|
Zambezi Belt
The Zambezi Belt is an area of orogenic deformation in southern Zambia and northern Zimbabwe. It is a segment of a broader belt lying between the Congo Craton and the Kalahari Craton, which also includes the Lufilian Arc and the Damaran Belt. The eastern margin of the belt interacts with the north-south Eastern African orogen. The Zambezi belt shows evidence of two large tectonothermal events, one between about 890-880 Ma and the other about 550-520 Ma. Both events reworked existing Archean to Mesoproterozoic components, with small additions of younger material. The second event was caused by the collision of the Congo and Kalahari cratons during the assembly of the Gondwana supercontinent at the end of the Neoproterozoic. The belt includes the Kadunguri Whiteschists, which were formed by metasomatic alteration at high pressures of ocean-island-type metabasalts during the Pan-African orogeny. The Mwembeshi Shear Zone forms the northern boundary of the Zambezi Belt, sepa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
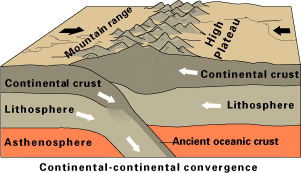
Orogeny
Orogeny is a mountain building process. An orogeny is an event that takes place at a convergent plate margin when plate motion compresses the margin. An ''orogenic belt'' or ''orogen'' develops as the compressed plate crumples and is uplifted to form one or more mountain ranges. This involves a series of geological processes collectively called orogenesis. These include both structural deformation of existing continental crust and the creation of new continental crust through volcanism. Magma rising in the orogen carries less dense material upwards while leaving more dense material behind, resulting in compositional differentiation of Earth's lithosphere ( crust and uppermost mantle). A synorogenic process or event is one that occurs during an orogeny. The word "orogeny" () comes from Ancient Greek (, , + , , ). Although it was used before him, the term was employed by the American geologist G. K. Gilbert in 1890 to describe the process of mountain-building as distinguished f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoproterozoic
The Neoproterozoic Era is the unit of geologic time from 1 billion to 538.8 million years ago. It is the last era of the Precambrian Supereon and the Proterozoic Eon; it is subdivided into the Tonian, Cryogenian, and Ediacaran periods. It is preceded by the Mesoproterozoic Era and succeeded by the Paleozoic Era of the Phanerozoic Eon. The most severe glaciation known in the geologic record occurred during the Cryogenian, when ice sheets may have reached the equator and formed a " Snowball Earth". The earliest fossils of complex multicellular life are found in the Ediacaran Period. These organisms make up the Ediacaran biota, including the oldest definitive animals in the fossil record. According to Rino and co-workers, the sum of the continental crust formed in the Pan-African orogeny and the Grenville orogeny makes the Neoproterozoic the period of Earth's history that has produced most continental crust. Geology At the onset of the Neoproterozoic the supercontine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orogenies Of Africa
Orogeny is a mountain building process. An orogeny is an event that takes place at a convergent plate margin when plate motion compresses the margin. An ''orogenic belt'' or ''orogen'' develops as the compressed plate crumples and is uplifted to form one or more mountain ranges. This involves a series of geological processes collectively called orogenesis. These include both structural deformation of existing continental crust and the creation of new continental crust through volcanism. Magma rising in the orogen carries less dense material upwards while leaving more dense material behind, resulting in compositional differentiation of Earth's lithosphere ( crust and uppermost mantle). A synorogenic process or event is one that occurs during an orogeny. The word "orogeny" () comes from Ancient Greek (, , + , , ). Although it was used before him, the term was employed by the American geologist G. K. Gilbert in 1890 to describe the process of mountain-building as distinguished ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ediacaran Orogenies
The Ediacaran Period ( ) is a geological period that spans 96 million years from the end of the Cryogenian Period 635 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Cambrian Period 538.8 Mya. It marks the end of the Proterozoic Eon, and the beginning of the Phanerozoic Eon. It is named after the Ediacara Hills of South Australia. The Ediacaran Period's status as an official geological period was ratified in 2004 by the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS), making it the first new geological period declared in 120 years. Although the period takes its name from the Ediacara Hills where geologist Reg Sprigg first discovered fossils of the eponymous Ediacaran biota in 1946, the type section is located in the bed of the Enorama Creek within Brachina Gorge in the Flinders Ranges of South Australia, at . The Ediacaran marks the first appearance of widespread multicellular fauna following the end of Snowball Earth glaciation events, the so-called Ediacaran biota, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambrian Orogenies
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ago (mya) to the beginning of the Ordovician Period mya. Its subdivisions, and its base, are somewhat in flux. The period was established as "Cambrian series" by Adam Sedgwick, who named it after Cambria, the Latin name for 'Cymru' (Wales), where Britain's Cambrian rocks are best exposed. Sedgwick identified the layer as part of his task, along with Roderick Murchison, to subdivide the large "Transition Series", although the two geologists disagreed for a while on the appropriate categorization. The Cambrian is unique in its unusually high proportion of sedimentary deposits, sites of exceptional preservation where "soft" parts of organisms are preserved as well as their more resistant shells. As a result, our understanding of the Cambrian bio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vergence (geology)
In structural geology, vergence refers to the direction of the overturned component of an asymmetric fold.Compton, Robert R. ''Geology in the field''. New York. . In simpler terms, vergence can be described as the horizontal direction in which the upper-component of rotation is directed.Bell, A. M. (1981). "Vergence: an evaluation". ''Journal of Structural Geology''. 3 (3): 197–202. Vergence can be observed and recorded in folds to help a geologist determine characteristics of larger fold areas. Vergence is used to provide an overall characterization, in the symmetry (or asymmetry) of folds, and can be used to observe changes in small-scale structures in relation to the axis of a large fold.Marjoribanks, Roger W. (2010). ''Geological methods in mineral exploration and mining'' (2nd ed.). Berlin: Springer. . https://gatech.on.worldcat.org/oclc/654396234 The vergence of a fold lies parallel to the surrounding surfaces of a fold, so if these surrounding surfaces are not horizontal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shear Zone
In geology, a shear zone is a thin zone within the Earth's crust or upper mantle that has been strongly deformed, due to the walls of rock on either side of the zone slipping past each other. In the upper crust, where rock is brittle, the shear zone takes the form of a fracture called a Fault (geology), fault. In the lower crust and mantle, the extreme conditions of pressure and temperature make the rock ductile. That is, the rock is capable of slowly deforming without fracture, like hot metal being worked by a blacksmith. Here the shear zone is a wider zone, in which the ductile rock has slowly flowed to accommodate the relative motion of the rock walls on either side. Because shear zones are found across a wide depth-range, a great variety of different rock types with their characteristic structures are associated with shear zones. General introduction A shear zone is a zone of strong deformation (with a high strain rate) surrounded by rocks with a lower state of Deforma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mwembeshi Shear Zone
The Mwembeshi Shear Zone is a ductile shear zone about 550 million years old that extends ENE-WSW across Zambia. In Zambia, it separates the Lufilian Belt to the northwest from the Zambezi Belt to the southeast. It is associated with a sinistral strike slip movement. The Mwembeshi Shear Zone lies between the Congo craton to the NW and the Kalahari craton to the SE, to the west (in today's orientation) of the Mozambique Belt, which is on the north and east side of the Kalahari Craton. It was formed during the Pan-African orogeny when "North" and "South" Gondwana were amalgamated along the Kuunga orogeny zone between 580 Ma and 480 Ma. The date of around 550 Ma for the Mwembeshi shear zone is based on U-Pb zircon ages of syntectonic granites from the Hook massif and of associated hypabyssal rhyolite. During the amalgamation there was sinistral transpression along the boundary between the Kalahari craton and the Congo and Tanzanian Tanzania (; ), offic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pan-African Orogeny
The Pan-African orogeny was a series of major Neoproterozoic orogenic events which related to the formation of the supercontinents Gondwana and Pannotia about 600 million years ago. This orogeny is also known as the Pan-Gondwanan or Saldanian Orogeny. The Pan-African orogeny and the Grenville orogeny are the largest known systems of orogenies on Earth. The sum of the continental crust formed in the Pan-African orogeny and the Grenville orogeny makes the Neoproterozoic the period of Earth's history that has produced most continental crust. History and terminology The term ''Pan-African'' was coined by for a tectono-thermal event at about 500 Ma when a series of mobile belts in Africa formed between much older African cratons. At the time, other terms were used for similar orogenic events on other continents, i.e. '' Brasiliano'' in South America; ''Adelaidean'' in Australia; and ''Beardmore'' in Antarctica. Later, when plate tectonics became generally accepted, the term ''Pan-A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabasalt
Amphibolite () is a metamorphic rock that contains amphibole, especially hornblende and actinolite, as well as plagioclase feldspar, but with little or no quartz. It is typically dark-colored and dense, with a weakly foliated or schistose (flaky) structure. The small flakes of black and white in the rock often give it a salt-and-pepper appearance. Amphibolite frequently forms by metamorphism of mafic igneous rocks, such as basalt. However, because metamorphism creates minerals entirely based upon the chemistry of the protolith, certain 'dirty marls' and volcanic sediments may also metamorphose to an amphibolite assemblage. Deposits containing dolomite and siderite also readily yield amphibolite (tremolite-schist, grunerite-schist, and others) especially where there has been a certain amount of contact metamorphism by adjacent granitic masses. Metamorphosed basalt (metabasalt) creates ''ortho-amphibolite'' and other chemically appropriate lithologies create ''para-amphibolite''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whiteschist
A whiteschist is an uncommon metamorphic rock formed at high to ultra-high pressures. It has the characteristic mineral assemblage of kyanite + talc, responsible for its white colour. The name was introduced in 1973 by German mineralogist and petrologist Werner Schreyer. This rock is associated with the metamorphism of some pelites, evaporite sequences or altered basaltic or felsic intrusions. Whiteschists form in the MgO–––– (MFASH) system. Rocks of this primary chemistry are extremely uncommon and they are in most cases thought to be the result of metasomatism, metasomatic alteration, with the removal of various mobile elements. Occurrence Whiteschists occur as lenses or tectonic slices on a metre to kilometre scale within nine orogenic belts around the world. There are two occurrences in Central Africa, one in Tasmania, one in the Norwegian Caledonides, two in the Alps and three in Asia. One of the most extensive outcrops of whiteschist occurs within the L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is the assembly of most or all of Earth's continent, continental blocks or cratons to form a single large landmass. However, some geologists use a different definition, "a grouping of formerly dispersed continents", which leaves room for interpretation and is easier to apply to Precambrian times. To separate supercontinents from other groupings, a limit has been proposed in which a continent must include at least about 75% of the continental crust then in existence in order to qualify as a supercontinent. Supercontinents have assembled and dispersed multiple times in the geologic past (see table). According to modern definitions, a supercontinent does not exist today; the closest in existence to a supercontinent is the current Afro-Eurasian landmass, which covers approx. 57% of Earth's total land area. The last time the continental landmasses were near to one another was 336 to 175 million years ago as the supercontinent, Pangaea. The positions of con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |