|
YTHDC1
YTH domain-containing protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''YTHDC1'' gene. YTHDC1 is a nuclear protein involved in splice site selection that localises to YT bodies; dynamic subnuclear compartments, which first appear at the beginning of S-phase in the cell cycle and disperse during mitosis. Interactions YTHDC1 has been shown to interact with: * Abl gene, * C-src tyrosine kinase, * Emerin, * KHDRBS1. and * Metadherin Role in disease Alternative splicing is altered in a number of diseases and is particularly relevant to cancer. Cancer YTHDC1 has been shown to splice mRNA transcripts which have oncological importance, regulating tumour functions such as hypoxia associated vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), DNA damage associated breast cancer 1 (BRCA1) and hormonal growth driver; the progesterone receptor (PGR). In prostate cancer, YTHDC1 has also been shown to interact with the protein metadherin, encoded by the oncogene MTDH acting to in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD44
The CD44 antigen is a cell-surface glycoprotein involved in cell–cell interactions, cell adhesion and migration. In humans, the CD44 antigen is encoded by the ''CD44'' gene on chromosome 11. CD44 has been referred to as HCAM (homing cell adhesion molecule), Pgp-1 (phagocytic glycoprotein-1), Hermes antigen, lymphocyte homing receptor, ECM-III, and HUTCH-1. Tissue distribution and isoforms CD44 is expressed in a large number of mammalian cell types. The standard isoform, designated CD44s, comprising exons 1–5 and 16–20 is expressed in most cell types. CD44 splice variants containing variable exons are designated CD44v. Some epithelial cells also express a larger isoform (CD44E), which includes exons v8–10. Function CD44 participates in a wide variety of cellular functions including lymphocyte activation, recirculation and homing, hematopoiesis, and tumor metastasis. CD44 is a receptor for hyaluronic acid and can also interact with other ligands, such as osteop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abl Gene
Tyrosine-protein kinase ABL1 also known as ABL1 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''ABL1'' gene (previous symbol ''ABL'') located on chromosome 9. c-Abl is sometimes used to refer to the version of the gene found within the mammalian genome, while v-Abl refers to the viral gene, which was initially isolated from the Abelson murine leukemia virus. Function The ''ABL1'' proto-oncogene encodes a cytoplasmic and nuclear protein tyrosine kinase that has been implicated in processes of cell differentiation, cell division, cell adhesion, and stress response such as DNA repair. Activity of ABL1 protein is negatively regulated by its SH3 domain, and deletion of the SH3 domain turns ABL1 into an oncogene. The t(9;22) translocation results in the head-to-tail fusion of the '' BCR'' and ''ABL1'' genes, leading to a fusion gene present in many cases of chronic myelogenous leukemia. The DNA-binding activity of the ubiquitously expressed ABL1 tyrosine kinase is regulated by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emerin
Emerin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''EMD'' gene, also known as the ''STA'' gene. Emerin, together with LEMD3, is a LEM domain-containing Transmembrane protein, integral protein of the Inner nuclear membrane proteins, inner Cell nucleus, nuclear membrane in vertebrates. Emerin is highly expressed in cardiac muscle, cardiac and skeletal muscle. In cardiac muscle, emerin localizes to adherens junctions within intercalated discs where it appears to function in mechanotransduction of cellular strain and in CTNNB1, beta-catenin signaling. Mutations in emerin cause X-linked recessive inheritance, X-linked recessive Emery–Dreifuss muscular dystrophy, cardiac conduction abnormalities and dilated cardiomyopathy. It is named after Alan Emery. Structure Emerin is a 29.0 kDa (34 kDa observed MW) protein composed of 254 amino acids. Emerin is a serine-rich protein with an N-terminus, N-terminal 20-amino acid hydrophobic region that is flanked by charged residues; the hydr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KHDRBS1
KH domain-containing, RNA-binding, signal transduction-associated protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KHDRBS1'' gene. This gene encodes a member of the K homology domain-containing, RNA-binding, signal transduction-associated protein family. The encoded protein appears to have many functions and may be involved in a variety of cellular processes, including alternative splicing, cell cycle regulation, RNA 3'-end formation, tumorigenesis, and regulation of human immunodeficiency virus gene expression. Function Sam68 (the Src-Associated substrate in Mitosis of 68 kDa) is officially called KHDRBS1 (KH domain containing, RNA binding, signal transduction associated 1). Sam68 is a KH-type RNA binding protein that recognizes U(U/A)AA direct repeats with relative high affinity. Sam68 is predominantly nuclear and its major function in the nucleus is to regulate alternative splicing by recognizing RNA sequences neighboring the included/excluded exon(s). Clinical si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MTDH
Metadherin, also known as protein LYRIC or astrocyte elevated gene-1 protein (AEG-1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MTDH'' gene. Function MTDH (AEG-1) is involved in HIF-1alpha mediated angiogenesis. MTDH also interacts with SND1 and involved in RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) and plays very important role in RISC and miRNA functions. MTDH has been shown to interact with spliceosome proteins in the cell nucleus and regulate the process of alternative splicing. MTDH induces an oncogene called Late SV40 factor (LSF/TFCP2) which is involved in thymidylate synthase (TS) induction and DNA biosynthesis synthesis. Late SV40 factor (LSF/TFCP2) enhances angiogenesis by transcriptionally up-regulating matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP9). Clinical significance MTDH acts as an oncogene in melanoma, malignant glioma, breast cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma. It is highly expressed in these cancers and helps in their progression and development. It is induced by c- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-src Tyrosine Kinase
Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK also known as C-terminal Src kinase is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the CSK gene. This enzyme phosphorylates tyrosine residues located in the C-terminal end of Src-family kinases (SFKs) including SRC, HCK, FYN, LCK, LYN and YES1. Function This Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase plays an important role in the regulation of cell growth, differentiation, migration and immune response. CSK acts by suppressing the activity of the Src family of protein kinases by phosphorylation of Src family members at a conserved C-terminal tail site in Src. Upon phosphorylation by other kinases, Src-family members engage in intramolecular interactions between the phosphotyrosine tail and the SH2 domain that result in an inactive conformation. To inhibit SFKs, CSK is then recruited to the plasma membrane via binding to transmembrane proteins or adapter proteins located near the plasma membrane and ultimately suppresses signaling through various surface ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) IRES A
This family represents the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) internal ribosome entry site (IRES) A. VEGF is an endothelial cell mitogen with many crucial functions such as embryogenic development and wound healing. The 5' UTR of VEGF mRNA contains two IRES elements which are able to promote efficient translation at the AUG start codon The genetic code is the set of rules used by living cells to translate information encoded within genetic material ( DNA or RNA sequences of nucleotide triplets, or codons) into proteins. Translation is accomplished by the ribosome, which links ..., this family represents IRES A. References External links * Cis-regulatory RNA elements {{molecular-cell-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
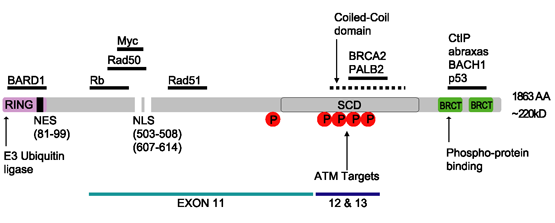
BRCA1
Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BRCA1'' () gene. Orthologs are common in other vertebrate species, whereas invertebrate genomes may encode a more distantly related gene. ''BRCA1'' is a human tumor suppressor gene (also known as a caretaker gene) and is responsible for repairing DNA. ''BRCA1'' and '' BRCA2'' are unrelated proteins, but both are normally expressed in the cells of breast and other tissue, where they help repair damaged DNA, or destroy cells if DNA cannot be repaired. They are involved in the repair of chromosomal damage with an important role in the error-free repair of DNA double-strand breaks. If ''BRCA1'' or ''BRCA2'' itself is damaged by a BRCA mutation, damaged DNA is not repaired properly, and this increases the risk for breast cancer. ''BRCA1'' and ''BRCA2'' have been described as "breast cancer susceptibility genes" and "breast cancer susceptibility proteins". The predominant allele has a normal, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progesterone Receptor
The progesterone receptor (PR), also known as NR3C3 or nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group C, member 3, is a protein found inside cells. It is activated by the steroid hormone progesterone. In humans, PR is encoded by a single ''PGR'' gene residing on chromosome 11q22, it has two isoforms, PR-A and PR-B, that differ in their molecular weight. The PR-B is the positive regulator of the effects of progesterone, while PR-A serve to antagonize the effects of PR-B. Mechanism Progesterone is necessary to induce the progesterone receptors. When no binding hormone is present the carboxyl terminal inhibits transcription. Binding to a hormone induces a structural change that removes the inhibitory action. Progesterone antagonists prevent the structural reconfiguration. After progesterone binds to the receptor, restructuring with dimerization follows and the complex enters the nucleus and binds to DNA. There transcription takes place, resulting in formation of messenger RNA that is tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |