|
Yabasic
Yabasic (Yet Another BASIC) is a free, open-source BASIC interpreter for Windows and Unix platforms. Yabasic was originally developed by Marc-Oliver Ihm, who released the last stable version 2.77.3 in 2016. From version 2.77.1, the project has adopted the MIT License as well as the source code being moved to GitHub to encourage others to participate in its development. Features * No line numbers * Line graphics in color * Structured programming—various block structures, named subroutines with local variables and return values * Code modules/libraries with separate namespaces (On the other hand, composite data structures are missing) * Option to use a graphical user interface based on the GTK library * Self-modifying code * "Binding" a Yabasic program to the interpreter, creating a standalone executable in a single file Other versions Flyab A port of Yabasic to the Fltk toolkit called "Flyab" was under development. It would have been source-compatible with programs w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PlayStation 2
The PlayStation 2 (PS2) is a home video game console developed and marketed by Sony Computer Entertainment. It was first released in Japan on 4 March 2000, in North America on 26 October 2000, in Europe on 24 November 2000, and in Australia on 30 November 2000. It is the successor to the original PlayStation (console), PlayStation, as well as the second installment in the PlayStation brand of consoles. As a sixth generation of video game consoles, sixth-generation console, it competed with Nintendo's GameCube, and Microsoft's Xbox (console), Xbox. It is the List of best-selling game consoles, best-selling video game console of all time, having sold over 155 million units worldwide. Announced in 1999, Sony began developing the console after the immense success of its predecessor. The PS2 offered Backward compatibility, backward-compatibility for its predecessor's DualShock#DualShock, DualShock controller, as well as its games. The PlayStation 2 received widespread critical accla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
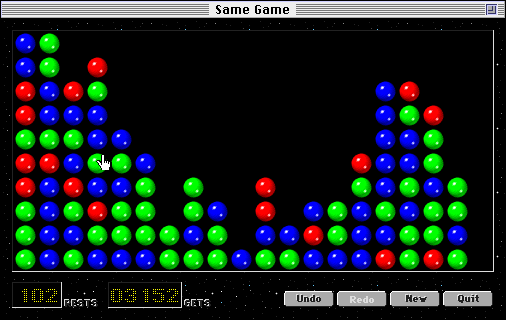
SameGame
is a tile-matching puzzle originally released under the name ''Chain Shot!'' in 1985 by Kuniaki Moribe (Morisuke). It has since been ported to numerous computer platforms, handheld devices, and even TiVo, with new versions as of 2016. History ''SameGame'' was originally created as ''Chain Shot!'' in 1985 by Kuniaki Moribe. It was distributed for Fujitsu's FM-8 and FM-7 platforms in a Japanese monthly personal computer magazine called '' Gekkan ASCII''. In 1992, the game was ported as ''SameGame'' to Unix platforms by Eiji Fukumoto, and to the NEC PC-9801 series by Wataru Yoshioka. In 1993, it was ported to Windows 3.1 by Ikuo Hirohata. This version was translated into English by Hitoshi Ozawa, and is still available from his software archive. In 1994, Takahiro Sumiya ported it to Macintosh. This version has some gameplay differences—three, instead of five, colors—and is probably the most widely distributed of the original series. It was the basis for the ''Same Gnome'' and ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composite Type
In computer science, a composite data type or compound data type is any data type which can be constructed in a program using the programming language's primitive data types and other composite types. It is sometimes called a structure or aggregate data type, although the latter term may also refer to arrays, lists, etc. The act of constructing a composite type is known as composition. Composite data types are often contrasted with scalar variables. C/C++ structures and classes A struct is C's and C++'s notion of a composite type, a datatype that composes a fixed set of labeled fields or members. It is so called because of the struct keyword used in declaring them, which is short for ''structure'' or, more precisely, ''user-defined data structure''. In C++, the only difference between a struct and a class is the default access level, which is ''private'' for classes and ''public'' for structs. Note that while classes and the class keyword were completely new in C++, the C pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BASIC Programming Language Family
BASIC (Beginners' All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) is a family of general-purpose, high-level programming languages designed for ease of use. The original version was created by John G. Kemeny and Thomas E. Kurtz at Dartmouth College in 1963. They wanted to enable students in non-scientific fields to use computers. At the time, nearly all computers required writing custom software, which only scientists and mathematicians tended to learn. In addition to the program language, Kemeny and Kurtz developed the Dartmouth Time Sharing System (DTSS), which allowed multiple users to edit and run BASIC programs simultaneously on remote terminals. This general model became very popular on minicomputer systems like the PDP-11 and Data General Nova in the late 1960s and early 1970s. Hewlett-Packard produced an entire computer line for this method of operation, introducing the HP2000 series in the late 1960s and continuing sales into the 1980s. Many early video games trace their hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BASIC Interpreters
BASIC (Beginners' All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) is a family of general-purpose, high-level programming languages designed for ease of use. The original version was created by John G. Kemeny and Thomas E. Kurtz at Dartmouth College in 1963. They wanted to enable students in non-scientific fields to use computers. At the time, nearly all computers required writing custom software, which only scientists and mathematicians tended to learn. In addition to the program language, Kemeny and Kurtz developed the Dartmouth Time Sharing System (DTSS), which allowed multiple users to edit and run BASIC programs simultaneously on remote terminals. This general model became very popular on minicomputer systems like the PDP-11 and Data General Nova in the late 1960s and early 1970s. Hewlett-Packard produced an entire computer line for this method of operation, introducing the HP2000 series in the late 1960s and continuing sales into the 1980s. Many early video games trace their hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Articles With Example BASIC Code
Article often refers to: * Article (grammar), a grammatical element used to indicate definiteness or indefiniteness * Article (publishing), a piece of nonfictional prose that is an independent part of a publication Article may also refer to: Government and law * Article (European Union), articles of treaties of the European Union * Articles of association, the regulations governing a company, used in India, the UK and other countries * Articles of clerkship, the contract accepted to become an articled clerk * Articles of Confederation, the predecessor to the current United States Constitution *Article of Impeachment, a formal document and charge used for impeachment in the United States * Articles of incorporation, for corporations, U.S. equivalent of articles of association * Articles of organization, for limited liability organizations, a U.S. equivalent of articles of association Other uses * Article, an HTML element, delimited by the tags and * Article of clothing, an ite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux
Linux ( or ) is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution, which includes the kernel and supporting system software and libraries, many of which are provided by the GNU Project. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free Software Foundation uses the name "GNU/Linux" to emphasize the importance of GNU software, causing some controversy. Popular Linux distributions include Debian, Fedora Linux, and Ubuntu, the latter of which itself consists of many different distributions and modifications, including Lubuntu and Xubuntu. Commercial distributions include Red Hat Enterprise Linux and SUSE Linux Enterprise. Desktop Linux distributions include a windowing system such as X11 or Wayland, and a desktop environment such as GNOME or KDE Plasma. Distributions intended for ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mac OS X
macOS (; previously OS X and originally Mac OS X) is a Unix operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc. since 2001. It is the primary operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. Within the market of desktop and laptop computers it is the Usage share of operating systems#Desktop and laptop computers, second most widely used desktop OS, after Microsoft Windows and ahead of ChromeOS. macOS succeeded the classic Mac OS, a Mac operating system with nine releases from 1984 to 1999. During this time, Apple cofounder Steve Jobs had left Apple and started another company, NeXT Computer, NeXT, developing the NeXTSTEP platform that would later be acquired by Apple to form the basis of macOS. The first desktop version, Mac OS X 10.0, was released in March 2001, with its first update, 10.1, arriving later that year. All releases from Mac OS X Leopard, Mac OS X 10.5 Leopard and after are UNIX 03 certified, with an exception for OS X Lion, OS X 10. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnussoft ZETA
magnussoft ZETA, earlier yellowTAB ZETA, was an operating system formerly developed by yellowTAB of Germany based on the Be Operating System developed by Be Inc.; because of yellowTAB's insolvency, ZETA was later being developed by an independent team of which little was known, and distributed by magnussoft. As of February 28, 2007 the current version of ZETA is 1.5. On March 28, 2007, magnussoft announced that it has discontinued funding the development of ZETA by March 16, because the sales figures had fallen far short of the company's expectations, so that the project was no longer economically viable.ZETA-os.com: Continuity of magnussoft Zeta'', March 26, 2007 A few days later, the company also stopped the distribution of ZETA in reaction to allegations that ZETA constituted an illegal unlicensed derivative of the BeOS source code and binaries.ZETA-OS.com: Magnussoft cease distribution of Zeta'', April 5, 2007 Development ZETA was an effort to bring BeOS up to date, adding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BeOS
BeOS is an operating system for personal computers first developed by Be Inc. in 1990. It was first written to run on BeBox hardware. BeOS was positioned as a multimedia platform that could be used by a substantial population of desktop users and a competitor to Classic Mac OS and Microsoft Windows. It was ultimately unable to achieve a significant market share, and did not prove commercially viable for Be Inc. The company was acquired by Palm Inc. Today BeOS is mainly used, and derivatives developed, by a small population of enthusiasts. The open-source operating system Haiku is a continuation of BeOS concepts and most of the application level compatibility. The latest version, Beta 4 released December 2022, still retains BeOS 5 compatibility in its x86 32-bit images. History Initially designed to run on AT&T Hobbit-based hardware, BeOS was later modified to run on PowerPC-based processors: first Be's own systems, later Apple Computer's PowerPC Reference Platform and Commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)