|
Yìhéquán
The Boxer Rebellion, also known as the Boxer Uprising, the Boxer Insurrection, or the Yihetuan Movement, was an anti-foreign, anti-colonial, and anti-Christian uprising in China between 1899 and 1901, towards the end of the Qing dynasty, by the Society of Righteous and Harmonious Fists (), known as the "Boxers" in English because many of its members had practised Chinese martial arts, which at the time were referred to as "Chinese boxing". After the Sino-Japanese War of 1895, villagers in North China feared the expansion of foreign spheres of influence and resented the extension of privileges to Christian missionaries, who used them to shield their followers. In 1898 Northern China experienced several natural disasters, including the Yellow River flooding and droughts, which Boxers blamed on foreign and Christian influence. Beginning in 1899, Boxers spread violence across Shandong and the North China Plain, destroying foreign property such as railroads and attacking or mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yihetuan
The Boxer Rebellion, also known as the Boxer Uprising, the Boxer Insurrection, or the Yihetuan Movement, was an anti-foreign, anti-colonial, and anti-Christian uprising in China between 1899 and 1901, towards the end of the Qing dynasty, by the Society of Righteous and Harmonious Fists (), known as the "Boxers" in English because many of its members had practised Chinese martial arts, which at the time were referred to as "Chinese boxing". After the Sino-Japanese War of 1895, villagers in North China feared the expansion of foreign spheres of influence and resented the extension of privileges to Christian missionaries, who used them to shield their followers. In 1898 Northern China experienced several natural disasters, including the Yellow River flooding and droughts, which Boxers blamed on foreign and Christian influence. Beginning in 1899, Boxers spread violence across Shandong and the North China Plain, destroying foreign property such as railroads and attacking or m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of The International Legations
The siege of the International Legations occurred in 1900 in Peking, the capital of the Qing Empire, during the Boxer Rebellion. Menaced by the Boxers; an anti-Christian anti-foreign peasant movement, 900 soldiers, sailors, marines, and civilians, largely from Europe, Japan, and the United States, and about 2,800 Chinese Christians took refuge in the Peking Legation Quarter. The Qing government took the side of the Boxers after the Eight-Nation Alliance invaded Tianjin at the Battle of the Taku Forts (1900), without a formal declaration of war. The foreigners and Chinese Christians in the Legation Quarter survived a 55-day siege by the Qing Army and Boxers. The siege was broken by an international military force, which marched from the coast of China, defeated the Qing Army, and occupied Peking (now known as Beijing). The siege was called by the ''New York Sun'' "the most exciting episode ever known to civilization." Legation Quarter The Legation Quarter was approximately ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yihetuan Flag
The Boxer Rebellion, also known as the Boxer Uprising, the Boxer Insurrection, or the Yihetuan Movement, was an anti-foreign, anti-colonial, and anti-Christian uprising in China between 1899 and 1901, towards the end of the Qing dynasty, by the Society of Righteous and Harmonious Fists (), known as the "Boxers" in English because many of its members had practised Chinese martial arts, which at the time were referred to as "Chinese boxing". After the Sino-Japanese War of 1895, villagers in North China feared the expansion of foreign spheres of influence and resented the extension of privileges to Christian missionaries, who used them to shield their followers. In 1898 Northern China experienced several natural disasters, including the Yellow River flooding and droughts, which Boxers blamed on foreign and Christian influence. Beginning in 1899, Boxers spread violence across Shandong and the North China Plain, destroying foreign property such as railroads and attacking or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Peking, Boxer Rebellion
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition warfare, attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characterized by one party holding a strong, static, defensive position. Consequently, an opportunity for negotiation between combatants is common, as proximity and fluctuating advantage can encourage diplomacy. The art of conducting and resisting sieges is called siege warfare, siegecraft, or poliorcetics. A siege occurs when an attacker encounters a city or fortress that cannot be easily taken by a quick assault, and which refuses to Surrender (military), surrender. Sieges involve surrounding the target to block the provision of supplies and the reinforcement or escape of troops (a tactic known as "Investment (military), investment"). This is typically coupled with attempts to reduce the fortifications by means of siege engines, ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
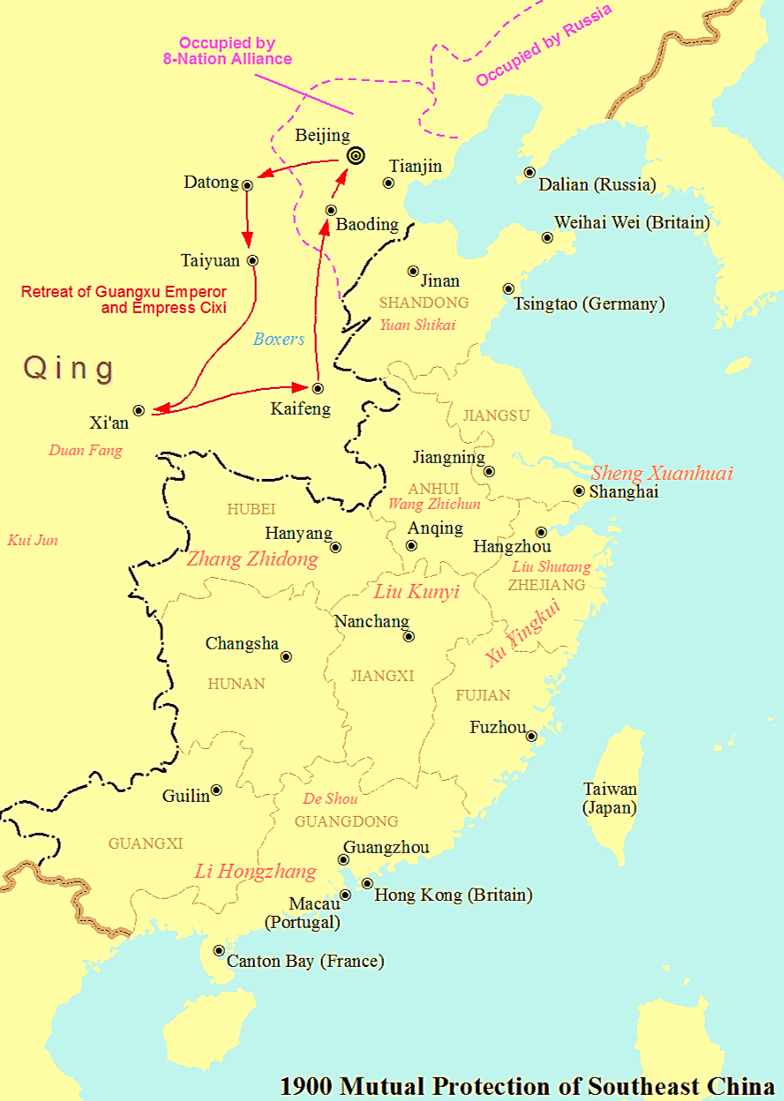
Mutual Defense Pact Of The Southeastern Provinces
The Mutual Defense Pact of the Southeastern Provinces () was an agreement reached in the summer of 1900 during the Boxer Rebellion by Qing dynasty governors of the provinces in southern, eastern and central China when the Eight-Nation Alliance invaded northern China. The governors, including Li Hongzhang ( governor-general of Guangdong, Guangxi), Xu Yingkui ( governor-general of Fujian, Zhejiang), Liu Kunyi ( governor-general of Jiangsu, Anhui, Jiangxi), Zhang Zhidong ( governor-general of Hubei, Hunan) and Yuan Shikai (provincial governor of Shandong), refused to carry out the imperial decree promulgated by the Qing imperial court to declare war on 11 foreign states, with the aim of preserving peace in their own provinces. Some other Han-majority provincial authorities, such as the governor-general of Sichuan and the provincial governor of Shaanxi, did not formally join the mutual protection agreement but similarly disobeyed the imperial edict. Thus, for the first time, the vast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleksey Kuropatkin
Aleksey Nikolayevich Kuropatkin (russian: Алексе́й Никола́евич Куропа́ткин; March 29, 1848January 16, 1925) served as the Russian Imperial Minister of War from January 1898 to February 1904 and as a field commander subsequently. Historians often hold him responsible for major Russian defeats in the Russo-Japanese War of 1904 to 1905, most notably at the Battle of Mukden (1905) and at the Battle of Liaoyang (August-September 1904). Biography Early years Kuropatkin was born in 1848 in Kholmsky Uyezd, Pskov Governorate, in the Russian Empire. His father, a retired army captain, came from landed gentry. Educated in the Cadet Corps and Pavlovsky Military School, Kuropatkin entered the Imperial Russian Army in 1864. On August 8, 1866, he was promoted to lieutenant in the 1st Turkestan Infantry Battalion, and took part in the conquest of Bukhara, the storming of Samarkand and other battles in the Russian conquest of Turkestan. He was promoted to ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Von Waldersee
Alfred Ludwig Heinrich Karl Graf von Waldersee (8 April 1832 in Potsdam5 March 1904 in Hanover) was a German field marshal (''Generalfeldmarschall'') who became Chief of the Imperial German General Staff. Born into a prominent military family, von Waldersee saw distinguished service as an artillery officer, and became Prussian military attaché at the Paris embassy in 1870. This gave him insight into the French defences that would prove crucial in the upcoming Franco-Prussian War, in which he played a significant role. Later, as principal assistant to Field-Marshal Helmuth Karl Bernhard von Moltke, Helmuth von Moltke the Elder, Chief of the Imperial General Staff, von Waldersee gained influence with the future Kaiser Wilhelm II, who promoted him Chief of Staff on his accession. When the Peking legation compound was besieged by the Boxer Rebellion, Boxer insurgents in 1900, von Waldersee was appointed as head of an 8-nation relief force. Although he arrived too late to take part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adna Chaffee
Adna Romanza Chaffee (April 14, 1842 – November 1, 1914) was a lieutenant general in the United States Army. Chaffee took part in the American Civil War and Indian Wars, played a key role in the Spanish–American War, and fought in the Boxer Rebellion in China. He was the Chief of Staff of the United States Army from 1904 to 1906, overseeing far-reaching transformation of organization and doctrine in the army. Early life and Civil War Chaffee was born in Orwell, Ohio. When the American Civil War broke out in July 1861, Chaffee enlisted in the Union Army as a private in the U.S. 6th Cavalry Regiment. In 1862, Chaffee was promoted to sergeant and took part in the Peninsular Campaign and the Battle of Antietam. In September of that year he was made the first sergeant of Company K. He was commissioned as a second lieutenant in May 1863. His 6th Cavalry, on detached service from General John Buford's 1st Union Cavalry Division, though outnumbered attacked a Confederate Cavalry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henri-Nicolas Frey
Henri-Nicolas Frey was a French major general of the Troupes coloniales. He led the French troops at the Battle of Peking in August 1900 where a multinational force ended the siege of foreign legations during the Boxer Rebellion. Biography Henri-Nicolas Frey was born on January 9, 1847 in Bocognano in Corsica, son of Henri Frey (1808–1887) who was a gendarmerie officer, then justice of the peace in Valensole, knight of the Legion of Honor, 2nd class and his mother being Jeanne Carréga (1814–1886). He got married on February 19, 1894 in Asnières-sur-Seine with Julie Bertrand, divorced wife of Charles Apert. He died on January 6, 1932 in Menton. Military career Frey was a student of the Lycée Thiers and then of the Prytanée national militaire, he entered the École spéciale militaire de Saint-Cyr on October 18, 1866. He was a second lieutenant in 1868, a lieutenant in 1870, a captain in 1874 in French Senegal, and a squadron leader in 1880. He served in the Bureau of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamaguchi Motomi
was a Japanese Samurai and an Imperial Japanese Army general who participated in the First Sino-Japanese War and the Boxer Rebellion. Nicknamed as the ''Warlord during the Warlord'', he was known for his extensive campaigns and service as he was a recipient of the Order of the Golden Kite. Biography Motomi was born into the Chōshū Domain during the Edo Period in Hagi as the son of Yoshiyoshi Yamamoto, a samurai of the Yamaguchi domain; he was adopted by Yoshiyoshi Yamaguchi, who was a samurai of the same domain. He partook in military service during the Boshin War within the Kiheitai. After the Meiji Restoration, he served in the Imperial Japanese Army. In September 1870, he joined the Second Guidance Corps of the Osaka Army and was appointed army sergeant in April 1871. During the same year, he was promoted from lieutenant to captain, and became an army major since October 1873. In January of the following year, when the First Regiment of the Konoye Infantry was establishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fukushima Yasumasa
Baron was a general in the Imperial Japanese Army. Life as a Samurai Fukushima was born to a ''samurai'' family; his father was a retainer to the ''daimyō'' of Matsumoto, in Shinano Province (modern Nagano Prefecture). He also became a retainer of Lord Toda Mitsunori. In 1867 he traveled to Edo (later Tokyo) to attend the ''Kobusho'' military school for ''hatamoto'' located in Tsukiji. During the Boshin War (1868–1869), he saw service as a member of the Matsumoto contingent. In 1869, with Lord Toda, he again traveled to Tokyo and studied foreign languages at the Kaisei Gakko, a school specializing in foreign studies. After graduating the school in 1874, he joined the Ministry of Justice as a civilian personnel and later moved to the Ministry of War. He participated in the government forces in the Satsuma Rebellion (1877). His quick mind and ability to get along well with people earned him a posting at the Imperial Japanese Army General Staff at an early age. Early forei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolai Linevich
Nikolai Petrovich Linevich, also ''Lenevich'' and ''Linevitch'' (russian: Николай Петрович Линевич, uk, Ліневич Микола Петрович; – ) was a career military officer, General of Infantry (1903) and Adjutant general in the Imperial Russian Army in the Far East during the latter part of the Russo-Japanese War. Biography A nobleman born in Chernigov (today's Chernihiv in Ukraine), Linevich entered military service as a cadet in 1855. Stationed with the 75th Infantry Regiment at Sevastopol, his first combat experience was against the mountain tribes of the western Caucasus Mountains. He made a name for himself in the Russo-Turkish War (1877-1878), and was appointed commander of the South Ussuri Division in 1895. During the Boxer Rebellion, Linevich was commander of the 1st Siberian Army Corps. He participated in the Battle of Peking in 1900.Kowner, '' Historical Dictionary of the Russo-Japanese War'', p. 210-211. In 1903, he was appoin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |








.png)