|
XXYY
XXYY syndrome is a sex chromosome anomaly in which males have 2 extra chromosomes, one X and one Y chromosome. Human cells usually contain two sex chromosomes, one from the mother and one from the father. Usually, females have two X chromosomes (XX) and males have one X and one Y chromosome (XY). The appearance of at least one Y chromosome with a properly functioning SRY gene makes a male. Therefore, humans with XXYY are genotypically male. Males with XXYY syndrome have 48 chromosomes instead of the typical 46. This is why XXYY syndrome is sometimes written as 48, XXYY syndrome or 48, XXYY. It affects an estimated one in every 18,000–40,000 male births. Presentation Some signs and symptoms of this condition include: Cause 48,XXYY syndrome is a condition related to the X and Y chromosomes (the sex chromosomes). People normally have 46 chromosomes in each cell. Two of the 46 chromosomes, known as X and Y, are called sex chromosomes because they help determine whether a person ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X Chromosome
The X chromosome is one of the two sex-determining chromosomes (allosomes) in many organisms, including mammals (the other is the Y chromosome), and is found in both males and females. It is a part of the XY sex-determination system and XO sex-determination system. The X chromosome was named for its unique properties by early researchers, which resulted in the naming of its counterpart Y chromosome, for the next letter in the alphabet, following its subsequent discovery. Discovery It was first noted that the X chromosome was special in 1890 by Hermann Henking in Leipzig. Henking was studying the testicles of ''Pyrrhocoris'' and noticed that one chromosome did not take part in meiosis. Chromosomes are so named because of their ability to take up staining (''chroma'' in Greek means ''color''). Although the X chromosome could be stained just as well as the others, Henking was unsure whether it was a different class of object and consequently named it ''X element'', which later be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
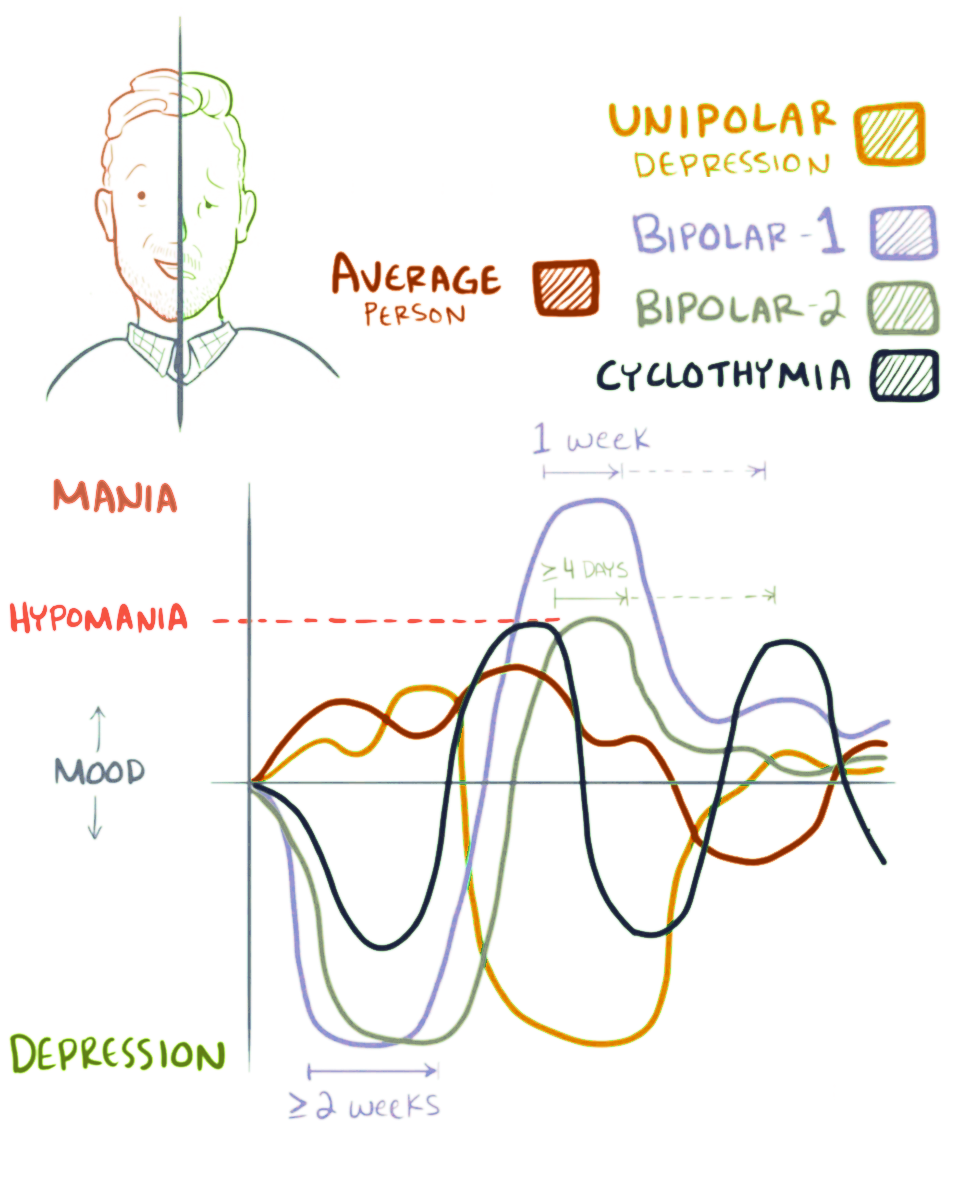
Mood Swings
A mood swing is an extreme or sudden change of Mood (psychology), mood. Such changes can play a positive part in promoting problem solving and in producing flexible forward planning, or be disruptive. When mood swings are severe, they may be categorized as part of a mental illness, such as bipolar disorder, where erratic and disruptive mood swings are a defining feature. Overview Speed and extent Mood swings can happen any time at any place, varying from the microscopic to the wild oscillations of bipolar disorder, so that a continuum can be traced from normal struggles around self-esteem, through cyclothymia, up to a depressive disease. However most people's mood swings remain in the mild to moderate range of emotional ups and downs. The duration of bipolar mood swings also varies. They may last a few hours - ''ultrarapid'' - or extend over days - ''ultradian'': clinicians maintain that only when four continuous days of hypomania, or seven days of mania, occur, is a diagnos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Y Chromosome
The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes (allosomes) in therian mammals, including humans, and many other animals. The other is the X chromosome. Y is normally the sex-determining chromosome in many species, since it is the presence or absence of Y that determines the male or female sex of offspring produced in sexual reproduction. In mammals, the Y chromosome contains the gene SRY, which triggers male development. The DNA in the human Y chromosome is composed of about 59 million base pairs, making it similar in size to chromosome 19. The Y chromosome is passed only from father to son. With a 30% difference between humans and chimpanzees, the Y chromosome is one of the fastest-evolving parts of the human genome. The human Y chromosome carries an estimated 100–200 genes, with between 45 and 73 of these being protein-coding. All single-copy Y-linked genes are hemizygous (present on only one chromosome) except in cases of aneuploidy such as XYY syndrome or XXYY syndrome. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinodactyly
Clinodactyly is a medical term describing the curvature of a digit (a finger or toe) in the plane of the palm, most commonly the fifth finger (the "little finger") towards the adjacent fourth finger (the "ring finger"). It is a fairly common isolated anomaly which often goes unnoticed, but also occurs in combination with other abnormalities in certain genetic syndromes. The term is from the Ancient Greek κλίνειν ' 'to bend' and δάκτυλος ' 'digit'. Genetics Clinodactyly is an autosomal dominant trait that has variable expressiveness and incomplete penetrance. Clinodactyly can be passed through inheritance and presents as either an isolated anomaly or a component manifestation of a genetic syndrome. Many syndromes are associated with clinodactyly, including those listed below. But the phenotype, by itself, is not a sensitive or specific diagnostic test for these syndromes (it is present in up to 18% of the normal population). * Down syndrome * Turner syndrome * Aa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nondisjunction
Nondisjunction is the failure of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate properly during cell division (mitosis/meiosis). There are three forms of nondisjunction: failure of a pair of homologous chromosomes to separate in meiosis I, failure of sister chromatids to separate during meiosis II, and failure of sister chromatids to separate during mitosis. Nondisjunction results in daughter cells with abnormal chromosome numbers (aneuploidy). Calvin Bridges and Thomas Hunt Morgan are credited with discovering nondisjunction in ''Drosophila melanogaster'' sex chromosomes in the spring of 1910, while working in the Zoological Laboratory of Columbia University. Types In general, nondisjunction can occur in any form of cell division that involves ordered distribution of chromosomal material. Higher animals have three distinct forms of such cell divisions: Meiosis I and meiosis II are specialized forms of cell division occurring during generation of gametes (eggs and sperm) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudoautosomal Region
The pseudoautosomal regions, PAR1, PAR2, are homologous sequences of nucleotides on the X and Y chromosomes. The pseudoautosomal regions get their name because any genes within them (so far at least 29 have been found for humans) are inherited just like any autosomal genes. PAR1 comprises 2.6 Mbp of the short-arm tips of both X and Y chromosomes in humans and great apes (X and Y are 155 Mbp and 59 Mbp in total). PAR2 is at the tips of the long arms, spanning 320 kbp. Location The locations of the PARs within GRCh38 are: The locations of the PARs within GRCh37 are: Inheritance and function Normal male mammals have two copies of these genes: one in the pseudoautosomal region of their Y chromosome, the other in the corresponding portion of their X chromosome. Normal females also possess two copies of pseudoautosomal genes, as each of their two X chromosomes contains a pseudoautosomal region. Crossing over between the X and Y chromosomes is normally restricted to the pseudoa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients and metabolites.Cell Movements and the Shaping of the Vertebrate Body in Chapter 21 of Molecular Biology of the Cell '' fourth edition, edited by Bruce Alberts (2002) published by Garland Science. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos. It is also common to describe small molecules such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexual Characteristics
Sexual characteristics are physical traits of an organism (typically of a sexually dimorphic organism) which are indicative of its biological sex. These can include sex organs used for reproduction and secondary sex characteristics which distinguish the sexes of a species, but which are not directly part of the reproductive system. Humans In humans, sex organs or primary sexual characteristics, which are those a person is born with, can be distinguished from secondary sex characteristics, which develop later in life, usually during puberty. The development of both is controlled by sex hormones produced by the body after the initial fetal stage where the presence or absence of the Y-chromosome and/or the SRY gene determine development. Hormones that express sexual differentiation in humans include: * estrogens * progesterone * androgens such as testosterone Typical sexual characteristics The following table lists the typical sexual characteristics in humans: Invertebr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testicle
A testicle or testis (plural testes) is the male reproductive gland or gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testes are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testosterone. Testosterone release is controlled by the anterior pituitary luteinizing hormone, whereas sperm production is controlled both by the anterior pituitary follicle-stimulating hormone and gonadal testosterone. Structure Appearance Males have two testicles of similar size contained within the scrotum, which is an extension of the abdominal wall. Scrotal asymmetry, in which one testicle extends farther down into the scrotum than the other, is common. This is because of the differences in the vasculature's anatomy. For 85% of men, the right testis hangs lower than the left one. Measurement and volume The volume of the testicle can be estimated by palpating it and comparing it to ellipsoids of known sizes. Another method is to use caliper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sex Chromosome
A sex chromosome (also referred to as an allosome, heterotypical chromosome, gonosome, heterochromosome, or idiochromosome) is a chromosome that differs from an ordinary autosome in form, size, and behavior. The human sex chromosomes, a typical pair of mammal allosomes, determine the sex of an individual created in sexual reproduction. Autosomes differ from allosomes because autosomes appear in pairs whose members have the same form but differ from other pairs in a diploid cell, whereas members of an allosome pair may differ from one another and thereby determine sex. Nettie Stevens and Edmund Beecher Wilson both independently discovered sex chromosomes in 1905. However, Stevens is credited for discovering them earlier than Wilson. Differentiation In humans, each cell nucleus contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, a total of 46 chromosomes. The first 22 pairs are called autosomes. Autosomes are homologous chromosomes i.e. chromosomes which contain the same genes (regions of DNA) i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heredity
Heredity, also called inheritance or biological inheritance, is the passing on of traits from parents to their offspring; either through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction, the offspring cells or organisms acquire the genetic information of their parents. Through heredity, variations between individuals can accumulate and cause species to evolve by natural selection. The study of heredity in biology is genetics. Overview In humans, eye color is an example of an inherited characteristic: an individual might inherit the "brown-eye trait" from one of the parents. Inherited traits are controlled by genes and the complete set of genes within an organism's genome is called its genotype. The complete set of observable traits of the structure and behavior of an organism is called its phenotype. These traits arise from the interaction of its genotype with the environment. As a result, many aspects of an organism's phenotype are not inherited. For example, suntanned skin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reproductive Cells
A gamete (; , ultimately ) is a Ploidy#Haploid and monoploid, haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as sex cells. In species that produce two Morphology (biology), morphologically distinct types of gametes, and in which each individual produces only one type, a female is any individual that produces the larger type of gamete—called an ovum— and a male produces the smaller type—called a sperm. Sperm cells or spermatozoa are small and motile due to the flagellum, a tail-shaped structure that allows the cell to propel and move. In contrast, each egg cell or ovum is relatively large and non-motile. In short a gamete is an egg cell (female gamete) or a sperm (male gamete). In animals, ova mature in the ovaries of females and sperm develop in the testes of males. During fertilization, a spermatozoon and ovum unite to form a ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |