|
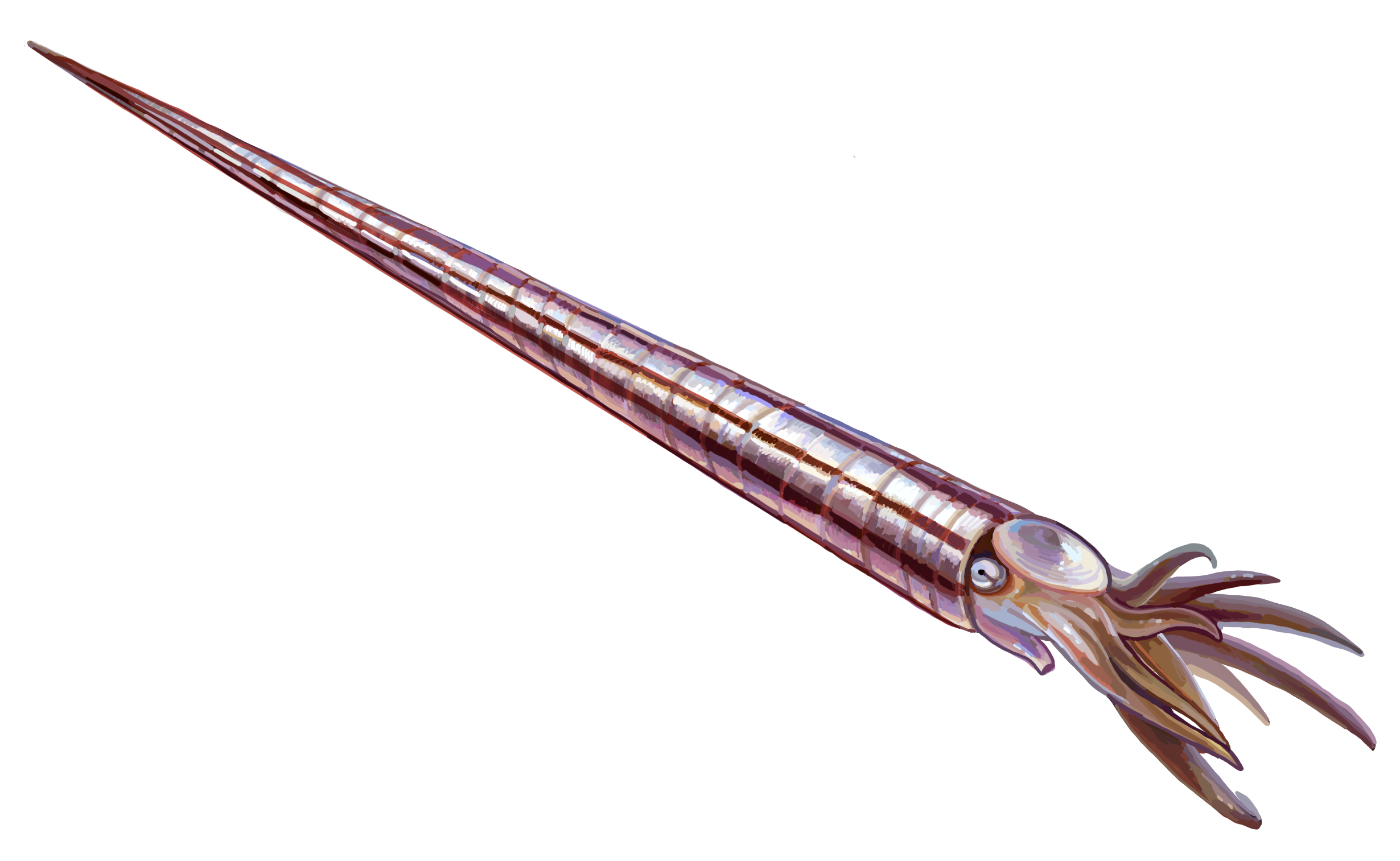
Yanheceratida
Yanhecerida is a small order of Late Cambrian (mid- Stage 10) nautiloid cephalopods. They were similar to the more diverse Plectronocerida and Ellesmerocerida, with short shells, closely-spaced septa, and diaphragms (partitions) within the siphuncle. Their most distinctive trait is the conical shape of the diaphragms, similar to the endocones which characterize the later nautiloid order Endocerida. While some authors have argued that Yanhecerida should be lumped into Ellesmerocerida, a phylogenetic analysis has maintained that Yanhecerida is a valid clade of early cephalopods closely related to a paraphyletic In taxonomy (general), taxonomy, a group is paraphyletic if it consists of the group's most recent common ancestor, last common ancestor and most of its descendants, excluding a few Monophyly, monophyletic subgroups. The group is said to be pa ... Ellesmerocerida (and by extension all post-Cambian cephalopods). References {{reflist Prehistoric nautiloids Prehist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nautiloid
Nautiloids are a group of marine cephalopods ( Mollusca) which originated in the Late Cambrian and are represented today by the living ''Nautilus'' and ''Allonautilus''. Fossil nautiloids are diverse and speciose, with over 2,500 recorded species. They flourished during the early Paleozoic era, when they constituted the main predatory animals. Early in their evolution, nautiloids developed an extraordinary diversity of shell shapes, including coiled morphologies and giant straight-shelled forms ( orthocones). Only a handful of rare coiled species, the nautiluses, survive to the present day. In a broad sense, "nautiloid" refers to a major cephalopod subclass or collection of subclasses (Nautiloidea ''sensu lato''). Nautiloids are typically considered one of three main groups of cephalopods, along with the extinct ammonoids (ammonites) and living coleoids (such as squid, octopus, and kin). While ammonoids and coleoids are monophyletic clades with exclusive ancestor-descendant rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siphuncle
The siphuncle is a strand of tissue passing longitudinally through the shell of a cephalopod mollusk. Only cephalopods with chambered shells have siphuncles, such as the extinct ammonites and belemnites, and the living nautiluses, cuttlefish, and ''Spirula''. In the case of the cuttlefish, the siphuncle is indistinct and connects all the small chambers of that animal's highly modified shell; in the other cephalopods it is thread-like and passes through small openings in the septa (walls) dividing the camerae (chambers). Some older studies have used the term siphon for the siphuncle, though this naming convention is uncommon in modern studies to prevent confusion with a mollusc organ of the same name. Function The siphuncle is used primarily in emptying water from new chambers as the shell grows. To perform this task, the cephalopod increases the saltiness of the blood in the siphuncle, and the water moves from the more dilute chamber into the blood through osmosis. At the sam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Cephalopod Orders
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Nautiloids
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraphyletic
In taxonomy (general), taxonomy, a group is paraphyletic if it consists of the group's most recent common ancestor, last common ancestor and most of its descendants, excluding a few Monophyly, monophyletic subgroups. The group is said to be paraphyletic ''with respect to'' the excluded subgroups. In contrast, a monophyletic group (a clade) includes a common ancestor and ''all'' of its descendants. The terms are commonly used in phylogenetics (a subfield of biology) and in the tree model of historical linguistics. Paraphyletic groups are identified by a combination of Synapomorphy and apomorphy, synapomorphies and symplesiomorphy, symplesiomorphies. If many subgroups are missing from the named group, it is said to be polyparaphyletic. The term was coined by Willi Hennig to apply to well-known taxa like Reptilia (reptiles) which, as commonly named and traditionally defined, is paraphyletic with respect to mammals and birds. Reptilia contains the last common ancestor of reptiles a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, the equivalent Latin term ''cladus'' (plural ''cladi'') is often used in taxonomical literature. The common ancestor may be an individual, a population, or a species (extinct or extant). Clades are nested, one in another, as each branch in turn splits into smaller branches. These splits reflect evolutionary history as populations diverged and evolved independently. Clades are termed monophyletic (Greek: "one clan") groups. Over the last few decades, the cladistic approach has revolutionized biological classification and revealed surprising evolutionary relationships among organisms. Increasingly, taxonomists try to avoid naming taxa that are not clades; that is, taxa that are not monophyletic. Some of the relationships between organisms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetic Analysis
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups of organisms. These relationships are determined by Computational phylogenetics, phylogenetic inference methods that focus on observed heritable traits, such as DNA sequences, protein amino acid sequences, or morphology. The result of such an analysis is a phylogenetic tree—a diagram containing a hypothesis of relationships that reflects the evolutionary history of a group of organisms. The tips of a phylogenetic tree can be living taxa or fossils, and represent the "end" or the present time in an evolutionary lineage. A phylogenetic diagram can be rooted or unrooted. A rooted tree diagram indicates the hypothetical common ancestor of the tree. An unrooted tree diagram (a network) makes no assumption about the ancestral line, and does n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lumpers And Splitters
Lumpers and splitters are opposing factions in any discipline that has to place individual examples into rigorously defined categories. The lumper–splitter problem occurs when there is the desire to create classifications and assign examples to them, for example schools of literature, biological taxa and so on. A "lumper" is a person who assigns examples broadly, assuming that differences are not as important as signature similarities. A "splitter" is one who makes precise definitions, and creates new categories to classify samples that differ in key ways. Origin of the terms The earliest known use of these terms was by Charles Darwin, in a letter to Joseph Dalton Hooker in 1857: ''It is good to have hair-splitters & lumpers''. They were introduced more widely by George G. Simpson in his 1945 work ''The Principles of Classification and a Classification of Mammals''. As he put it: A later use can be found in the title of a 1969 paper "On lumpers and splitters ..." by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocerida
Endocerida is an extinct nautiloid order, a group of cephalopods from the Lower Paleozoic with cone-like deposits in their siphuncle. Endocerida was a diverse group of cephalopods that lived from the Early Ordovician possibly to the Late Silurian. Their shells were variable in form. Some were straight (orthoconic), others curved (cyrtoconic); some were long (longiconic), others short (breviconic). Some long-shelled forms like '' Endoceras'' attained shell lengths close to . The related ''Cameroceras'' is anecdotally reported to have reached lengths approaching , but these claims are problematic. The overwhelming majority of endocerids and nautiloids in general are much smaller, usually less than a meter long when fully grown. Morphology Endocerids had a relatively small body chamber as well as a proportionally large siphuncle, which in some genera reached nearly half the shell diameter. This suggests that much of the visceral mass may have been housed within the siphuncle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septum (cephalopod)
Septa (singular septum) are thin walls or partitions between the internal chambers (camerae) of the shell of a cephalopod, namely nautiloids or ammonoids. As the creature grows, its body moves forward in the shell to a new living chamber, secreting septa behind it. This adds new chambers to the shell, which can be clearly seen in cross-sections of the shell of the living nautilus, or in ammonoid and nautiloid fossils. The septa are attached to the inside wall of the shell, thus dividing the phragmocone into camerae. Where the septum meets the shell a suture line forms; in some ammonoids these lines became extremely complex and elaborate, providing strength without the necessity of added weight. Elaborate sutures allowed for thinner shells, and hence less time needed for shell growth and less time spent in the vulnerable juvenile stage. The nature and structure of the septa, as with the camerae, and siphuncle, and the presence or absence of deposits, are important in classif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |