|
Ypupiara Lopai
''Ypupiara'' (meaning "the one who lives in the water") is an extinct genus of unenlagiine theropod from the Late Cretaceous Serra da Galga Formation of Brazil.Brum, Arthur Souza, Pêgas, Rodrigo Vargas, Bandeira, Kamila Luisa Nogueira, Souza, Lucy Gomes de, Campos, Diogenes de Almeida, & Kellner, Alexander Wilhelm Armin. (2021). A new Unenlagiinae (Theropoda: Dromaeosauridae) from the Late Cretaceous of Brazil. https://doi.org/10.1002/spp2.1375 It was the first member of the Dromaeosauridae to be discovered in South America and the first member of the Unenlagiinae to be discovered, but not the first to be identified as such. The type and only species, ''Y. lopai'', is known solely from a specimen that was destroyed in a fire in 2018. Discovery and naming The holotype, DGM 921-R, a right maxilla and dentary (which was associated with a fish jaw), was discovered in a layer of the Late Cretaceous Serra da Galga Formation of Brazil. It was found by Alberto Lopa sometime in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the Latin word for the white limestone known as chalk. The chalk of northern France and the white cliffs of south-eastern England date from the Cretaceous Period. Climate During the Late Cretaceous, the climate was warmer than present, although throughout the period a cooling trend is evident. The tropics became restricted to equatorial regions and northern latitudes experienced markedly more seasonal climatic conditions. Geography Due to plate tectonics, the Americas were gradually moving westward, causing the Atlantic Ocean to expand. The Western Interior Seaway divided North America into eastern and western halves; Appalachia and Laramidia. India maintained a northward course towards Asia. In the Southern Hemisphere, Australia and Ant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tupi Language
Old Tupi, Ancient Tupi or Classical Tupi (also spelled as Tupí) is an extinct Tupian language which was spoken by the aboriginal Tupi people of Brazil, mostly those who inhabited coastal regions in South and Southeast Brazil. It belongs to the Tupi–Guarani language family, and has a written history spanning the 16th, 17th, and early 18th centuries. In the early colonial period, Tupi was used as a ''lingua franca'' throughout Brazil by Europeans and aboriginal Americans, and had literary usage, but it was later suppressed almost to extinction. Today, only one modern descendant is living, the Nheengatu language. The names Old Tupi or classical Tupi are used for the language in English and by modern scholars (it is referred to as in Portuguese), but native speakers called it variously "the good language", "common language", "human language", in Old Tupi, or, in Portuguese, "general language", "Amazonian general language", "Brazilian language". History Old Tupi was firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maastrichtian Life
The Maastrichtian () is, in the ICS geologic timescale, the latest age (uppermost stage) of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or Upper Cretaceous Series, the Cretaceous Period or System, and of the Mesozoic Era or Erathem. It spanned the interval from . The Maastrichtian was preceded by the Campanian and succeeded by the Danian (part of the Paleogene and Paleocene). The Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event (formerly known as the Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction event) occurred at the end of this age. In this mass extinction, many commonly recognized groups such as non-avian dinosaurs, plesiosaurs and mosasaurs, as well as many other lesser-known groups, died out. The cause of the extinction is most commonly linked to an asteroid about wide colliding with Earth, ending the Cretaceous. Stratigraphic definitions Definition The Maastrichtian was introduced into scientific literature by Belgian geologist André Hubert Dumont in 1849, after studying rock strata of the Chalk Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unenlagiines
Unenlagiinae is a subfamily of long-snouted paravian theropods. They are traditionally considered to be members of Dromaeosauridae, though some authors place them into their own family, Unenlagiidae, alongside the subfamily Halszkaraptorinae. Unenlagiines are known from South America, with possible unenlagiines being known from North America, Madagascar, Europe, and even Australia. Description Most unenlagiines have been discovered in Argentina. The largest was ''Austroraptor'', which measured up to 5–6 m (16.4–19.7 ft) in length, making it also one of the largest dromaeosaurids. The subfamily is distinguished from other dromaeosaurids by a tail stiffened by lengthy chevrons and superior processes, a reduced second pedal ungual, a posteriorly oriented pubis and very elongated snouts. Unenlagiines also had elongated, slender hindlimbs with a subarctometatarsalian metatarsus, which is characterized by the pinched metatarsal III at the upper end. Their distinct anatomy f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unenlagia Paynemili
''Unenlagia'' (meaning "half-bird" in Latinized Mapudungun) is a genus of dromaeosaurid theropod dinosaur that lived in South America during the Late Cretaceous period. The genus ''Unenlagia'' has been assigned two species: ''U. comahuensis'', the type species described by Novas and Puerta in 1997, and ''U. paynemili'', described by Calvo ''et al.'' in 2004. Discovery and naming In 1996 in the Neuquén province of Argentina a skeleton of a theropod was discovered in the Sierra del Portezuelo and reported the same year. In 1997 Fernando Emilio Novas and Pablo Puerta named and described ''Unenlagia comahuensis''. The generic name is derived from Mapuche ''uñùm'', 'bird', and ''llag'', 'half', in reference to the fact that the describers considered the species to be a link between birds and more basal theropods. The specific name refers to the Comahue, the region the find was made. The holotype specimen, MCF PVPH 78, was uncovered in layers of the Portezuelo Formation dating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unenlagia Comahuensis
''Unenlagia'' (meaning "half-bird" in Latinized Mapudungun) is a genus of dromaeosaurid theropod dinosaur that lived in South America during the Late Cretaceous period. The genus ''Unenlagia'' has been assigned two species: ''U. comahuensis'', the Type (biology), type species described by Novas and Puerta in 1997, and ''U. paynemili'', described by Calvo ''et al.'' in 2004. Discovery and naming In 1996 in the Neuquén province of Argentina a skeleton of a theropod was discovered in the Sierra del Portezuelo and reported the same year. In 1997 Fernando Emilio Novas and Pablo Puerta named and described ''Unenlagia comahuensis''. The generic name is derived from Mapuche ''uñùm'', 'bird', and ''llag'', 'half', in reference to the fact that the describers considered the species to be a link between birds and more basal theropods. The specific name (zoology), specific name refers to the Comahue, the region the find was made. The holotype specimen, MCF PVPH 78, was uncovered in lay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuquenraptor
''Neuquenraptor'' (meaning Neuquén thief) is a genus of dromaeosaurid theropod dinosaurs that lived in South America during the Late Cretaceous in what is now the Portezuelo Formation of Argentina. It is one of the first dromaeosaurids found in the Southern Hemisphere. Discovery and naming In January 1996 the remains of ''Neuquenraptor'' were found near Plaza Huincul in the Sierra del Portezuelo and reported that very year. In 1997 it was revealed the intended name was "Araucanoraptor argentinus". In 1999 it was provisionally described as a member of the Troodontidae. However, it was named as the type species ''Neuquenraptor argentinus'' in 2005 by Fernando Novas of the Bernardino Rivadavia Natural Sciences Museum and Diego Pol of Ohio State University and described as a dromaeosaurid. The generic name combines Neuquén, referring to the Neuquén Province and basin of northern Patagonia, Argentina, with Latin ''raptor'' meaning "thief". The specific name refers to Argentina. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
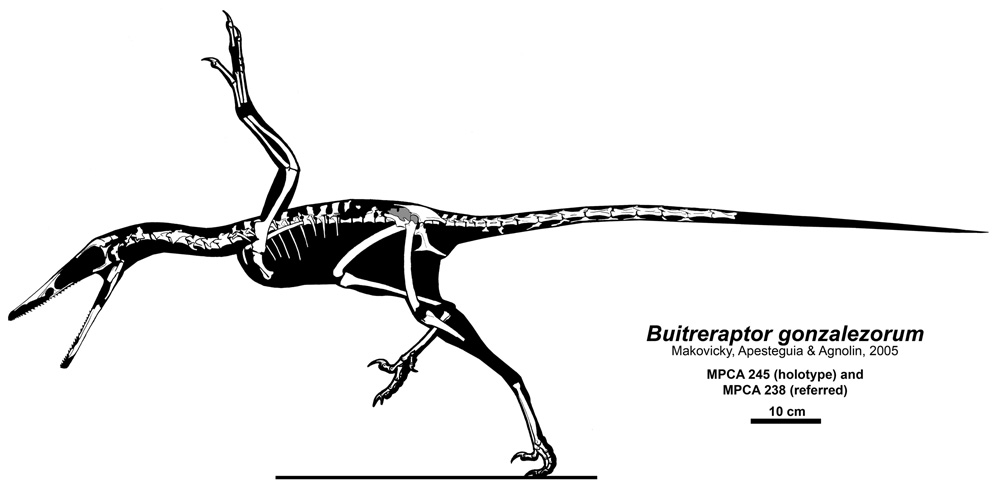
Buitreraptor
''Buitreraptor'' (meaning "La Buitrera seizer") is a genus of dromaeosaurid dinosaurs that lived during the Late Cretaceous of Argentina at the Candeleros Formation. ''Buitreraptor'' was described in 2005 and the type species is ''Buitreraptor gonzalezorum''. It was rooster-sized and had a very elongated head with many small teeth. History of discovery Four specimens of ''Buitreraptor'' were found in 2004 in sandstone in Patagonia, Argentina during an excavation led by Sebastián Apesteguia, researcher of CONICET at the Fundacion Felix de Azara - Maimonides University, and Peter Makovicky, curator of dinosaurs at the Field Museum in Chicago. ''Buitreraptor'' is from the early Late Cretaceous Candeleros Formation, dating to the Cenomanian-Turonian ages approximately 98 to 97 million years ago, when South America was an isolated continent like Australia today. It was uncovered in a famous fossil site named ''La Buitrera'', the "vulture roost". Although dinosaurs are rare in thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halszkaraptorinae
Halszkaraptorinae is a basal ("primitive") subfamily of Dromaeosauridae (or possibly Unenlagiidae) that includes the enigmatic genera ''Halszkaraptor'', ''Natovenator'', ''Mahakala'', and ''Hulsanpes''. Halszkaraptorines are definitively known only from Late Cretaceous strata in Asia, specifically in Mongolia. Following the recent discovery of ''Natovenator'', a member of the subfamily, the group is confirmed to have a semiaquatic lifestyle. History of discovery The first known remains of halszkaraptorines were found in sandstone sediments in 1970 during a Polish-Mongolian expedition at the Barun Goyot Formation, Gobi Desert. Later in 1982 they were described by Polish palaeontologist Halszka Osmólska and used as the holotype for the new genus and species '' Hulsanpes perlei'', honoring the Mongolian paleontologist Altangerel Perle. Although the affinities of these fossils were not fully understood, they were tentatively interpreted as belonging to Deinonychosauria. In 1992 dro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unenlagiinia
Unenlagiidae is a proposed family of eumaniraptoran paravians that includes the subfamilies Unenlagiinae and possibly Halszkaraptorinae. Fossils of both subfamilies have been found in both Gondwanan and Laurasian deposits. The biology of the group suggests that some members were semiaquatic specialists. Classification The family Unenlagiidae traditionally includes the same members as the previously named subfamily of Dromaeosauridae, Unenlagiinae, so Unenlagiidae was often seen as a synonym of Dromaeosauridae. However, since the 2010s, there have been subsequent studies that have questioned this placement, necessitating the revival of the family name. Some have placed unenlagiids as outside Dromaeosauridae, being the sister taxon or closely related to Avialae, while others have placed the newly recognized halszkaraptorines in the family, as basal deinonychosaurs outside Dromaeosauridae and Troodontidae Troodontidae is a clade of bird-like theropod dinosaurs. During most o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austroraptor
''Austroraptor'' ( ) is a genus of large dromaeosaurid dinosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous Period in what is now Argentina. ''Austroraptor'' was a large-sized, moderately-built, ground-dwelling, bipedal carnivore, estimated at in length. It is one of the largest dromaeosaurids known, with only ''Achillobator'', ''Dakotaraptor'', and ''Utahraptor'' approaching or surpassing it in length. Discovery and naming The type specimen of ''Austroraptor cabazai'', holotype MML-195, was recovered in the Bajo de Santa Rosa locality of the Allen Formation, in Río Negro, Argentina. The specimen was collected in 2002 by the team of Fernando Emilio Novas of the '' Museo Argentino de Ciencias Naturales''. It consists of a fragmentary skeleton including parts of the skull, lower jaw, a few neck and torso vertebrae, some ribs, a humerus, and assorted bones from both legs. The specimen was prepared by Marcelo Pablo Isasi and Santiago Reuil. In 2008, the type species ''Austroraptor cab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sister Taxon
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree. Definition The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram: Taxon A and taxon B are sister groups to each other. Taxa A and B, together with any other extant or extinct descendants of their most recent common ancestor (MRCA), form a monophyletic group, the clade AB. Clade AB and taxon C are also sister groups. Taxa A, B, and C, together with all other descendants of their MRCA form the clade ABC. The whole clade ABC is itself a subtree of a larger tree which offers yet more sister group relationships, both among the leaves and among larger, more deeply rooted clades. The tree structure shown connects through its root to the rest of the universal tree of life. In cladistic standards, taxa A, B, and C may represent specimens, species, genera, or any other taxonomic units. If A and B are at the same taxonomi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |








.png)