|
Xerxes Of Armenia
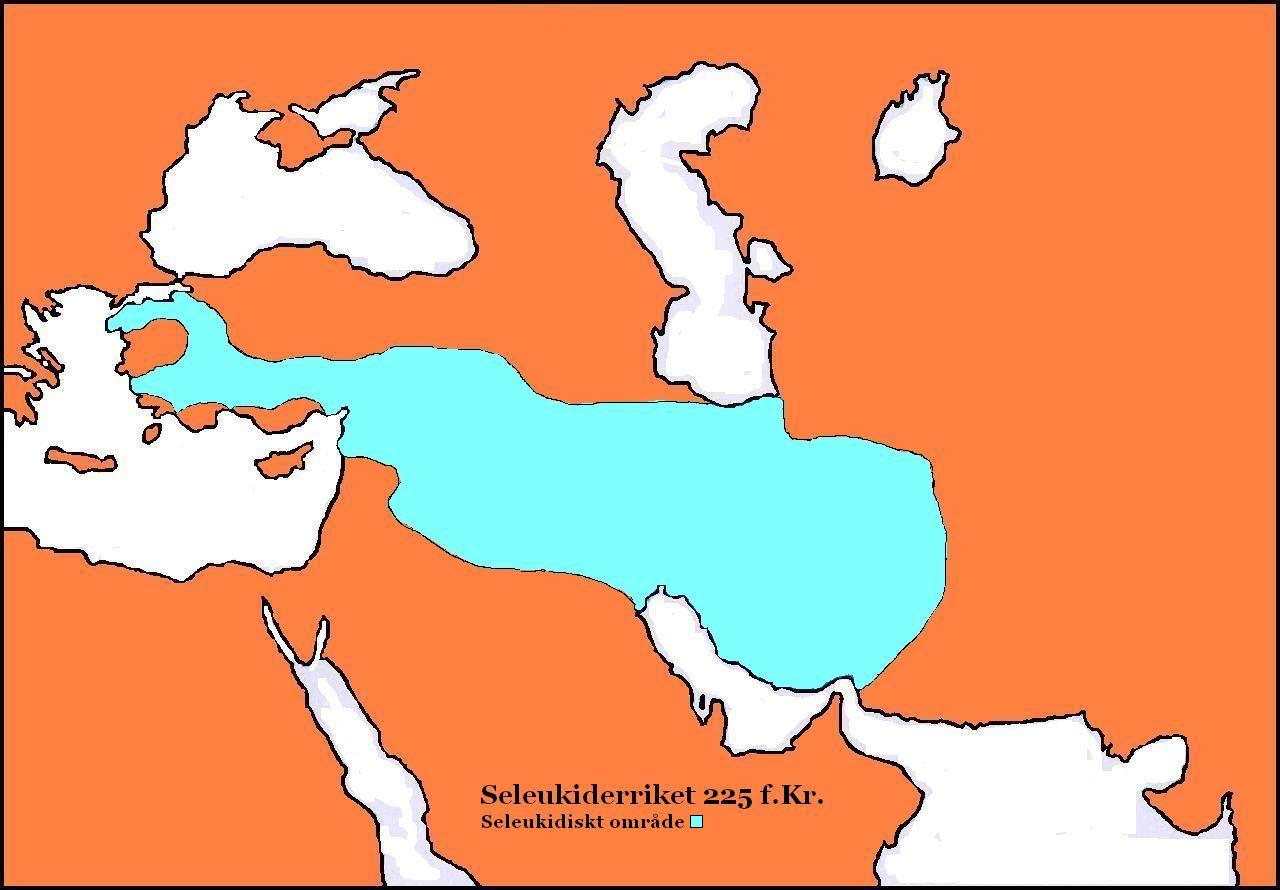
Xerxes ( grc, Ξέρξης; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐎹𐎠𐎼𐏁𐎠) was king of Sophene and Commagene from 228 BC to 212 BC. He was the son and successor of Arsames I. Name ''Xérxēs'' () is the Greek and Latin (''Xerxes'', ''Xerses'') transliteration of the Old Iranian ''Xšaya-ṛšā'' ("ruling over heroes"), a popular name amongst the rulers of the Persian Achaemenid Empire. Reign Xerxes belonged to the Iranian Orontid dynasty.; ; ; His father was Arsames I, who ruled Sophene, Commagene and possibly Armenia. Xerxes succeeded his father as the ruler of Sophene and Commagene in 228 BC, while his brother Orontes IV ruled Armenia. In 223 BC, several Seleucid satraps rebelled against King Antiochus III, including Artabazanes ( Upper Media), Molon ( Lower Media), Alexander (Persis), and Achaeus (Asia Minor). By 220 BC Antiochus had put down most of the rebellions; however, Achaeus was not defeated until 213 BC. These rebellions help explain Antiochus' subsequent aggressive p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Sophene
The Kingdom of Sophene ( hy, Ծոփք, translit=Tsopʻkʻ, grc, Σωφηνή, translit=Sōphēnḗ), was a Hellenistic-era political entity situated between ancient Armenia and Syria. Ruled by the Orontid dynasty, the kingdom was culturally mixed with Greek, Armenian, Iranian, Syrian, Anatolian and Roman influences. Founded around the 3rd century BCE, the kingdom maintained independence until when the Artaxiad king Tigranes the Great conquered the territories as part of his empire. Sophene laid near medieval Kharput, which is present day Elazığ. Name The name Sophene is thought to derive from the ethnonym ''Ṣuppani'', a people who lived in the region in the first half of the 1st millennium BCE and appear in Hittite and Assyrian sources. According to historian Nicholas Adontz, the Ancient Greek ''Sōphēnḗ'' was coined after the Armenian ''Tsopʻkʻ'', which stems directly from ''Ṣuppani''. History The Kingdom of Sophene was ruled by the Orontid dynasty of Iranian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiochus III The Great
Antiochus III the Great (; grc-gre, Ἀντίoχoς Μέγας ; c. 2413 July 187 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king and the 6th ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 222 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the rest of western Asia towards the end of the 3rd century BC. Rising to the throne at the age of eighteen in 222 BC, his early campaigns against the Ptolemaic Kingdom were unsuccessful, but in the following years Antiochus gained several military victories and substantially expanded the empire's territory. His traditional designation, ''the Great'', reflects an epithet he assumed. He also assumed the title ''Basileus Megas'' (Greek for "Great King"), the traditional title of the Persian kings. A militarily active ruler, Antiochus restored much of the territory of the Seleucid Empire, before suffering a serious setback, towards the end of his reign, in his war against Rome. Declaring himself the "champion of Greek freedom against Roman domina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Unknown
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3rd-century BC Rulers
The 3rd century was the period from 201 ( CCI) to 300 (CCC) Anno Domini (AD) or Common Era (CE) in the Julian calendar.. In this century, the Roman Empire saw a crisis, starting with the assassination of the Roman Emperor Severus Alexander in 235, plunging the empire into a period of economic troubles, barbarian incursions, political upheavals, civil wars, and the split of the Roman Empire through the Gallic Empire in the west and the Palmyrene Empire in the east, which all together threatened to destroy the Roman Empire in its entirety, but the reconquests of the seceded territories by Emperor Aurelian and the stabilization period under Emperor Diocletian due to the administrative strengthening of the empire caused an end to the crisis by 284. This crisis would also mark the beginning of Late Antiquity. In Persia, the Parthian Empire was succeeded by the Sassanid Empire in 224 after Ardashir I defeated and killed Artabanus V during the Battle of Hormozdgan. The Sassanids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kings Of Sophene
Kings or King's may refer to: *Monarchs: The sovereign heads of states and/or nations, with the male being kings *One of several works known as the "Book of Kings": **The Books of Kings part of the Bible, divided into two parts **The ''Shahnameh'', an 11th-century epic Persian poem **The Morgan Bible, a French medieval picture Bible **The Pararaton, a 16th-century Javanese history of southeast Asia *The plural of any king Business * Kings Family Restaurants, a chain of restaurants in Pennsylvania and Ohio *Kings Food Markets, a chain supermarket in northern New Jersey * King's Favourites, a brand of cigarettes *King's Variety Store, a chain of stores in the USA *King's (defunct discount store), a defunct chain of discount stores in the USA Education *King's College (other), various colleges * King's School (other), various schools * The King's Academy (other), various academies Electoral districts * King's (New Brunswick electoral district) (1867–1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3rd-century BC Iranian People
The 3rd century was the period from 201 ( CCI) to 300 (CCC) Anno Domini (AD) or Common Era (CE) in the Julian calendar.. In this century, the Roman Empire saw a crisis, starting with the assassination of the Roman Emperor Severus Alexander in 235, plunging the empire into a period of economic troubles, barbarian incursions, political upheavals, civil wars, and the split of the Roman Empire through the Gallic Empire in the west and the Palmyrene Empire in the east, which all together threatened to destroy the Roman Empire in its entirety, but the reconquests of the seceded territories by Emperor Aurelian and the stabilization period under Emperor Diocletian due to the administrative strengthening of the empire caused an end to the crisis by 284. This crisis would also mark the beginning of Late Antiquity. In Persia, the Parthian Empire was succeeded by the Sassanid Empire in 224 after Ardashir I defeated and killed Artabanus V during the Battle of Hormozdgan. The Sassanids t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arsamosata
Arsamosata (Middle Persian ''*Aršāmšād''; Old Persian ''*Ṛšāma-šiyāti-'', grc, Ἀρσαμόσατα, ) was an ancient and medieval city situated on the bank of the Murat River, near the present-day city of Elâzığ. It was founded in by Arsames I, the Orontid king of Sophene, Commagene and possibly Armenia. The city served as a central center and royal residence of the Orontids of Sophene. The origin of its name was Persian, meaning "Joy of Arsames". Naming cities such the "joy of" or "happiness of" was a Orontid (and later Artaxiad) practice that recalled the Achaemenid royal discourse. It was left and destroyed in the 1st century BC. In the Middle Ages it was called Ashmushat. In Roman and Byzantine times, it bore the names Armosota (Ἀρμόσοτα) and Arsamosota (Ἀρσαμόσοτα). It was also known in Byzantine times as Asmosaton. It was called Shimshāṭ in Arabic. A prominent native of Arsamosata was the 10th-century poet Abu'l-Hasan Ali al-Shimshat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The region is bounded by the Turkish Straits to the northwest, the Black Sea to the north, the Armenian Highlands to the east, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and the Aegean Sea to the west. The Sea of Marmara forms a connection between the Black and Aegean seas through the Bosporus and Dardanelles straits and separates Anatolia from Thrace on the Balkan peninsula of Southeast Europe. The eastern border of Anatolia has been held to be a line between the Gulf of Alexandretta and the Black Sea, bounded by the Armenian Highlands to the east and Mesopotamia to the southeast. By this definition Anatolia comprises approximately the western two-thirds of the Asian part of Turkey. Today, Anatolia is sometimes considered to be synonymous with Asia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaeus (general)
Achaeus ( grc, Ἀχαιός, ''Akhaios''; died 213 BC) was a general and later a separatist ruler of part of the Greek Seleucid kingdom. He was the son of Andromachus, whose sister Laodice II married Seleucus Callinicus, the father of Antiochus III the Great He accompanied Seleucus Ceraunus, the son of Callinicus, in his expedition across mount Taurus against Attalus I, and after the assassination of Seleucus Ceraunus revenged his death; and though he might easily have assumed the royal power, he remained faithful to the family of Seleucus. In 223 BC Antiochus III, the successor of Seleucus Ceraunus, appointed him to the command of all Asia Minor on the western side of Mount Taurus. Achaeus recovered all the districts which Attalus had gained on the Seleucids once more; but being falsely accused by Hermeias, the minister to Antiochus, of intending to revolt, Achaeus assumed the title of king in self-defence, and ruled over the whole of Asia on the western side of the Tauru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
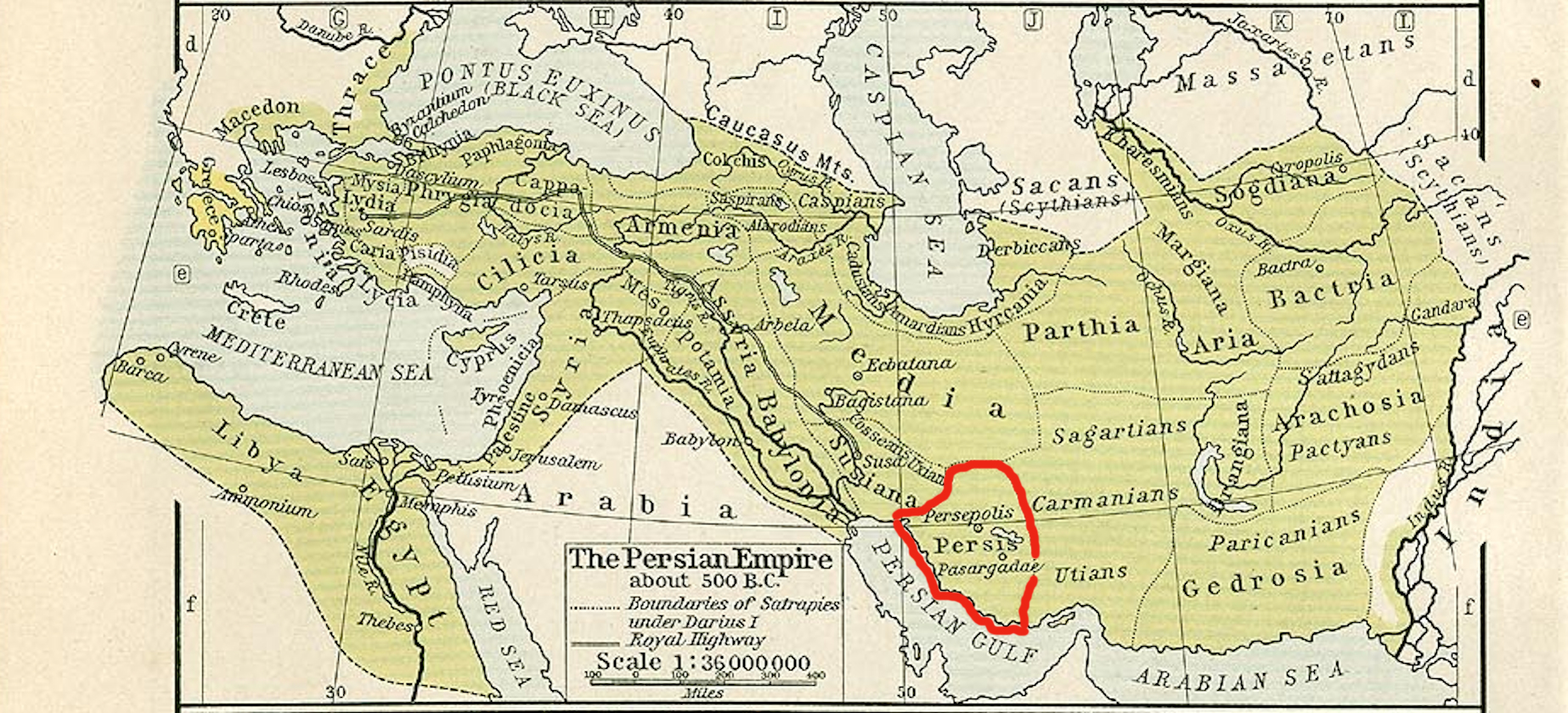
Persis
Persis ( grc-gre, , ''Persís''), better known in English as Persia ( Old Persian: 𐎱𐎠𐎼𐎿, ''Parsa''; fa, پارس, ''Pârs''), or Persia proper, is the Fars region, located to the southwest of modern-day Iran, now a province. The Persians are thought to have initially migrated either from Central Asia or, more probably, from the north through the Caucasus. They would then have migrated to the current region of Persis in the early 1st millennium BC. The country name Persia was derived directly from the Old Persian ''Parsa''. Achaemenid Empire The ancient Persians were present in the region of Persis from about the 10th century BC. They became the rulers of the largest empire the world had yet seen under the Achaemenid dynasty which was established in the late 6th century BC, at its peak stretching from Thrace- Macedonia, Bulgaria- Paeonia and Eastern Europe proper in the west, to the Indus Valley in its far east. The ruins of Persepolis and Pasargadae, two o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander (satrap)
Alexander (in Greek Αλέξανδρος; died 220 BC) was brother of Molon. On the accession of the Seleucid king Antiochus III, afterwards called the Great, in 223 BC, he entrusted Alexander with the government of the satrapy of Persis and Molon received Media. Up to that time, local rulers of Persis, the Fratarakas seem to have been in charge of the region, between circa 295 and 220 BC. Antiochus was then only fifteen years of age, and this circumstance together with the fact that Hermeias, a crafty intriguer whom every one had to fear, was all-powerful at his court, induced the two brothers to form the plan of causing the upper satrapies of the kingdom to revolt. It seems to have been the secret wish of Hermeias to see the king involved as many difficulties as possible, and it was on his advice that the war against the rebels was entrusted to men without courage and ability. In 220, however, Antiochus himself undertook the command. Molon was deserted by his troops, and to avoid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Media
Media ( peo, 𐎶𐎠𐎭, Māda, Middle Persian: ''Mād'') is a region of north-western Iran, best known for having been the political and cultural base of the Medes. During the Achaemenid period, it comprised present-day Azerbaijan, Iranian Kurdistan and western Tabaristan. As a satrapy under Achaemenid rule, it would eventually encompass a wider region, stretching to southern Dagestan in the north. However, after the wars of Alexander the Great, the northern parts were separated due to the Partition of Babylon and became known as ''Atropatene'', while the remaining region became known as ''Lesser Media''. History Under the Medes In 678 BC, Deioces united the Median tribes of Media and made the first Iranian Empire. His grandson Cyaxares managed to unite all Iranian tribes of Ancient Iran and made his empire a major power. When Cyaxares died he was succeeded by his son, Astyages, who was the last king of the Median Empire. Under the Achaemenids In 553 BC, Cyrus the Great ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |