|
Xiphosurida
Xiphosura () is an order of arthropods related to arachnids. They are more commonly known as horseshoe crabs (a name applied more specifically to the only extant family, Limulidae). They first appeared in the Hirnantian (Late Ordovician). Currently, there are only four living species. Xiphosura contains one suborder, Xiphosurida, and several stem-genera. The group has hardly changed in appearance in hundreds of millions of years; the modern horseshoe crabs look almost identical to prehistoric genera and are considered to be living fossils. The most notable difference between ancient and modern forms is that the abdominal segments in present species are fused into a single unit in adults. Xiphosura were historically placed in the class Merostomata, although this term was intended to encompass also the eurypterids, whence it denoted what is now known to be an unnatural (paraphyletic) group (although this is a grouping recovered in some recent cladistic analyses). Although the name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horseshoe Crab
Horseshoe crabs are marine and brackish water arthropods of the family Limulidae and the only living members of the order Xiphosura. Despite their name, they are not true crabs or crustaceans: they are chelicerates, most closely related to arachnids, such as spiders and scorpions. Horseshoe crabs live primarily in and around shallow coastal waters on soft, sandy or muddy bottoms. They are generally found in the intertidal zone at spring high tides. They are eaten in some parts of Asia, and used as fishing bait, in fertilizer and in science (especially ''Limulus'' amebocyte lysate). In recent years, population declines have occurred as a consequence of coastal habitat destruction and overharvesting. Tetrodotoxin may be present in one horseshoe crab species, '' Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda''. Fossil records for horseshoe crabs extend back as far as 480 million years ago, with extant forms being living fossils. A 2019 molecular analysis places them as the sister group of Ricinule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurypterida
Eurypterids, often informally called sea scorpions, are a group of extinct arthropods that form the order Eurypterida. The earliest known eurypterids date to the Darriwilian stage of the Ordovician period 467.3 million years ago. The group is likely to have appeared first either during the Early Ordovician or Late Cambrian period. With approximately 250 species, the Eurypterida is the most diverse Paleozoic chelicerate order. Following their appearance during the Ordovician, eurypterids became major components of marine faunas during the Silurian, from which the majority of eurypterid species have been described. The Silurian genus ''Eurypterus'' accounts for more than 90% of all known eurypterid specimens. Though the group continued to diversify during the subsequent Devonian period, the eurypterids were heavily affected by the Late Devonian extinction event. They declined in numbers and diversity until becoming extinct during the Permian–Triassic extinction event (or sometim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maldybulakia
''Maldybulakia'' is a genus of freshwater arthropod which lived during the Devonian period. ''Maldybulakia'' is known from three species, ''M. angusi'' and ''M. malcolmi'' from Australia, and ''M. mirabilis'' from Kazakhstan. Although it was originally described as a myriapod-like animal, it was later considered related to the xiphosurans, a group including modern horseshoe crabs. Discovery and etymology In 1992, the type species of ''Maldybulakia'' is described from the Pragian to Emsian-aged Sheshen'karinskaya Formation (also known as the Sheshenkarinskoy Suite) in central Kazakhstan, with scientific name ''Lophodesmus mirabilis''. The genus name ''Lophodesmus'' came from the Greek ''lophos'' ("tubercle") and ''desmos'' ("bond"), and the species name ''mirabilis'' means "wonderful" in Latin. However, this genus name is already used for an extant genus of myriapod, and in 1998, the new genus name ''Maldybulakia'', named after Maldybulak Farm in the Bayanaul District, Pavl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willwerathia
''Willwerathia'' is a genus of synziphosurine, a paraphyletic group of horseshoe crab-like fossil chelicerate arthropods. ''Willwerathia'' known only by one species, ''Willwerathia laticeps'', discovered in deposits of the Devonian period from the Klerf Formation, in the Rhenish Slate Mountains of Germany. Morphology As a synziphosurine, ''Willwerathia'' is unusually large and so far the largest known synziphosurine, with largest carapace measured about 90mm in width. Prosoma of ''Willwerathia'' covered by a vaulted carapace with pointed genal spines, recurved (M-shaped) ophthalmic ridges and pairs of dorsal nodes. Tergites of the opisthosoma are either incomplete or disarticulated in available fossil materials, making it difficult to reveal the original number of opisthosomal segments. The opisthosoma of ''Willwerathia'' most likely compose of 10 segments, each expressed by a tergite that bore a median dorsal spine and a pair of tergopleurae (lateral extensions). The opisth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hirnantian
The Hirnantian is the final internationally recognized stage of the Ordovician Period of the Paleozoic Era. It was of short duration, lasting about 1.4 million years, from to Ma (million years ago). The early part of the Hirnantian was characterized by cold temperatures, major glaciation, and a severe drop in sea level. In the latter part of the Hirnantian, temperatures rose, the glaciers melted, and sea level returned to the same or to a slightly higher level than it had been prior to the glaciation. Most scientists believe that this climatic oscillation caused the major extinction event that took place during this time. In fact, the Hirnantian (also known as the End Ordovician and the Ordovician-Silurian) mass extinction event represents the second largest such event in geologic history. Approximately 85% of marine (sea-dwelling) species died. Only the End Permian mass extinction was larger. Unlike many smaller extinction events, however, the long-term consequences of the E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
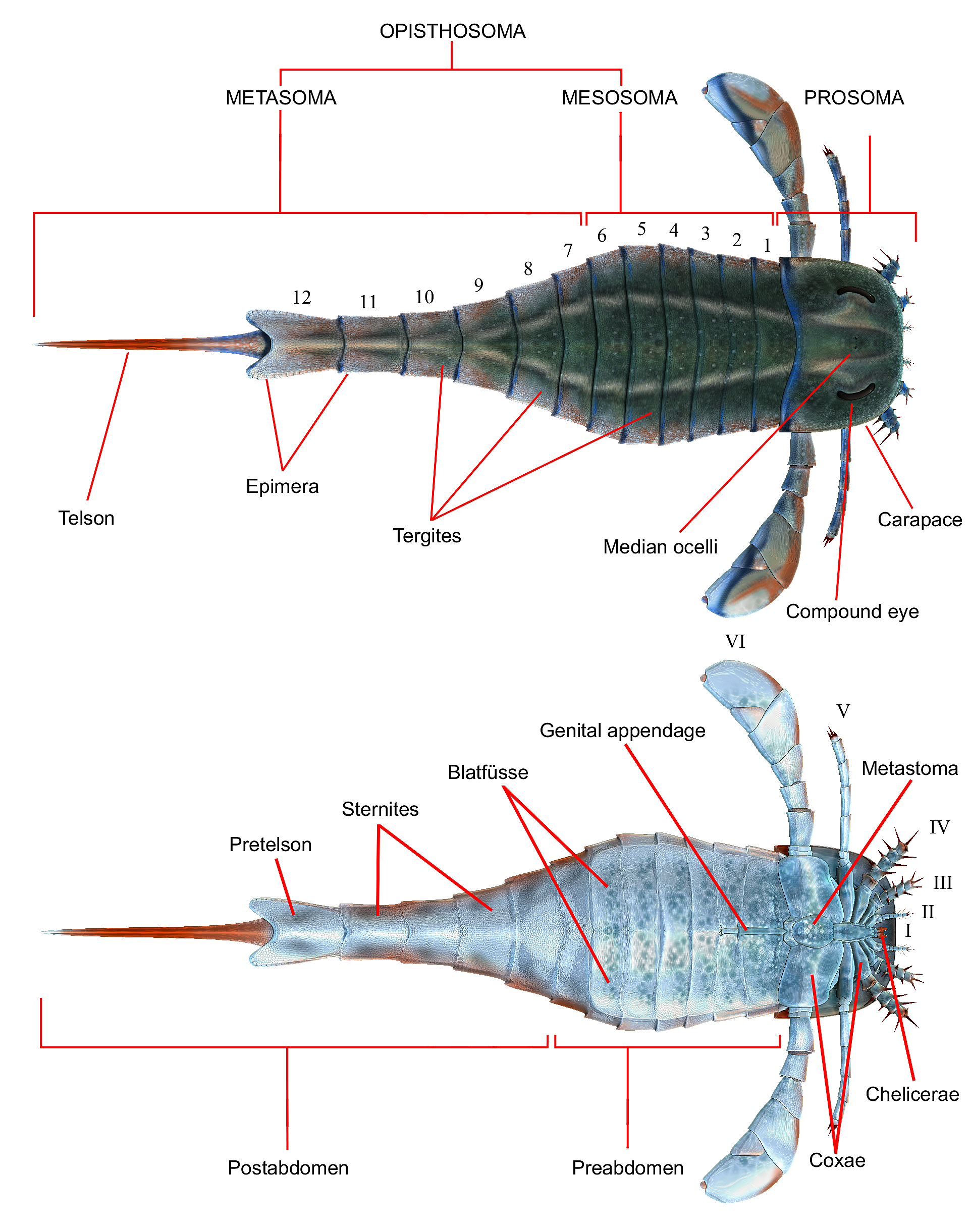
Opisthosoma
The opisthosoma is the posterior part of the body in some arthropods, behind the prosoma (cephalothorax). It is a distinctive feature of the subphylum Chelicerata (arachnids, horseshoe crabs and others). Although it is similar in most respects to an abdomen (and is often referred to as such), the opisthosoma is differentiated by its inclusion of the respiratory organs (book lungs or book gills) and the heart. Segments The number of segments and appendages on the opisthosoma vary. Scorpions have 13, but the first is only seen during its embryological development. Other arachnids have fewer; harvestmen, for instance, have only ten. In general, appendages are absent or reduced, although in horseshoe crabs they persist as large plate-like limbs, called opercula or branchiophores, bearing the book gills, and that function in locomotion and gas exchange. In most chelicerates the opisthosomal limbs are greatly reduced and persist only as specialized structures, such as the silk-producing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ricinulei
Ricinulei is a small order of arachnids. Like most arachnids, they are predatory, eating small arthropods. They occur today in west-central Africa (''Ricinoides'') and the Neotropics (''Cryptocellus'' and ''Pseudocellus'') as far north as Texas. As of 2021, 91 extant species of ricinuleids have been described worldwide, all in the single family Ricinoididae. In older works they are sometimes referred to as Podogona. Due to their obscurity they do not have a proper common name, though in academic literature they are occasionally referred to as hooded tickspiders. In addition to the three living genera, there are fossil species from the upper Carboniferous of Euramerica and the Cretaceous Burmese amber. Description The most important general account of ricinuleid anatomy remains the 1904 monograph by Hans Jacob Hansen and William Sørensen. Useful further studies can be found in, e.g., the work of Pittard and Mitchell, Gerald Legg and L. van der Hammen. Body Ricinulei are typical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838 by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ''zōḗ'' (), "life", meaning "ancient life" ). It is the longest of the Phanerozoic eras, lasting from , and is subdivided into six geologic periods (from oldest to youngest): # Cambrian # Ordovician # Silurian # Devonian # Carboniferous # Permian The Paleozoic comes after the Neoproterozoic Era of the Proterozoic Eon and is followed by the Mesozoic Era. The Paleozoic was a time of dramatic geological, climatic, and evolutionary change. The Cambrian witnessed the most rapid and widespread diversification of life in Earth's history, known as the Cambrian explosion, in which most modern phyla first appeared. Arthropods, molluscs, fish, amphibians, reptiles, and synapsids all evolved during the Paleozoic. Life began in the ocean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosoma
The cephalothorax, also called prosoma in some groups, is a tagma of various arthropods, comprising the head and the thorax fused together, as distinct from the abdomen behind. (The terms ''prosoma'' and ''opisthosoma'' are equivalent to ''cephalothorax'' and ''abdomen'' in some groups.) The word ''cephalothorax'' is derived from the Greek words for head (, ') and thorax (, '). This fusion of the head and thorax is seen in chelicerates and crustaceans; in other groups, such as the Hexapoda (including insects), the head remains free of the thorax. In horseshoe crabs and many crustaceans, a hard shell called the carapace covers the cephalothorax. Arachnid anatomy Fovea The fovea is the centre of the cephalothorax and is located behind the head (only in spiders).Dalton, Steve (2008). ''Spiders; The Ultimate Predators''. A & C Black, London. P.p. 19. . It is often important in identification. It can be transverse or procurved Smith, A. M. (1990c). Baboon spiders: Tarantulas of Afr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelicera
The chelicerae () are the mouthparts of the subphylum Chelicerata, an arthropod group that includes arachnids, horseshoe crabs, and sea spiders. Commonly referred to as "jaws", chelicerae may be shaped as either articulated fangs, or similarly to pincers. Some chelicerae, such as those found on nearly all spiders, are hollow and contain (or are connected to) venom glands, and are used to inject venom into prey or a perceived threat. In ''Pisaurina mira'', also known as the nursery web spider, the chelicerae are utilized to snatch the prey once it becomes within reach, facilitating the "sit-and-wait ambush predator" behavior. Both pseudoscorpions and harvestmen have structures on their chelicerae that are used for grooming (papillae in pseudoscorpions, cheliceral teeth in Opiliones). Types Chelicerae can be divided into three kinds: jackknife chelicerae, scissor chelicerae, and 3-segmented chelate chelicerae. Jackknife chelicerae The jackknife chelicera is subchelate (with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carapace
A carapace is a Dorsum (biology), dorsal (upper) section of the exoskeleton or shell in a number of animal groups, including arthropods, such as crustaceans and arachnids, as well as vertebrates, such as turtles and tortoises. In turtles and tortoises, the underside is called the plastron. Crustaceans In crustaceans, the carapace functions as a protective cover over the cephalothorax (i.e., the fused head and thorax, as distinct from the abdomen behind). Where it projects forward beyond the eyes, this projection is called a rostrum (anatomy), rostrum. The carapace is Calcification, calcified to varying degrees in different crustaceans. Zooplankton within the phylum Crustacea also have a carapace. These include Cladocera, ostracods, and Isopoda, isopods, but isopods only have a developed "cephalic shield" carapace covering the head. Arachnids In arachnids, the carapace is formed by the fusion of prosomal tergites into a single Plate (animal anatomy), plate which carries the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arachnid
Arachnida () is a class of joint-legged invertebrate animals (arthropods), in the subphylum Chelicerata. Arachnida includes, among others, spiders, scorpions, ticks, mites, pseudoscorpions, harvestmen, camel spiders, whip spiders and vinegaroons. Almost all adult arachnids have eight legs, although the front pair of legs in some species has converted to a sensory function, while in other species, different appendages can grow large enough to take on the appearance of extra pairs of legs. The term is derived from the Greek word (''aráchnē'', 'spider'), from the myth of the hubristic human weaver Arachne, who was turned into a spider. Almost all extant arachnids are terrestrial, living mainly on land. However, some inhabit freshwater environments and, with the exception of the pelagic zone, marine environments as well. They comprise over 100,000 named species, of which 47,000 are species of spiders. Morphology Almost all adult arachnids have eight legs, unlike adult inse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_(cropped).jpg)



