|
You've Passed Where You'll Find Me Now
A contraction is a shortened version of the spoken and written forms of a word, syllable, or word group, created by omission of internal letters and sounds. In linguistic analysis, contractions should not be confused with crasis, abbreviations and initialisms (including acronyms), with which they share some semantic and phonetic functions, though all three are connoted by the term "abbreviation" in layman’s terms. Contraction is also distinguished from morphological clipping, where beginnings and endings are omitted. The definition overlaps with the term portmanteau (a linguistic '' blend''), but a distinction can be made between a portmanteau and a contraction by noting that contractions are formed from words that would otherwise appear together in sequence, such as ''do'' and ''not'', whereas a portmanteau word is formed by combining two or more existing words that all relate to a singular concept that the portmanteau describes. English English has a number o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elision
In linguistics, an elision or deletion is the omission of one or more sounds (such as a vowel, a consonant, or a whole syllable) in a word or phrase. However, these terms are also used to refer more narrowly to cases where two words are run together by the omission of a final sound. An example is the elision of word-final /t/ in English if it is preceded and followed by a consonant: "first light" is often pronounced /fɜ:s laɪt/. Many other terms are used to refer to particular cases where sounds are omitted. Citation forms and contextual forms A word may be spoken individually in what is called the Lemma (morphology), citation form. This corresponds to the pronunciation given in a dictionary. However, when words are spoken in context, it often happens that some sounds that belong to the citation form are omitted. Elision is not an all-or-nothing process: elision is more likely to occur in some styles of speaking and less likely in others. Many writers have described the styles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portmanteau
A portmanteau word, or portmanteau (, ) is a blend of wordsGarner's Modern American Usage , p. 644. in which parts of multiple words are combined into a new word, as in ''smog'', coined by blending ''smoke'' and ''fog'', or ''motel'', from ''motor'' and ''hotel''. In , a portmanteau is a single morph that is analyzed as representing two (or more) underlying s. When portmanteaus shorten es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oracle Bone Script
Oracle bone script () is an ancient form of Chinese characters that were engraved on oracle bonesanimal bones or turtle plastrons used in pyromantic divination. Oracle bone script was used in the late 2nd millennium BC, and is the earliest known form of Chinese writing. The vast majority of oracle bone inscriptions, of which about 150,000 pieces have been discovered, were found at the Yinxu site located in Xiaotun Village, Anyang, Henan Province. The latest significant discovery is the Huayuanzhuang storage of 1,608 pieces, 579 of which were inscribed, found near Xiaotun in 1993. They record pyromantic divinations of the last nine kings of the Shang dynasty, beginning with Wu Ding, whose accession is dated by different scholars at 1250 BC or 1200 BC. Oracle bone inscriptions of Wu Ding's reign have been radiocarbon dated to 1254–1197 BC±10 years. After the Shang were overthrown by the Zhou dynasty in c. 1046 BC, divining with milfoil became more common, and a much smaller ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
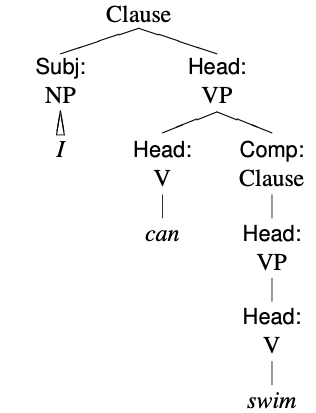
Subject–auxiliary Inversion
Subject–auxiliary inversion (SAI; also called subject–operator inversion) is a frequently occurring type of inversion in English, whereby a finite auxiliary verb – taken here to include finite forms of the copula ''be'' – appears to "invert" (change places) with the subject. The word order is therefore Aux-S (auxiliary–subject), which is the opposite of the canonical SV ( subject–verb) order of declarative clauses in English. The most frequent use of subject–auxiliary inversion in English is in the formation of questions, although it also has other uses, including the formation of condition clauses, and in the syntax of sentences beginning with negative expressions (negative inversion). In certain types of English sentences, inversion is also possible with verbs other than auxiliaries; these are described in the article on subject-verb inversion. Overview Subject–auxiliary inversion involves placing the subject after a finite auxiliary verb, rather than before i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Night Before Christmas
''A Visit from St. Nicholas'', more commonly known as ''The Night Before Christmas'' and ''Twas the Night Before Christmas'' from its first line, is a poem first published anonymously under the title ''Account of a Visit from St. Nicholas'' in 1823 and later attributed to Clement Clarke Moore, who claimed authorship in 1837. The poem has been called "arguably the best-known verses ever written by an American" Burrows, Edwin G. & Wallace, Mike. '' Gotham: A History of New York City to 1898''. New York: Oxford University Press, 1999. pp. 462–63 and is largely responsible for some of the conceptions of Santa Claus from the mid-nineteenth century to today. It has had a massive effect on the history of Christmas gift-giving. Before the poem gained wide popularity, American ideas had varied considerably about Saint Nicholas and other Christmastide visitors. ''A Visit from St. Nicholas'' eventually was set to music and has been recorded by many artists. Plot On the night of Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
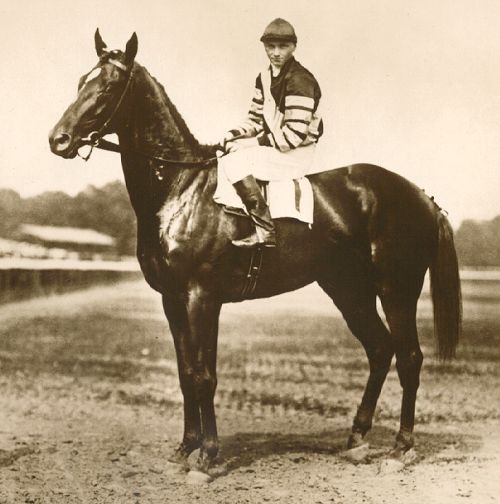
Man O' War (other)
Man o' War (March 29, 1917 – November 1, 1947) was an American Thoroughbred racehorse who is widely regarded as the greatest racehorse of all time. Several sports publications, including ''The Blood-Horse'', ''Sports Illustrated'', ESPN, and the Associated Press, voted Man o' War as the best American racehorse of the 20th century. During his racing career, just after World War I, Man o' War won 20 of 21 races and $249,465 () in purses. He was the unofficial 1920 American horse of the year and was honored with Babe Ruth as the outstanding athlete of the year by ''The New York Times''. He was inducted into the National Museum of Racing and Hall of Fame in 1957. On March 29, 2017, the museum opened a special exhibit in his honor, "Man o' War at 100". In 1919, Man o' War won 9 of 10 starts, including the Hopeful Stakes and Belmont Futurity, then the most important races for two-year-old horses in the United States. His only loss came at Saratoga Race Course, later nicknamed the Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Will-o'-wisp
In folklore, a will-o'-the-wisp, will-o'-wisp or ''ignis fatuus'' (, plural ''ignes fatui''), is an atmospheric ghost light seen by travellers at night, especially over bogs, swamps or marshes. The phenomenon is known in English folk belief, English folklore and much of European folklore by a variety of names, including jack-o'-lantern, friar's lantern, hinkypunk and is said to mislead travellers by resembling a flickering lamp or lantern. In literature, will-o'-the-wisp metaphorically refers to a hope or goal that leads one on, but is impossible to reach, or something one finds strange or sinister. Wills-o'-the-wisp appear in folk tales and traditional legends of numerous countries and cultures; notable wills-o'-the-wisp include St. Louis Light in Saskatchewan, the Spooklight in Southwestern Missouri and Northeastern Oklahoma, the Marfa lights of Texas, the Naga fireballs on the Mekong in Thailand, the Paulding Light in Upper Peninsula of Michigan and the Hessdalen light i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
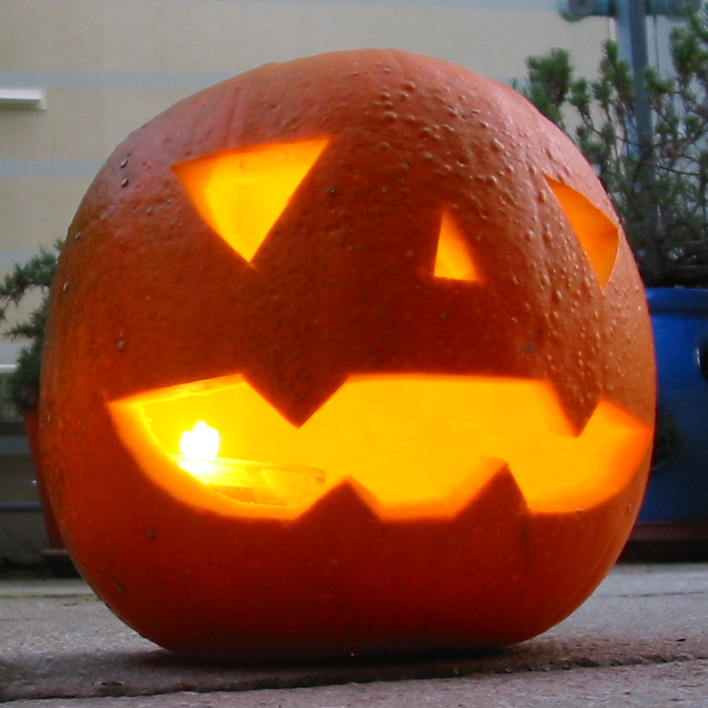
Jack-o'-lantern
A jack-o'-lantern (or jack o'lantern) is a carved lantern, most commonly made from a pumpkin or a root vegetable such as a rutabaga or turnip. Jack-o'-lanterns are associated with the Halloween holiday. Its name comes from the reported phenomenon of strange lights flickering over peat bogs, called ''will-o'-the-wisp, will-o'-the-wisps'' or ''jack-o'-lanterns''. The name is also tied to the Irish mythology, Irish legend of Stingy Jack, a drunkard who bargains with Satan and is doomed to roam the Earth with only a hollowed turnip to light his way. Jack-o'-lanterns carved from pumpkins are a yearly Halloween tradition that developed in the United States when Irish Americans, Irish immigrants brought their root vegetable carving tradition with them. It is common to see jack-o'-lanterns used as external and internal decorations prior to and on Halloween. To make a jack-o'-lantern, the top of a pumpkin or turnip is cut off to form a lid, the inside flesh is scooped out, and an image ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cat O' Nine Tails
The cat o' nine tails, commonly shortened to the cat, is a type of multi-tailed whip or flail that originated as an implement for severe physical punishment, notably in the Royal Navy and British Army, and as a judicial punishment in Britain and some other countries. Etymology The term first appears in 1681 in reports of a London murder. The term came into wider circulation in 1695 after its mention by a character in William Congreve's play ''Love for Love'', although the design is much older. It was probably so called in reference to its "claws", which inflict parallel wounds. There are equivalent terms in many languages, usually strictly translating, and also some analogous terms referring to a similar instrument's number of tails (cord or leather), such as the Dutch ''zevenstaart'' (seven tail , ''negenstaart'' (nine tail , the Spanish ''gato de nueve colas'' or the Italian ''gatto a nove code''. Description The cat is made up of nine knotted thongs of cotton cord, about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
O'clock
The 12-hour clock is a time convention in which the 24 hours of the day are divided into two periods: a.m. (from Latin , translating to "before midday") and p.m. (from Latin , translating to "after midday"). For different opinions on representation of midday and midnight, see #Confusion at noon and midnight Each period consists of 12 hours numbered: 12 (acting as 0), 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 and 11. The daily cycle starts at 12 midnight, runs through 12 noon, and continues until just before midnight at the end of the day. There is no widely accepted convention for how midday and midnight should be represented. The 12-hour clock was developed from the second millennium BC and reached its modern form in the 16th century AD. The 12-hour time convention is common in several English-speaking nations and former British colonies, as well as a few other countries. History and use The natural day-and-night division of a calendar day forms the fundamental basis as to why e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Auxiliaries And Contractions
English auxiliary verbs are a small set of English verbs, which include the English modal verbs and a few others. Although definitions vary, as generally conceived an auxiliary lacks inherent semantic meaning but instead modifies the meaning of another verb it accompanies. In English, verb forms are often classed as auxiliary on the basis of certain grammatical properties, particularly as regards their syntax. They also participate in subject–auxiliary inversion and negation by the simple addition of ''not'' after them. History of the concept In English, the adjective ''auxiliary'' was "formerly applied to any formative or subordinate elements of language, e.g. prefixes, prepositions." As applied to verbs, its conception was originally rather vague and varied significantly. Some historical examples The first English grammar, ''Pamphlet for Grammar'' by William Bullokar, published in 1586, does not use the term "auxiliary", but says, All other verbs are called verbs-neuters-u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formal Writing
A literary language is the form (register) of a language used in written literature, which can be either a nonstandard dialect or a standardized variety of the language. Literary language sometimes is noticeably different from the spoken language (''lects''), but the difference between literary language and non-literary language is greater in some languages; thus a great divergence between a written form and a spoken vernacular, the language exhibits diglossia, a community's use of two forms of speech. The understanding of the term differs from one linguistic tradition to another and is dependent on the terminological conventions adopted. Notably, in Eastern European and Slavic linguistics, the term "literary language" has also been used as a synonym of "standard language". Literary English For much of its history, there has been a distinction in the English language between an elevated literary language and a colloquial idiom.Matti Rissanen, ''History of Englishes: New Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |