|
Yaw (ship Motion)
Ship motions are defined by the six degrees of freedom that a ship, boat or any other craft can experience. Reference axes The '' vertical/Z axis'', or ''yaw axis'', is an imaginary line running vertically through the ship and through its centre of mass . A yaw motion is a side-to side movement of the bow and stern of the ship. The '' transverse/Y axis'', ''lateral axis'', or ''pitch axis'' is an imaginary line running horizontally across the ship and through the centre of mass. A pitch motion is an up-or-down movement of the bow and stern of the ship. The '' longitudinal/X axis'', or ''roll axis'', is an imaginary line running horizontally through the length of the ship, through its centre of mass, and parallel to the ''waterline''. A roll motion is a side-to-side or port-starboard tilting motion of the superstructure around this axis. Rotational There are three special axes in any ship, called longitudinal, transverse and vertical axes. The movements around them a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Langley (CVL-27) And Battleship In Typhoon 1944
USS ''Langley'' may refer to: Ships: *, the first aircraft carrier of the United States Navy, converted from the collier ''Jupiter'' in 1922, and scuttled in February 1942 after being disabled by the Japanese *, laid down 10 July 1942 and renamed ''Hammann'' on 1 August 1942 *, a light aircraft carrier commissioned in 1943, active in World War II, and transferred to France in 1951 Others: *USS Langley, a Unix Space Server which provides proof of concept for global internet access via a nanosatellite constellation. The satellite was launched aboard the Atlas V Atlas V is an expendable launch system and the fifth major version in the Atlas (rocket family), Atlas launch vehicle family. It was originally designed by Lockheed Martin, now being operated by United Launch Alliance (ULA), a joint venture be ... mission designated as USA-261 on 20 May 2015. {{DEFAULTSORT:Langley United States Navy ship names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Translations
Translation is the communication of the meaning of a source-language text by means of an equivalent target-language text. The English language draws a terminological distinction (which does not exist in every language) between ''translating'' (a written text) and ''interpreting'' (oral or signed communication between users of different languages); under this distinction, translation can begin only after the appearance of writing within a language community. A translator always risks inadvertently introducing source-language words, grammar, or syntax into the target-language rendering. On the other hand, such "spill-overs" have sometimes imported useful source-language calques and loanwords that have enriched target languages. Translators, including early translators of sacred texts, have helped shape the very languages into which they have translated. Because of the laboriousness of the translation process, since the 1940s efforts have been made, with varying degrees o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stabilizer (ship)
Ship stabilizers (or stabilisers) are fins or rotors mounted beneath the waterline and emerging laterally from the hull to reduce a ship's roll due to wind or waves. ''Active fins'' are controlled by a gyroscopic control system. When the gyroscope senses the ship roll, it changes the fins' angle of attack so that the forward motion of the ship exerts force to counteract the roll. ''Fixed fins'' and bilge keels do not move; they reduce roll by hydrodynamic drag exerted when the ship rolls. Stabilizers are mostly used on ocean-going ships. Function Fins work by producing lift or downforce when the vessel is in motion. The lift produced by the fins should work against the roll moment of the vessel. To accomplish this, two wings, each installed underwater on either side of the ship, are used. Stabilizers can be: *Retractable - All medium and large cruise and ferry ships have the ability to retract the fins into a space inside the hull in order to avoid extra fuel consumption and r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiroll Tanks
Antiroll tanks are tanks fitted onto ships in order to improve the tank's response to roll motion. Fitted with baffles intended to slow the rate of water transfer from the port side of the tank to the starboard side and the reverse, the tanks are designed such that a larger amount of water is trapped on the higher side of the vessel. This is intended to reduce the roll period of the hull by acting in opposition to the free surface effect. They can be broadly classified into active and passive antiroll tanks. Passive antiroll tanks Free surface tanks A single partially filled tank that extends across the full breadth of the vessel. Its shape, size and internal baffles allow the liquid inside to slosh from side to side in response to the roll motion of the ship. The phasing of the roll moments acting on the ship and the resultant liquid motion will be such that it reduces the roll motion. This type of tank was first investigated by William Froude, but did not receive much attention un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bilge Keel
A bilge keel is a nautical device used to reduce a ship's tendency to roll. Bilge keels are employed in pairs (one for each side of the ship). A ship may have more than one bilge keel per side, but this is rare. Bilge keels increase hydrodynamic resistance to rolling, making the ship roll less. Bilge keels are passive stability systems. On commercial shipping the bilge keel is in the form of a strake, or small keel or blister, running along much of the length of the hull. They are typically fitted one on each side, low down on the side of the hull, so as not to increase the draft of the vessel. In battleships they were often quite large and used as part of the torpedo protection system. A bilge keel is often in a "V" shape, welded along the length of the ship at the turn of the bilge. Although not as effective as stabilizing fins, bilge keels have a major advantage in their low impact on internal ship arrangements. Unlike fins, bilge keels do not have any components inside the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skeg
A skeg (or skegg or skag) is a sternward extension of the keel of boats and ships which have a rudder mounted on the centre line. The term also applies to the lowest point on an outboard motor or the outdrive of an inboard/outboard."A small fin fitted aft of the keel to protect the rudder and propeller, and improve steering and tracking." "Skeg, or Skegg. A projecting stump formerly left on the keel, abaft the stern-post. The after-end of the keel. The composition piece supporting the heel of an equipoise rudder." at Internet Archive In more recent years, the name has been used for a fin on a surfboard which improves directional stability and to a movable fin on a kayak which adjusts the boat's centre of lateral resistance (it moves the center of resistance relative to the center of effort). The term is also often used for the fin on water skis in the U.S. It has been used for the vertical fin on seaplane hulls and floats. The wear-bar on the bottom of snowmobile ski may also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear
Linearity is the property of a mathematical relationship (''function'') that can be graphically represented as a straight line. Linearity is closely related to '' proportionality''. Examples in physics include rectilinear motion, the linear relationship of voltage and current in an electrical conductor (Ohm's law), and the relationship of mass and weight. By contrast, more complicated relationships are ''nonlinear''. Generalized for functions in more than one dimension, linearity means the property of a function of being compatible with addition and scaling, also known as the superposition principle. The word linear comes from Latin ''linearis'', "pertaining to or resembling a line". In mathematics In mathematics, a linear map or linear function ''f''(''x'') is a function that satisfies the two properties: * Additivity: . * Homogeneity of degree 1: for all α. These properties are known as the superposition principle. In this definition, ''x'' is not necessarily a real ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port And Starboard
Port and starboard are nautical terms for watercraft and aircraft, referring respectively to the left and right sides of the vessel, when aboard and facing the bow (front). Vessels with bilateral symmetry have left and right halves which are mirror images of each other. One asymmetric feature is where access to a boat, ship, or aircraft is at the side, it is usually only on the port side (hence the name). Side Port and starboard unambiguously refer to the left and right side of the vessel, not the observer. That is, the port side of the vessel always refers to the same portion of the vessel's structure, and does not depend on which way the observer is facing. The port side is the side of the vessel which is to the left of an observer aboard the vessel and , that is, facing forward towards the direction the vehicle is heading when underway, and starboard side is to the right of such an observer. This convention allows orders and information to be given unambiguously, withou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
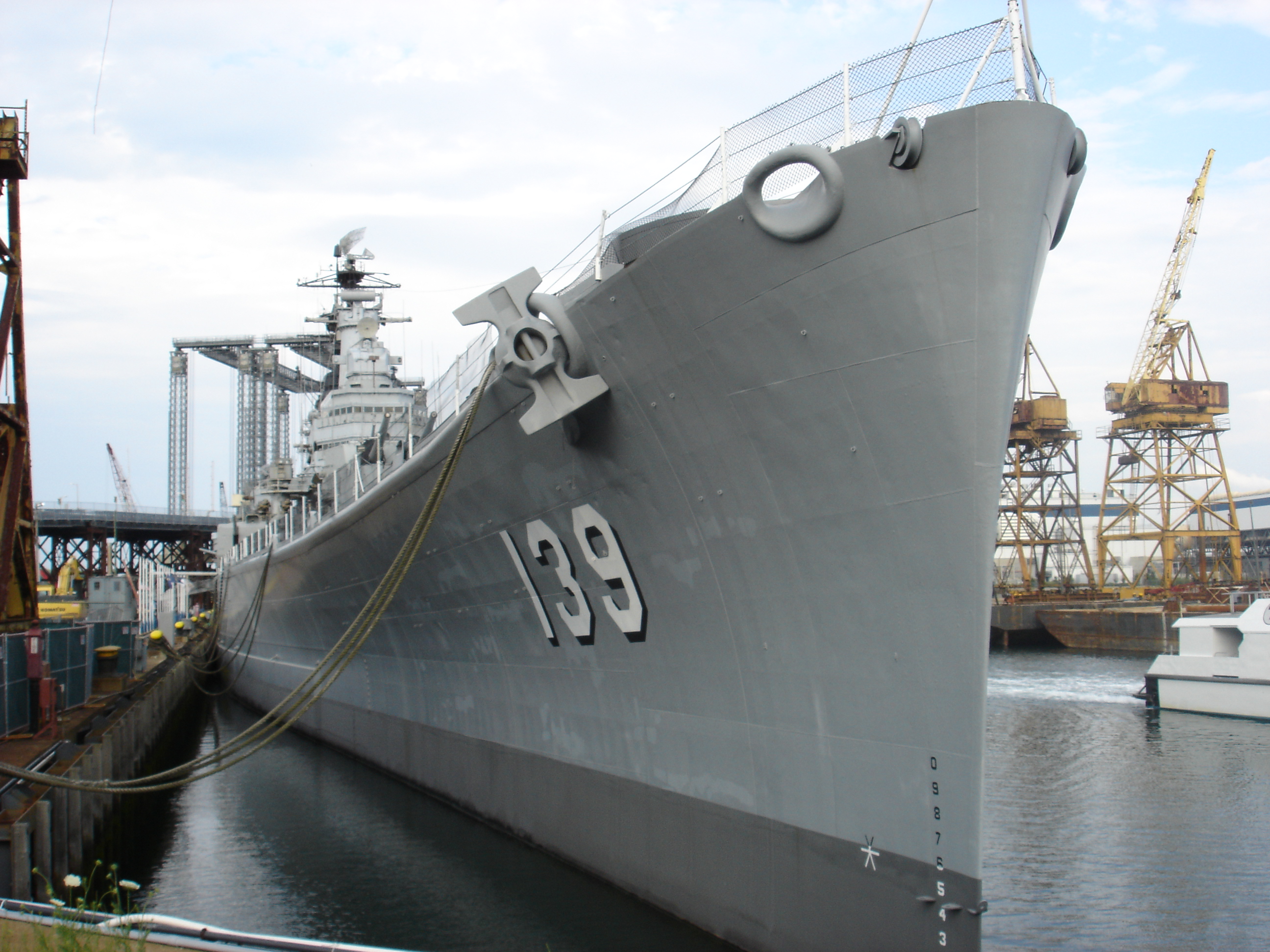
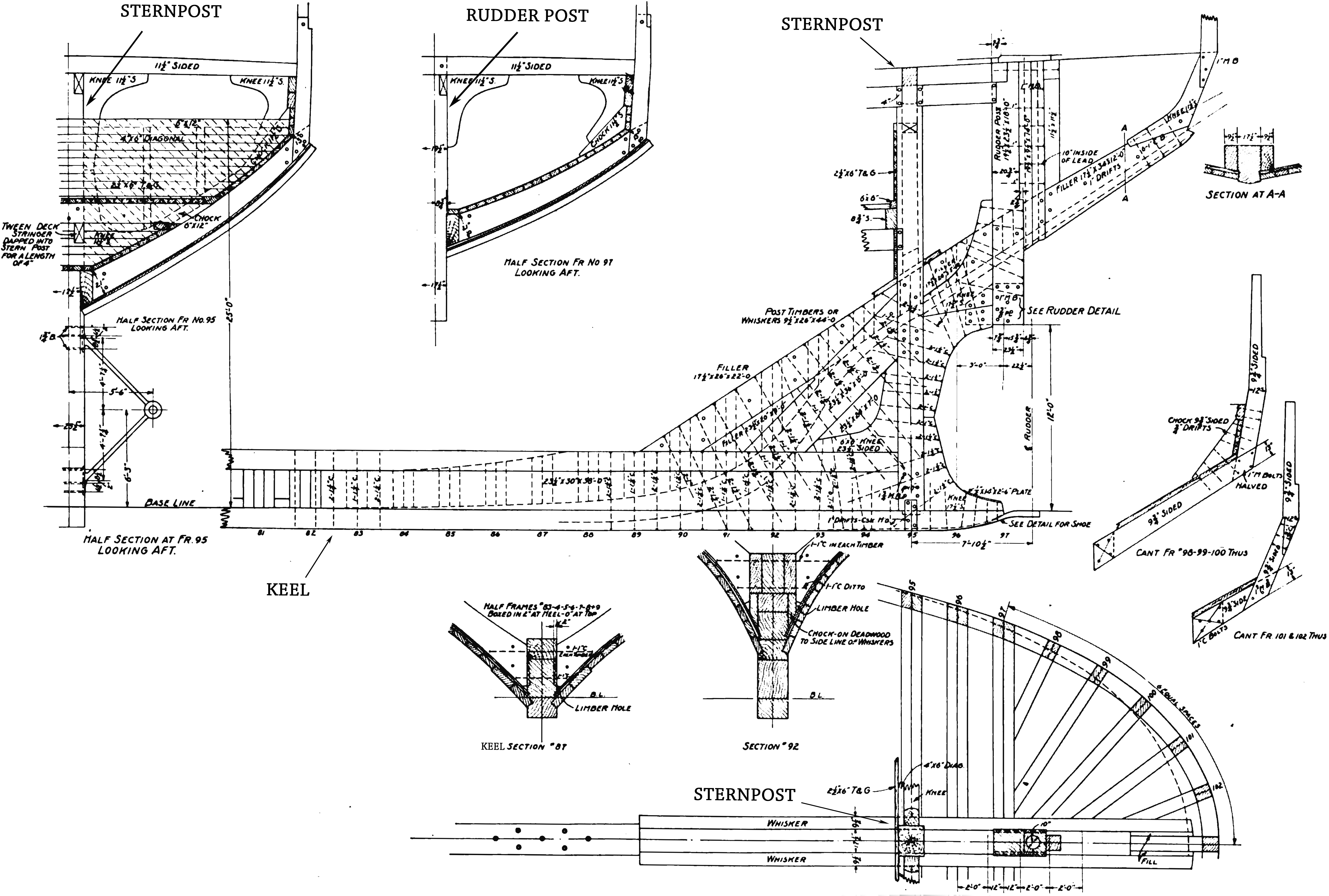
Stern
The stern is the back or aft-most part of a ship or boat, technically defined as the area built up over the sternpost, extending upwards from the counter rail to the taffrail. The stern lies opposite the bow, the foremost part of a ship. Originally, the term only referred to the aft port section of the ship, but eventually came to refer to the entire back of a vessel. The stern end of a ship is indicated with a white navigation light at night. Sterns on European and American wooden sailing ships began with two principal forms: the ''square'' or ''transom'' stern and the ''elliptical'', ''fantail'', or ''merchant'' stern, and were developed in that order. The hull sections of a sailing ship located before the stern were composed of a series of U-shaped rib-like frames set in a sloped or "cant" arrangement, with the last frame before the stern being called the ''fashion timber(s)'' or ''fashion piece(s)'', so called for "fashioning" the after part of the ship. This frame is d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bow (ship)
The bow () is the forward part of the hull of a ship or boat, the point that is usually most forward when the vessel is underway. The aft end of the boat is the stern. Prow may be used as a synonym for bow or it may mean the forward-most part of the bow above the waterline. Function A ship's bow should be designed to enable the hull to pass efficiently through the water. Bow shapes vary according to the speed of the boat, the seas or waterways being navigated, and the vessel's function. Where sea conditions are likely to promote pitching, it is useful if the bow provides reserve buoyancy; a flared bow (a raked stem with flared topsides) is ideal to reduce the amount of water shipped over the bow. Ideally, the bow should reduce the resistance and should be tall enough to prevent water from regularly washing over the top of it. Large commercial barges on inland waterways rarely meet big waves and may have remarkably little freeboard at the bow, whereas fast military ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometric Term Of Location
{{unreferenced, date=March 2014 Geometric terms of location describe directions or positions relative to the shape of an object. These terms are used in descriptions of engineering, physics, and other sciences, as well as ordinary day to day discourse. Though these terms by themselves may be somewhat ambiguous, they are usually used in a context in which their meaning is clear. For example, when referring to a drive shaft it is clear what is meant by axial or radial directions. Or, in a free body diagram, one may similarly infer a sense of orientation by the forces or other vectors represented. Examples Common geometric terms of location are: * Axial – along the center of a round body, or the axis of rotation of a body * Radial – along a direction pointing along a radius from the center of an object, or perpendicular to a curved path. * Circumferential (or azimuthal) – following around a curve or circumference of an object. For instance: the pattern of cells in Taylor–Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bearing (navigation)
In navigation, bearing or azimuth is the horizontal angle between the direction of an object and north or another object. The angle value can be specified in various angular units, such as degrees, mils, or grad. More specifically: * Absolute bearing refers to the angle between the magnetic north (''magnetic bearing'') or true north (''true bearing'') and an object. For example, an object to due east would have an absolute bearing of 90 degrees. Thus, it is the same as azimuth.U.S. Army, ''Advanced Map and Aerial Photograph Reading'', Headquarters, War Department, Washington, D.C. (17 September 1941), pp. 24-2/ref> * #Relative, Relative bearing refers to the angle between the craft's forward direction (heading) and the location of another object. For example, an object relative bearing of 0 degrees would be immediately in front; an object relative bearing 180 degrees would be behind. Bearings can be measured in mils, points, or degrees. Thus, it is the same as an ''azimuth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_and_battleship_in_typhoon_1944.jpeg)


.jpg)