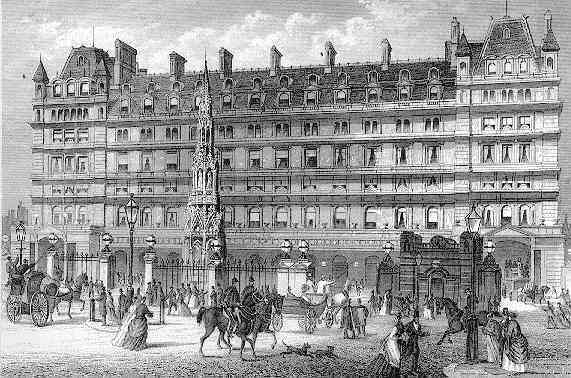|
York Water Gate
York House (formerly Norwich Place or Norwich Palace) was one of a string of mansion houses which formerly stood on the Strand, the principal route from the City of London to the Palace of Westminster. Building Norwich Palace It was built as the London townhouse of the Bishops of Norwich not later than 1237, and on 4 February 1536 it was given by King Henry VIII to his favourite Charles Brandon, 1st Duke of Suffolk in exchange for Suffolk House in Southwark, the Bishop having been provided with a new residence in Cannon Row, Westminster. York House It came to be known as York House when it was granted to the Archbishop of York in 1556 and retained that name for the rest of its existence. Its neighbours were on the west Suffolk House (later Northumberland House), the townhouse of the Earls of Suffolk, a branch of the Howard family headed by the Dukes of Norfolk, and in the 1640s sold to the Earl of Northumberland; and on the east Durham House, the London residence of the Bis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
York Watergate And Adelphi Buildings, London
York is a cathedral city with Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers Ouse and Foss in North Yorkshire, England. It is the historic county town of Yorkshire. The city has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a minster, castle, and city walls. It is the largest settlement and the administrative centre of the wider City of York district. The city was founded under the name of Eboracum in 71 AD. It then became the capital of the Roman province of Britannia Inferior, and later of the kingdoms of Deira, Northumbria, and Scandinavian York. In the Middle Ages, it became the northern England ecclesiastical province's centre, and grew as a wool-trading centre. In the 19th century, it became a major railway network hub and confectionery manufacturing centre. During the Second World War, part of the Baedeker Blitz bombed the city; it was less affected by the war than other northern cities, with several historic buildings being gutted and restored u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Durham House (London)
Durham House, or Durham Inn, was the historic London town house of the Bishop of Durham in the Strand. Its gardens descended to the River Thames. History Origins Bishop Thomas Hatfield built the opulent Durham House in about 1345. It had a large chapel and a high-ceilinged great hall supported by marble pillars. On the Strand side its gatehouse led to a large courtyard. The hall and chapel faced the entrance, and private apartments overlooked the river. Accounts describe Durham House as a noble palace befitting a prince. King Henry IV, his son Henry, Prince of Wales (later Henry V), and their retinues stayed once at the residence. Tudor and Jacobean era While Durham House remained an episcopal palace, Catherine of Aragon lived as a virtual prisoner there between her marriages to Arthur, Prince of Wales and King Henry VIII. Eventually, Bishop Cuthbert Tunstall relinquished it to King Henry VIII, who contracted to give the bishop in return Coldharbour in Dowgate Ward, Lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charing Cross Railway Station
Charing Cross railway station (also known as London Charing Cross) is a central London railway terminus between the Strand and Hungerford Bridge in the City of Westminster. It is the terminus of the South Eastern Main Line to Dover via Ashford. All trains are operated by Southeastern, which provides the majority of commuter and regional services to south-east London and Kent. It is connected to Charing Cross Underground station and is near to Embankment Underground station and Embankment Pier. The station was originally opened by the South Eastern Railway in 1864. It takes its name from its proximity to the road junction Charing Cross, the notional "centre of London" from which distances from the city are measured. During the 19th century the station became the main London terminus for continental traffic via boat trains, and served several prestigious international services. It was badly damaged by an engineering accident in 1905 and extensively rebuilt, subsequently beco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villiers Street
Villiers Street is a street in London connecting the Strand with the Embankment. It is partly pedestrianised; traffic runs northbound only up to John Adam Street, where vehicles must turn right. It was built by Nicholas Barbon in the 1670s on the site of York House, the property of George Villiers, Duke of Buckingham, whom the street commemorates. A watergate in nearby Embankment Gardens is the only remnant of the mansion and shows the original position of the north bank of the River Thames. John Evelyn lived here in the 17th century and the Irish writer Richard Steele, who founded ''The Spectator'' and ''The Tatler'' magazines, lodged here from 1712. The Charing Cross Hospital Medical School, now a part of the Imperial College Faculty of Medicine, was founded here in 1834. Prior to 1865, Villiers Street ran down the hill directly to a wharf by the river, known as Villiers Wharf. This was swept away in 1865 by the construction of the Victoria Embankment, with its sewers, and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Villiers, 2nd Duke Of Buckingham
George Villiers, 2nd Duke of Buckingham, 20th Baron de Ros, (30 January 1628 – 16 April 1687) was an English statesman and poet. Life Early life George was the son of George Villiers, 1st Duke of Buckingham, favourite of James I and Charles I, and his wife Katherine Manners. He was only seven months old when his father was assassinated at Portsmouth by the disaffected officer John Felton. Subsequently, he was brought up in the royal household of Charles I, together with his younger brother Francis and the King's own children, the future Charles II and James II. He was educated at Trinity College, Cambridge, where he obtained the degree of Master of Arts in 1642. For a time he was taught geometry by Thomas Hobbes. During this time he was also acquainted with George Aglionby, whose influence he later accredited with persuading him to follow the English King in the Civil War. Involvement in the English Civil War In the Civil War he fought for the King, and too ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Civil War
The English Civil War (1642–1651) was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Parliamentarians (" Roundheads") and Royalists led by Charles I ("Cavaliers"), mainly over the manner of England's governance and issues of religious freedom. It was part of the wider Wars of the Three Kingdoms. The first (1642–1646) and second (1648–1649) wars pitted the supporters of King Charles I against the supporters of the Long Parliament, while the third (1649–1651) saw fighting between supporters of King Charles II and supporters of the Rump Parliament. The wars also involved the Scottish Covenanters and Irish Confederates. The war ended with Parliamentarian victory at the Battle of Worcester on 3 September 1651. Unlike other civil wars in England, which were mainly fought over who should rule, these conflicts were also concerned with how the three Kingdoms of England, Scotland and Ireland should be governed. The outcome was threefold: the trial of and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Pepys
Samuel Pepys (; 23 February 1633 – 26 May 1703) was an English diarist and naval administrator. He served as administrator of the Royal Navy and Member of Parliament and is most famous for the diary he kept for a decade. Pepys had no maritime experience, but he rose to be the Chief Secretary to the Admiralty under both King Charles II and King James II through patronage, diligence, and his talent for administration. His influence and reforms at the Admiralty were important in the early professionalisation of the Royal Navy. The detailed private diary that Pepys kept from 1660 until 1669 was first published in the 19th century and is one of the most important primary sources for the English Restoration period. It provides a combination of personal revelation and eyewitness accounts of great events, such as the Great Plague of London, the Second Dutch War, and the Great Fire of London. Early life Pepys was born in Salisbury Court, Fleet Street, London, on 23 Februar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wenceslas Hollar
Wenceslaus Hollar (23 July 1607 – 25 March 1677) was a prolific and accomplished Bohemian graphic artist of the 17th century, who spent much of his life in England. He is known to German speakers as ; and to Czech speakers as . He is particularly noted for his engravings and etchings. He was born in Prague, died in London, and was buried at St Margaret's Church, Westminster. Early life After his family was ruined by the Sack of Prague in the Thirty Years' War, the young Hollar, who had been destined for the legal profession, decided to become an artist. The earliest of his works that have come down to us are dated 1625 and 1626; they are small plates, and one of them is a copy of a "Virgin and Child" by Dürer, whose influence upon Hollar's work was always great. In 1627 he was in Frankfurt where he was apprenticed to the renowned engraver Matthäus Merian. In 1630 he lived in Strasbourg, Mainz and Koblenz, where Hollar portrayed the towns, castles, and landscapes of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Villiers, 1st Duke Of Buckingham
George Villiers, 1st Duke of Buckingham, 28 August 1592 – 23 August 1628), was an English courtier, statesman, and patron of the arts. He was a favourite and possibly also a lover of King James I of England. Buckingham remained at the height of royal favour for the first three years of the reign of James's son, King Charles I, until a disgruntled army officer assassinated him. Early life Villiers was born in Brooksby, Leicestershire, on 28 August 1592, the son of the minor gentleman Sir George Villiers (1550–1606). His mother, Mary (1570–1632), daughter of Anthony Beaumont of Glenfield, Leicestershire, was widowed early. She educated her son for a courtier's life and sent him to travel in France with John Eliot. Villiers took to the training set by his mother: he could dance and fence well, spoke a little French, and overall became an excellent student. Godfrey Goodman (Bishop of Gloucester from 1624 to 1655) declared Villiers "the handsomest-bodied man in all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Bacon
Francis Bacon, 1st Viscount St Alban (; 22 January 1561 – 9 April 1626), also known as Lord Verulam, was an English philosopher and statesman who served as Attorney General and Lord Chancellor of England. Bacon led the advancement of both natural philosophy and the scientific method and his works remained influential even in the late stages of the Scientific Revolution. Bacon has been called the father of empiricism. He argued for the possibility of scientific knowledge based only upon inductive reasoning and careful observation of events in nature. He believed that science could be achieved by the use of a sceptical and methodical approach whereby scientists aim to avoid misleading themselves. Although his most specific proposals about such a method, the Baconian method, did not have long-lasting influence, the general idea of the importance and possibility of a sceptical methodology makes Bacon one of the later founders of the scientific method. His portion of the method ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Egerton, 1st Viscount Brackley
Thomas Egerton, 1st Viscount Brackley, (1540 – 15 March 1617), known as 1st Baron Ellesmere from 1603 to 1616, was an English nobleman, judge and statesman from the Egerton family who served as Lord Keeper and Lord Chancellor for twenty-one years. Early life, education and legal career Thomas Egerton was born in 1540 in the parish of Dodleston, Cheshire, England. He was the illegitimate son of Sir Richard Egerton and an unmarried woman named Alice Sparks from Bickerton. He was acknowledged by his father's family, who paid for his education. He studied Liberal Arts at Brasenose College, Oxford, and received a bachelor's degree in 1559. He then studied law at Lincoln's Inn and called a barrister by 1572. He was a Roman Catholic, until a point in 1570 when his lack of conformity with the Church of England became an issue when his Inn passed on a complaint from the Privy Council. He built a respectable legal practice pleading cases in the Courts of Queen's Bench, Chance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas Bacon (Lord Keeper)
Sir Nicholas Bacon (28 December 1510 – 20 February 1579) was Lord Keeper of the Great Seal during the first half of the reign of Queen Elizabeth I of England. He was the father of the philosopher and statesman Sir Francis Bacon (philosopher), Francis Bacon. Life He was born at Chislehurst, Kent, the second son of Robert Bacon (1479–1548) of Drinkstone, Suffolk, by his wife Eleanor (Isabel) Cage. He graduated from Corpus Christi College, Cambridge in 1527, and, after a period in Paris, he entered Gray's Inn, being called to the Bar in 1533. Following the Dissolution of the Monasteries, Henry VIII gave him a grant of the manors of Redgrave, Suffolk, Redgrave, Botesdale and Gislingham in Suffolk, and Gorhambury, Hertfordshire. Gorhambury belonged to St Albans Abbey and lay near the site of the vanished Roman city of Verulamium (modern day St Albans). From 1563 to 1568 he built a new house, Old Gorhambury House (now a ruin), which later became the home of Francis Bacon (philos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |