|
Xyris Tennesseensis
''Xyris tennesseensis'' is a rare species of flowering plant in the family Xyridaceae known by the common name Tennessee yellow-eyed grass. It is native to a small section of the Southeastern United States, including parts of the states of Alabama, Georgia, and Tennessee. A federally listed endangered species, it is threatened by the loss and degradation of its habitat. ''Xyris tennesseensis'' is a perennial herb growing tall. The branching stem is bulbous and fleshy at the base. The leaves are long and narrow and originate at the swollen stem base. They are up to 45 centimeters (18 inches) long and not more than a centimeter (0.4 inch) 45/2.5wide. They are flat but sometimes twisted, and green with reddish or pink bases.''Xyris tennesseensis''. ''Flora of North America''. Retrieved August 27, 2011. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Kral
Robert Joseph Kral (born 5 July 1967) is an Australian film and television composer. He is best known for composing music scores for horror, superhero, and many animated WB productions. He scored the TV series, ''Angel (1999 TV series), Angel'' (the spin-off of ''Buffy the Vampire Slayer (TV series), Buffy the Vampire Slayer''), for most of the entire series (1999–2004, Seasons 1 through 5). In February 2005, a soundtrack album, ''Angel: Live Fast, Die Never'', was released, with 18 out of 25 tracks composed by Kral. He also composed the scores for the TV series ''Miracles (TV series), Miracles'' (2003) for ABC / Touchstone, ''Jake 2.0'' (2003–04), ''Duck Dodgers (TV series), Duck Dodgers'' (2003–05) for Warner Bros. Animation, ''The Inside (TV series), The Inside'' (2005) for Fox Television, and the Lionsgate / Sci Fi series, ''The Lost Room'' (2006). His animated film scores include ''Superman: Doomsday'' (2007), ''Green Lantern: First Flight'' (2009), ''Scooby-Doo! Legend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xyris
''Xyris'' is a genus of flowering plants, the yelloweyed grasses, in the yellow-eyed-grass family. The genus counts over 250 species, widespread over much of the world, with the center of distribution in the Guianas. The leaves are mostly distichous, linear, flat, and thin or round with a conspicuous sheath at the base. They are arranged in a basal aggregation. The small, yellow flowers are borne on a spherical or cylindrical spike or head (inflorescence). Each flower grows from the axil of a leathery bract. The fruit is a nonfleshy, dehiscent capsule. In ''Xyris complanata'', a single flower bud on the spike appears in the morning, and expands into a conspicuous flower during the afternoon hours. The APG IV system, of 2016, places the genus in family Xyridaceae, into the order Poales in the clade commelinids, in the monocots Monocotyledons (), commonly referred to as monocots, (Lilianae ''sensu'' Chase & Reveal) are grass and grass-like flowering plants (angiosperms), th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
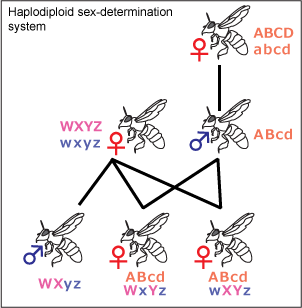
Lasioglossum Zephyrum
''Lasioglossum zephyrus'' is a sweat bee of the family Halictidae, found in the U.S. and Canada. It appears in the literature primarily under the misspelling "''zephyrum''". It is considered a primitively eusocial bee (meaning that they do not have a permanent division of labor within colonies),Batra, S. W. T. 1966. The life cycle and behavior of the primitively social bee ''Lasioglossum zephyrum'' (Halictidae). Univ. Kansas Sci. Bull. 46:359–423. although it may be facultatively solitary (i.e., displaying both solitary and eusocial behaviors).Interactions in colonies of primitively social bees: Artificial colonies of ''Lasioglossum zephyrum '. ''PNAS''. Retrieved 08-27-2011. The species nests in burrows in the soil. Taxonomy and phylogeny |
Microstegium Vimineum
''Microstegium vimineum'', commonly known as Japanese stiltgrass, packing grass, or Nepalese browntop, is an annual plant, annual grass that is common in a wide variety of habitats and is well adapted to low light levels. Despite being non-native in the United States, it serves as a host plant for some native satyr butterflies, such as the Carolina satyr ''Hermeuptychia sosybius'' and the endangered Mitchell's satyr ''Neonympha mitchellii''. Owing to its invasive potential, the plant has been put on the European list of invasive alien species. This means the plant can no longer be imported into or traded in the European Union. Distribution It is native in much of South Asia, East Asia, and parts of Southeast Asia, and has since moved to the United States. Description It typically grows to heights between and is capable of rooting at each Node (botany), node. The plant flowers in late summer and produces its seeds in the form of a caryopsis shortly thereafter. It is quite simi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Introduced Species
An introduced species, alien species, exotic species, adventive species, immigrant species, foreign species, non-indigenous species, or non-native species is a species living outside its native distributional range, but which has arrived there by human activity, directly or indirectly, and either deliberately or accidentally. Non-native species can have various effects on the local ecosystem. Introduced species that become established and spread beyond the place of introduction are considered naturalized. The process of human-caused introduction is distinguished from biological colonization, in which species spread to new areas through "natural" (non-human) means such as storms and rafting. The Latin expression neobiota captures the characteristic that these species are ''new'' biota to their environment in terms of established biological network (e.g. food web) relationships. Neobiota can further be divided into neozoa (also: neozoons, sing. neozoon, i.e. animals) and neophyt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Management
Land management is the process of managing the use and development (in both urban and rural settings, but it is mostly managed in Urban places.) of land resources. Land resources are used for a variety of purposes which may include organic agriculture, reforestation, water resource management and eco-tourism projects. Land management can have positive or negative effects on the terrestrial ecosystems. Land being over- or misused can degrade and reduce productivity and disrupt natural equilibriums. See also * Conservation grazing * Environmental management scheme * Habitat conservation * Holistic management * Land change science * Land registration * Sustainable agriculture *Wildlife management References Further reading * Dale P.D. and McLaughlin, J.D. 1988. ''Land Information Management'', Clarendon Press: Oxford. * Larsson G. 2010. ''Land Management as Public Policy'', University Press of America. . * United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs Agenda 21 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germination
Germination is the process by which an organism grows from a seed or spore. The term is applied to the sprouting of a seedling from a seed of an angiosperm or gymnosperm, the growth of a sporeling from a spore, such as the spores of fungi, ferns, bacteria, and the growth of the pollen tube from the pollen grain of a seed plant. Seed plants Germination is usually the growth of a plant contained within a seed; it results in the formation of the seedling. It is also the process of reactivation of metabolic machinery of the seed resulting in the emergence of radicle and plumule. The seed of a vascular plant is a small package produced in a fruit or cone after the union of male and female reproductive cells. All fully developed seeds contain an embryo and, in most plant species some store of food reserves, wrapped in a seed coat. Some plants produce varying numbers of seeds that lack embryos; these are empty seeds which never germinate. Dormant seeds are viable seeds that do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbicide
Herbicides (, ), also commonly known as weedkillers, are substances used to control undesired plants, also known as weeds.EPA. February 201Pesticides Industry. Sales and Usage 2006 and 2007: Market Estimates. Summary in press releasMain page for EPA reports on pesticide use ihere Selective herbicides control specific weed species, while leaving the desired crop relatively unharmed, while non-selective herbicides (sometimes called total weedkillers in commercial products) can be used to clear waste ground, industrial and construction sites, railways and railway embankments as they kill all plant material with which they come into contact. Apart from selective/non-selective, other important distinctions include ''persistence'' (also known as ''residual action'': how long the product stays in place and remains active), ''means of uptake'' (whether it is absorbed by above-ground foliage only, through the roots, or by other means), and ''mechanism of action'' (how it works). Historica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clearcutting
Clearcutting, clearfelling or clearcut logging is a forestry/ logging practice in which most or all trees in an area are uniformly cut down. Along with shelterwood and seed tree harvests, it is used by foresters to create certain types of forest ecosystems and to promote select species that require an abundance of sunlight or grow in large, even-age stands. Logging companies and forest-worker unions in some countries support the practice for scientific, safety and economic reasons, while detractors consider it a form of deforestation that destroys natural habitats and contributes to climate change. Clearcutting is the most common and economically profitable method of logging. However, it also may create detrimental side effects, such as the loss of topsoil, the costs of which are intensely debated by economic, environmental and other interests. In addition to the purpose of harvesting wood, clearcutting is used to create land for farming. Ultimately, the effects of clearcutt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lumber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into dimensional lumber, including beams and planks or boards, a stage in the process of wood production. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, window frames). Lumber has many uses beyond home building. Lumber is sometimes referred to as timber as an archaic term and still in England, while in most parts of the world (especially the United States and Canada) the term timber refers specifically to unprocessed wood fiber, such as cut logs or standing trees that have yet to be cut. Lumber may be supplied either rough- sawn, or surfaced on one or more of its faces. Beside pulpwood, ''rough lumber'' is the raw material for furniture-making, and manufacture of other items requiring cutting and shaping. It is available in many species, including hardwoods and softwoods, such as white pine and red pine, because of their low cost. ''Finished lumber'' is supplied in standard sizes, mostly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habitat Destruction
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss and habitat reduction) is the process by which a natural habitat becomes incapable of supporting its native species. The organisms that previously inhabited the site are displaced or dead, thereby reducing biodiversity and species abundance. Habitat destruction is the leading cause of biodiversity loss. Fragmentation and loss of habitat have become one of the most important topics of research in ecology as they are major threats to the survival of endangered species. Activities such as harvesting natural resources, industrial production and urbanization are human contributions to habitat destruction. Pressure from agriculture is the principal human cause. Some others include mining, logging, trawling, and urban sprawl. Habitat destruction is currently considered the primary cause of species extinction worldwide. Environmental factors can contribute to habitat destruction more indirectly. Geological processes, climate change, introdu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Extinction
Local extinction, also known as extirpation, refers to a species (or other taxon) of plant or animal that ceases to exist in a chosen geographic area of study, though it still exists elsewhere. Local extinctions are contrasted with global extinctions. Local extinctions mark a change in the ecology of an area. In recent times, local extinction has sometimes been followed by a replacement of the species taken from other locations; wolf reintroduction is an example of this. The term "local extinction" is highly vernacular. The more proper biological term is ''extirpation''. Discussion Glaciation can lead to local extinction. This was the case during the Pleistocene glaciation event in North America. During this period, most of the native North American species of earthworm were killed in places covered by glaciation. This left them open for colonization by European earthworms brought over in soil from Europe. Species naturally become extirpated from islands over time. The number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |