in Algeria Egypt * Zawyet El Aryan, an Egyptian town * Unfinished Northern Pyramid of Zawyet El Aryan, an Egyptian pyramid * Zawyat Razin, an Egyptian city Israel * Kh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad IV Of Morocco
''Mawlay'' Muhammad bin Abd al-Rahman ( ar, محمد بن عبد الرحمن), known as Muhammad IV ( ar, محمد الرابع), born in Fes in 1803 and died in Marrakesh in 1873, was the Sultan of Morocco from 28 August 1859 to 16 September 1873 as a ruler of the 'Alawi dynasty. He was proclaimed sultan after the death of his father, Abd al-Rahman. His reign marked a series of reform to tackle European influence on Morocco, as Ottoman Algeria had just been conquered by France in 1830, leading to European nations entering military conflicts with Morocco, such as the Battle of Isly with France in 1844 and the Battle of Tetuan with Spain in 1860. He was succeeded by his son Hassan I. Biography Military commander Born in 1803 in Fes, Mawlay Muhammad was a son of the 'Alawi sultan of Morocco Abd al-Rahman. During his father's reign, neighbouring Ottoman Algeria was invaded by France in 1830, and Muhammad commanded the Moroccan army which was defeated by the French at the Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohammed Ben Abdallah
''Sidi'' Mohammed ben Abdallah ''al-Khatib'' ( ar, سيدي محمد بن عبد الله الخطيب), known as Mohammed III ( ar, محمد الثالث), born in 1710 in Fes and died on 9 April 1790 in Meknes, was the Sultan of Morocco from 1757 to 1790 as a member of the 'Alawi dynasty. He was the governor of Marrakesh around 1750. He was also briefly sultan in 1748. He rebuilt many cities after the earthquake of 1755, including Mogador, Casablanca, and Rabat, and Abdallah Laroui described him as "the architect of modern Morocco." He also defeated the French in the Larache expedition in 1765 and expelled the Portuguese from Mazagan ( ''al-Jadīda'') in 1769. He is notable for having been the leader of one of the first nations to recognize American independence in his alliance with Luis de Unzaga 'le Conciliateur' through correspondence and Unzaga's secret intelligence service and led by his brothers-in-law Antonio and Matías de Gálvez from the Canary Islands. He was the son o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jama Masjid
A congregational mosque or Friday mosque (, ''masjid jāmi‘'', or simply: , ''jāmi‘''; ), or sometimes great mosque or grand mosque (, ''jāmi‘ kabir''; ), is a mosque for hosting the Friday noon prayers known as ''jumu'ah''.* * * * * * * * * It can also host the Eid prayers in situations when there is no ''musalla'' or ''eidgah'' available nearby to host the prayers. In early Islamic history, the number of congregational mosques in one city was strictly limited. As cities and populations grew over time, it became more common for many mosques to host Friday prayers in the same area. Etymology The full Arabic term for this kind of mosque is ''masjid jāmi‘'' (), which is typically translated as "mosque of congregation" or "congregational mosque". "Congregational" is used to translate ''jāmi‘'' (), which comes from the Arabic root "ج - م - ع" which has a meaning ‘to bring together’ or ‘to unify’ (verbal form: and ). In Arabic, the term is typically simplifie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cupola
In architecture, a cupola () is a relatively small, most often dome-like, tall structure on top of a building. Often used to provide a lookout or to admit light and air, it usually crowns a larger roof or dome. The word derives, via Italian, from lower Latin ''cupula'' (classical Latin ''cupella''), (Latin ''cupa''), indicating a vault resembling an upside-down cup. Background The cupola evolved during the Renaissance from the older oculus. Being weatherproof, the cupola was better suited to the wetter climates of northern Europe. The chhatri, seen in Indian architecture, fits the definition of a cupola when it is used atop a larger structure. Cupolas often serve as a belfry, belvedere, or roof lantern above a main roof. In other cases they may crown a spire, tower, or turret. Barns often have cupolas for ventilation. Cupolas can also appear as small buildings in their own right. The square, dome-like segment of a North American railroad train caboose that contains the seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ismail Ibn Sharif
Moulay Ismail Ibn Sharif ( ar, مولاي إسماعيل بن الشريف), born around 1645 in Sijilmassa and died on 22 March 1727 at Meknes, was a Sultan of Morocco from 1672–1727, as the second ruler of the Alaouite dynasty. He was the seventh son of Moulay Sharif and was governor of the province of Fez and the north of Morocco from 1667 until the death of his half-brother, Sultan Moulay Rashid in 1672. He was proclaimed sultan at Fez, but spent several years in conflict with his nephew Moulay Ahmed ben Mehrez, who also claimed the throne, until the latter's death in 1687. Moulay Ismail's 55-year reign is the longest of any sultan of Morocco. The reign of Moulay Ismail marked a high watermark for Moroccan power. His military successes are explained by the creation of a strong army, originally relying on the 'Guichs' (especially the Udaya) and on the Black Guard (or Abid al-Bukhari), black slaves who were totally devoted to him. As a result, the central power could be le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaouite Dynasty
The Alawi dynasty ( ar, سلالة العلويين الفيلاليين, translit=sulālat al-ʿalawiyyīn al-fīlāliyyīn) – also rendered in English as Alaouite, Alawid, or Alawite – is the current Morocco, Moroccan royal family and reigning dynasty. They are an Arab Sharifism, sharifian dynasty and claim descent from the Islamic prophet Muhammad through his grandson, Hasan ibn Ali. Their ancestors originally migrated to the Tafilalt region, in present-day Morocco, from Yanbu on the coast of the Hejaz in the 12th or 13th century. The dynasty rose to power in the 17th century, beginning with Sharif ibn Ali, Mawlay al-Sharif who was declared sultan of the Tafilalt in 1631. His son Al-Rashid of Morocco, Al-Rashid, ruling from 1664 to 1672, was able to unite and pacify the country after a long period of regional divisions caused by the weakening of the Saadi Dynasty. His brother Ismail Ibn Sharif, Isma'il presided over a period of strong central rule between 1672 and 1727, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)




.jpg)

