|
Xinglongwa
The Xinglongwa culture () ( 6200– 5400 BC) was a Neolithic culture in northeastern China, found mainly around the Inner Mongolia- Liaoning border at the Liao River basin. Xinglongwa pottery was primarily cylindrical and baked at low temperatures. The Xinglongwa culture showed several signs of communal planning. At three Xinglongwa sites, houses were built in rows. Several Xinglongwa sites also featured a large central building. In addition, several Xinglongwa sites were surrounded by ditches. The type site at Xinglongwa is located on the southwest side of a hill at Aohan Banner, Chifeng, Inner Mongolia; the site is named after a village 1.3 km to the southeast of the site. 120 pit-houses were discovered at Xinglongwa. Each home had a hearth at its center. Xinglongwa also featured a large building in the center of the village. Xinglongwa is the earliest discovered site in China to be surrounded by a ditch. Xinglongwa also featured an unusual burial custom, as some bodies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xinglonggou
Xinglonggou is a Neolithic through Bronze Age archaeological site complex consisting of three separate sites. The sites are located on a loess slope above the left bank of the Mangniu River north of the Qilaotu Mountains in Aohan Banner, Inner Mongolia, China. Xinglonggou is one of the most important sites of the early Neolithic Xinglongwa culture and provides evidence for the development of millet cultivation. The millet assemblage at Xinglonggou consists primarily of broomcorn millet. Xinglonggou is one of the few, early Neolithic sites in China for which systematic flotation (archaeology), flotation has been performed. Description Xinglonggou was discovered in 1982. Xinglonggou consists of three separate sites, each corresponding to a different archaeological culture. In chronological order, the oldest site (''Xinglonggou 1'') dates from around 8000 to 7500 Before Present, BP and is associated with the Xinglongwa culture; the next site (''Xinglonggou 2'') dates from around 5500 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
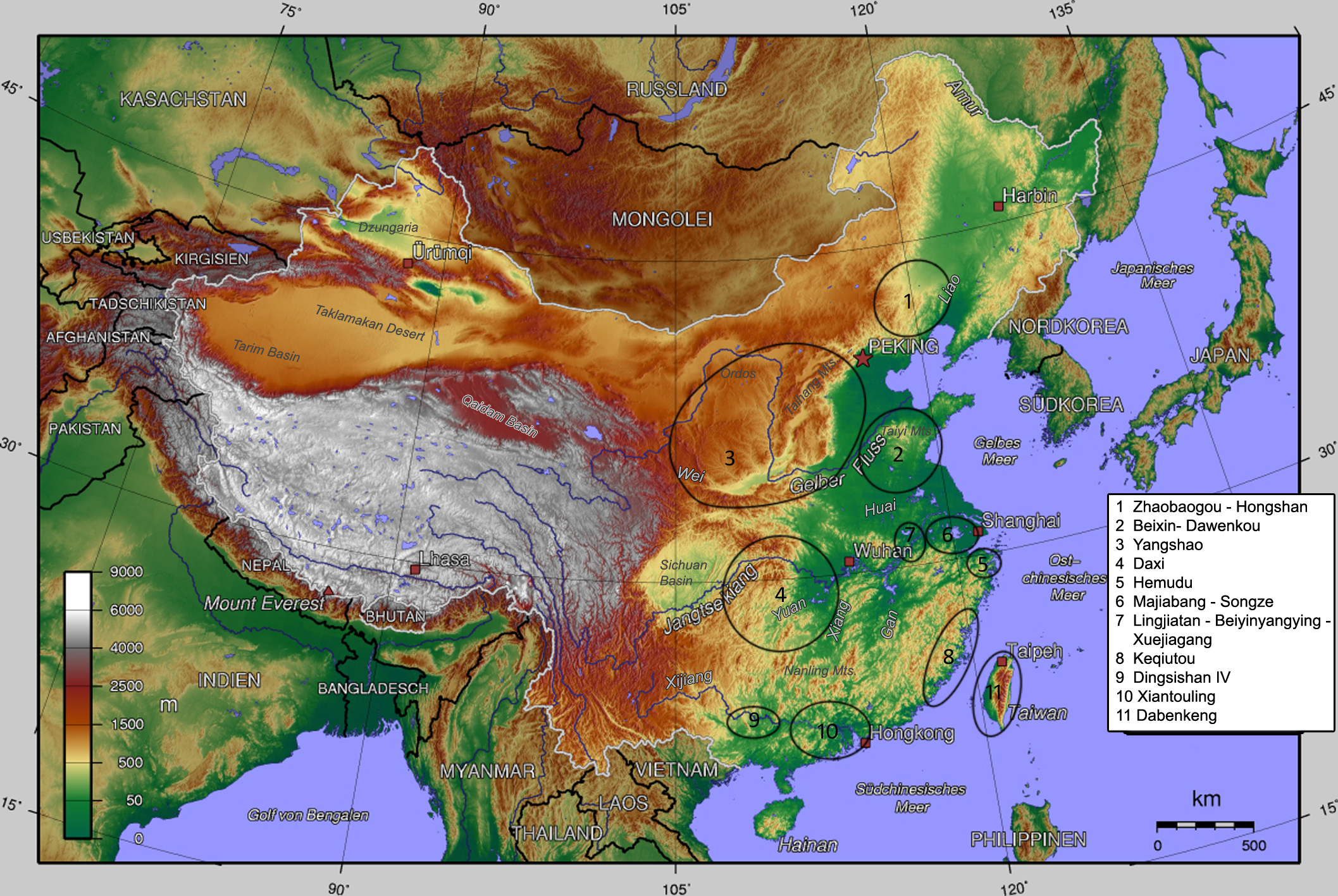
List Of Neolithic Cultures Of China
This is a list of Neolithic cultures of China that have been unearthed by archaeologists. They are sorted in chronological order from earliest to latest and are followed by a schematic visualization of these cultures. It would seem that the definition of Neolithic in China is undergoing changes. The discovery in 2012 of pottery about 20,000 years BC indicates that this measure alone can no longer be used to define the period. It will fall to the more difficult task of determining when cereal domestication started. List Schematic outline These cultures are existed for the period from 8500 to 1500 BC. Neolithic cultures remain unmarked and Bronze Age cultures (from 2000 BC) are marked with *. There are many differences in opinion by dating these cultures, so the dates chosen here are tentative: For this schematic outline of its neolithic cultures China has been divided into the following nine parts: #Northeast China: Inner Mongolia, Heilongjiang, Jilin and Liaoning. #Northwes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic Cultures Of China
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of settlement. It began about 12,000 years ago when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East, and later in other parts of the world. The Neolithic lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BC), marked by the development of metallurgy, leading up to the Bronze Age and Iron Age. In other places the Neolithic followed the Mesolithic (Middle Stone Age) and then lasted until later. In Ancient Egypt, the Neolithic lasted until the Protodynastic period, 3150 BC.Karin Sowada and Peter Grave. Egypt in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic Pottery Jar, Xinglongwa Culture, Liaoning, 1990
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of settlement. It began about 12,000 years ago when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East, and later in other parts of the world. The Neolithic lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BC), marked by the development of metallurgy, leading up to the Bronze Age and Iron Age. In other places the Neolithic followed the Mesolithic (Middle Stone Age) and then lasted until later. In Ancient Egypt, the Neolithic lasted until the Protodynastic period, 3150 BC.Karin Sowada and Peter Grave. Egypt in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of settlement. It began about 12,000 years ago when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East, and later in other parts of the world. The Neolithic lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BC), marked by the development of metallurgy, leading up to the Bronze Age and Iron Age. In other places the Neolithic followed the Mesolithic (Middle Stone Age) and then lasted until later. In Ancient Egypt, the Neolithic lasted until the Protodynastic period, 3150 BC.Karin Sowada and Peter Grave. Egypt in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Beifudi Site
Beifudi () is an archaeological site and Neolithic village in Yi County, Hebei, China. The site, an area of 3 ha on the northern bank of the Yishui River, contains artifacts of a culture contemporaneous with the Cishan and Xinglongwa cultures of about 8000–7000 BP, two known Neolithic cultures east of the Taihang Mountains, and thus fills an archaeological gap between the two Northern Chinese cultures. The total excavated area is more than 1,200 square meters and the collection of neolithic findings at the site has been conducted in two phases. This archaeological site was voted Number One in the Top Ten most outstanding archaeological findings in 2004 by Chinese archaeologists in their annual poll. Findings The most significant discovery in the first phase of the site's excavation is the large number of pottery masks in the shape of human and animal faces, the oldest extant carvings to date. A dozen carved clay masks, in cat, monkey and pig as well as human likenes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comb Ceramic
Comb Ceramic or Pit-Comb Ware (in Europe), Jeulmun pottery or Jeulmun vessel (in Korea) is a type of pottery subjected to geometric patterns from a comb-like tool. This type of pottery was widely distributed in the Baltic, Finland, the Volga upstream flow, south Siberia, Lake Baikal, Mongolian Plateau, the Liaodong Peninsula and the Korean Peninsula. The oldest Comb Ceramic is found in the remains of Liao civilization: Xinglongwa culture (6200 BC - 5400 BC). 王 巍(中国社会科学院考古研究所・副所長) (in Japanese)A Zhimin (1988) [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhaobaogou Culture
The Zhaobaogou culture (Chinese: 趙宝溝文化) (5400–4500 BC) was a Neolithic culture in northeast China, found primarily in the Luan River valley in Inner Mongolia and northern Hebei. The culture produced sand- tempered, incised pottery vessels with geometric and zoomorphic designs. The culture also produced stone and clay human figurines. The type site at Zhaobaogou, excavated in 1986, was discovered in Aohan Banner, Chifeng, Inner Mongolia. The site covers an area of around 90,000 m2.''The Archaeology of Northeast China: Beyond the Great Wall'', p. 54 See also * List of Neolithic cultures of China * Hongshan culture * Xinglongwa culture The Xinglongwa culture () ( 6200– 5400 BC) was a Neolithic culture in northeastern China, found mainly around the Inner Mongolia-Liaoning border at the Liao River basin. Xinglongwa pottery was primarily cylindrical and baked at low temperatures ... Notes References * * * {{PRChina-archaeology-stub History of Inner Mongolia Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chifeng
Chifeng ( zh, s=赤峰市), also known as Ulanhad ( mn, (Улаанхад хот), ''Ulaɣanqada qota'', , "red cliff"), is a prefecture-level city in Southeastern Inner Mongolia, People's Republic of China. It borders Xilin Gol League to the north and west, Tongliao to the northeast, Chaoyang ( Liaoning) to the southeast and Chengde (Hebei) to the south. The city has a total administrative area of and as of the 2020 census, had a population of 4,035,967 inhabitants (4,341,245 in 2010). However, 1,175,391 of those residents lived in the built-up (or metro) area made of the 2 urban districts of Hongshan and Songshan, as Yuanbaoshan is not conurbated yet. However, a large part of Songshan is still rural and Yuanbaoshan is a de facto separate town 27 kilometers away from the core district of Chifeng. The city was the administrative center of the defunct Ju Ud League ( zh, s=昭乌达盟, labels=no; ). History According to archeological studies, human occupation of the Chifen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hongshan Culture
The Hongshan culture () was a Neolithic culture in the West Liao river basin in northeast China. Hongshan sites have been found in an area stretching from Inner Mongolia to Liaoning, and dated from about 4700 to 2900 BC. The culture is named after (), a site in Hongshan District, Chifeng. The site was discovered by the Japanese archaeologist Torii Ryūzō in 1908 and extensively excavated in 1935 by Kōsaku Hamada and Mizuno Seiichi. Historical context In northeast China, Hongshan culture was preceded by Xinglongwa culture (6200–5400 BC), Xinle culture (5300–4800 BC), and Zhaobaogou culture, which may be contemporary with Xinle and a little later. The Yangshao culture of the Yellow River existed contemporaneously with the Hongshan culture (see map). These two cultures interacted with each other. Hongshan culture was succeeded by the Lower Xiajiadian culture (2200–1600 BC), which was replaced by a different Upper Xiajiadian culture (1000-600 BC) with a shift from farmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Liaoning
Liaoning () is a coastal province in Northeast China that is the smallest, southernmost, and most populous province in the region. With its capital at Shenyang, it is located on the northern shore of the Yellow Sea, and is the northernmost coastal province of the People's Republic of China. Historically a gateway between China proper and Manchuria, the modern Liaoning province was established in 1907 as Fengtian or Fengtien province and was renamed Liaoning in 1929. It was also known at that time as Mukden Province for the Manchu name of ''Shengjing'', the former name of Shenyang. Under the Japanese-puppet Manchukuo regime, the province reverted to its 1907 name, but the name Liaoning was restored for a brief time in 1945 and then again in 1954. Liaoning borders the Yellow Sea (Korea Bay) and Bohai Sea in the south, North Korea's North Pyongan and Chagang provinces in the southeast, Jilin to the northeast, Hebei to the southwest, and Inner Mongolia to the northwest. The Yalu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6200 BC
The 7th millennium BC spanned the years 7000 BC to 6001 BC (c. 9 ka to c. 8 ka). It is impossible to precisely date events around this millennium, and all dates mentioned here are estimates mostly based on geological and anthropological analysis. Towards the end of this millennium, the islands of Great Britain, and Ireland were severed from continental Europe by rising seawater. Communities Population Neolithic culture and technology were established in the Near East by 7000 BC and there is increasing evidence through the millennium of its spread or introduction to Europe and the Far East. In most of the world, however, including north and western Europe, people still lived in scattered Palaeolithic hunter-gatherer communities. The Mehrgarh chalcolithic civilization began around 7000 BC. The world population is believed to have been stable and slowly increasing. It has been estimated that there were perhaps ten million people worldwide at the end of this millennium, growing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)