|
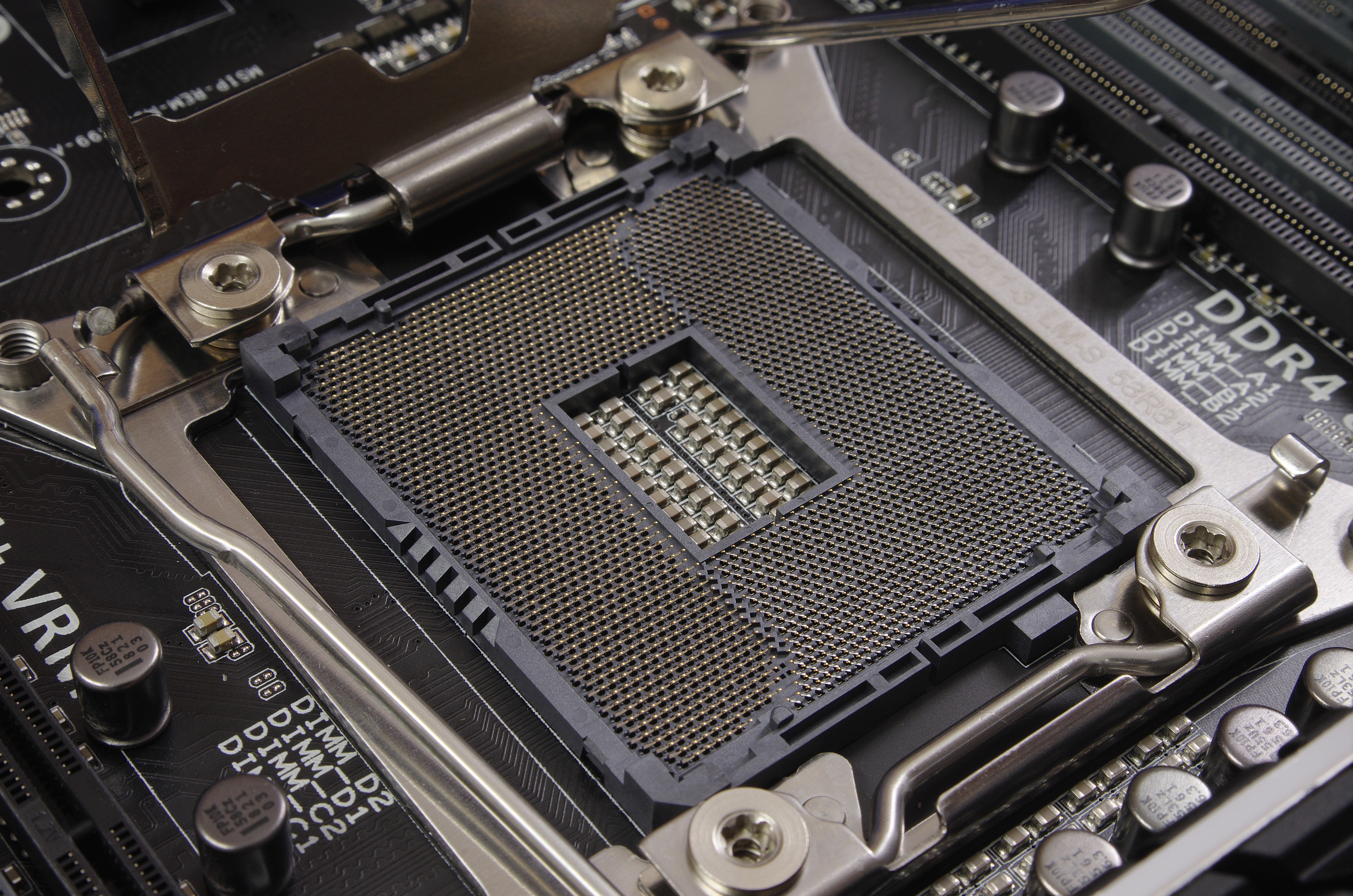
X99
Intel X99, List of Intel codenames, codenamed "Wellsburg", is a Platform Controller Hub (PCH) designed and manufactured by Intel, targeted at the Desktop computer, high-end desktop (HEDT) and enthusiast segments of the Intel product lineup. The X99 chipset supports both Intel Core i7 Extreme and Intel Xeon E5-16xx v3 and E5-26xx v3 Central processing unit, processors, which belong to the Haswell-E and Haswell-EP variants of the Haswell (microarchitecture), Haswell microarchitecture, respectively. All supported processors use the LGA 2011-v3 CPU socket, socket. The X99 chipset was released in late August 2014, while the supported processors were released in late August 2014 (Haswell-E) and early September 2014 (Haswell-EP). In May 2016, X99's processor support was extended to the Broadwell (microarchitecture), Broadwell variants of the Intel Core i7 Extreme and Intel Xeon E5-16xx v4 and E5-26xx v4 processors, which belong to the Broadwell-E a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haswell-E
Haswell is the List of Intel codenames, codename for a Central processing unit, processor microarchitecture developed by Intel as the "fourth-generation core" successor to the Ivy Bridge (microarchitecture), Ivy Bridge (which is a die shrink/Tick–tock model, tick of the Sandy Bridge, Sandy Bridge microarchitecture). Intel officially announced CPUs based on this microarchitecture on June 4, 2013, at Computex Taipei 2013, while a working Haswell chip was demonstrated at the 2011 Intel Developer Forum. With Haswell, which uses a 22 nanometer, 22 nm process, Intel also introduced low-power processors designed for convertible or "hybrid" ultrabooks, designated by the "U" suffix. Haswell CPUs are used in conjunction with the Intel 8 Series chipsets, Intel 9 Series chipsets, and Intel Xeon chipsets#Haswell-based Xeon chipsets, Intel C220 series chipsets. At least one Haswell-based processor is still being sold as of 2022, the Pentium G3420. Design The Haswell archite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haswell (microarchitecture)
Haswell is the codename for a processor microarchitecture developed by Intel as the "fourth-generation core" successor to the Ivy Bridge (which is a die shrink/tick of the Sandy Bridge microarchitecture). Intel officially announced CPUs based on this microarchitecture on June 4, 2013, at Computex Taipei 2013, while a working Haswell chip was demonstrated at the 2011 Intel Developer Forum. With Haswell, which uses a 22 nm process, Intel also introduced low-power processors designed for convertible or "hybrid" ultrabooks, designated by the "U" suffix. Haswell CPUs are used in conjunction with the Intel 8 Series chipsets, Intel 9 Series chipsets, and Intel C220 series chipsets. At least one Haswell-based processor is still being sold as of 2022, the Pentium G3420. Design The Haswell architecture is specifically designed to optimize the power savings and performance benefits from the move to FinFET (non-planar, "3D") transistors on the improved 22 nm pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel X299
Intel X299, codenamed "Basin Falls", is a Platform Controller Hub (PCH) designed and manufactured by Intel, targeted at the high-end desktop (HEDT) or enthusiast segment of the Intel product lineup. The X299 chipset supports the Intel Core X-series processors, which are codenamed Skylake-X, Kaby Lake-X and Cascade Lake-X. All supported processors use the LGA 2066 socket. The X299 chipset was released in June 2017, with the Intel Core i9-7900X. See also * List of Intel chipsets Features The X299 chipset uses the new Direct Media Interface (DMI) 3.0. 24 PCI Express 3.0 lanes are provided by the chipset, a sizable increase from the X99 Intel X99, List of Intel codenames, codenamed "Wellsburg", is a Platform Controller Hub (PCH) designed and manufactured by Intel, targeted at the Desktop computer, high-end desktop (HEDT) and enthusiast segments of the Intel product lineup. Th ... chipset's 8 PCI-e 2.0 lanes. Many features from the X99 chipset are carried over to the X29 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platform Controller Hub
The Platform Controller Hub (PCH) is a family of Intel's single-chip chipsets, first introduced in 2009. It is the successor to the Intel Hub Architecture, which used two chips - a Northbridge (computing), northbridge and Southbridge (computing), southbridge, and first appeared in the Intel 5 Series. The PCH controls certain data paths and support functions used in conjunction with Intel CPUs. These include clocking (the system clock), Flexible Display Interface (FDI) and Direct Media Interface (DMI), although FDI is used only when the chipset is required to support a processor with integrated graphics. As such, I/O functions are reassigned between this new central hub and the CPU compared to the previous architecture: some northbridge functions, the memory controller and PCI Express, PCIe lanes, were integrated into the CPU while the PCH took over the remaining functions in addition to the traditional roles of the southbridge. AMD has its equivalent for the PCH, known simply as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LGA 2011-v3
LGA 2011, also called ''Socket R'', is a CPU socket by Intel released on November 14, 2011. It launched along with LGA 1356 to replace its predecessor, LGA 1366 (Socket B) and LGA 1567. While LGA 1356 was designed for dual-processor or low-end servers, LGA 2011 was designed for high-end desktops and high-performance servers. The socket has 2011 protruding pins that touch contact points on the underside of the processor. The LGA 2011 socket uses QPI to connect the CPU to additional CPUs. DMI 2.0 is used to connect the processor to the PCH. The memory controller and 40 PCI Express (PCIe) lanes are integrated on the CPU. On a secondary processor an extra ×4 PCIe interface replaces the DMI interface. As with its predecessor LGA 1366, there is no provisioning for integrated graphics. This socket supports four DDR3 or DDR4 SDRAM memory channels with up to three unbuffered or registered DIMMs per channel, as well as up to 40 PCI Express 2.0 or 3.0 lanes. LGA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Media Interface
In computing, Direct Media Interface (DMI) is Intel's proprietary link between the northbridge and southbridge on a computer motherboard. It was first used between the 9xx chipsets and the ICH6, released in 2004. Previous Intel chipsets had used the Intel Hub Architecture to perform the same function, and server chipsets use a similar interface called ''Enterprise Southbridge Interface'' (ESI). While the "DMI" name dates back to ICH6, Intel mandates specific combinations of compatible devices, so the presence of a DMI interface does not guarantee by itself that a particular northbridge–southbridge combination is allowed. DMI shares many characteristics with PCI Express, using multiple lanes and differential signaling to form a point-to-point link. Most implementations use a ×4 link, while some mobile systems (e.g. 915GMS, 945GMS/GSE/GU and the Atom N450) use a ×2 link, halving the bandwidth. The original implementation provides 10 Gbit/s (1 GB/s) in each di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LGA 2011-v3
LGA 2011, also called ''Socket R'', is a CPU socket by Intel released on November 14, 2011. It launched along with LGA 1356 to replace its predecessor, LGA 1366 (Socket B) and LGA 1567. While LGA 1356 was designed for dual-processor or low-end servers, LGA 2011 was designed for high-end desktops and high-performance servers. The socket has 2011 protruding pins that touch contact points on the underside of the processor. The LGA 2011 socket uses QPI to connect the CPU to additional CPUs. DMI 2.0 is used to connect the processor to the PCH. The memory controller and 40 PCI Express (PCIe) lanes are integrated on the CPU. On a secondary processor an extra ×4 PCIe interface replaces the DMI interface. As with its predecessor LGA 1366, there is no provisioning for integrated graphics. This socket supports four DDR3 or DDR4 SDRAM memory channels with up to three unbuffered or registered DIMMs per channel, as well as up to 40 PCI Express 2.0 or 3.0 lanes. LGA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haswell-EP
Xeon ( ) is a brand of x86 microprocessors designed, manufactured, and marketed by Intel, targeted at the non-consumer workstation, server, and embedded system markets. It was introduced in June 1998. Xeon processors are based on the same architecture as regular desktop-grade CPUs, but have advanced features such as support for ECC memory, higher core counts, more PCI Express lanes, support for larger amounts of RAM, larger cache memory and extra provision for enterprise-grade reliability, availability and serviceability (RAS) features responsible for handling hardware exceptions through the Machine Check Architecture. They are often capable of safely continuing execution where a normal processor cannot due to these extra RAS features, depending on the type and severity of the machine-check exception (MCE). Some also support multi-socket systems with two, four, or eight sockets through use of the Ultra Path Interconnect (UPI) bus. Overview The ''Xeon'' brand has been maint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel Xeon
Xeon ( ) is a brand of x86 microprocessors designed, manufactured, and marketed by Intel, targeted at the non-consumer workstation, server, and embedded system markets. It was introduced in June 1998. Xeon processors are based on the same architecture as regular desktop-grade CPUs, but have advanced features such as support for ECC memory, higher core counts, more PCI Express lanes, support for larger amounts of RAM, larger cache memory and extra provision for enterprise-grade reliability, availability and serviceability (RAS) features responsible for handling hardware exceptions through the Machine Check Architecture. They are often capable of safely continuing execution where a normal processor cannot due to these extra RAS features, depending on the type and severity of the machine-check exception (MCE). Some also support multi-socket systems with two, four, or eight sockets through use of the Ultra Path Interconnect (UPI) bus. Overview The ''Xeon'' brand has been maint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel X79
The Intel X79 ( codenamed ''Patsburg'') is a Platform Controller Hub (PCH) designed and manufactured by Intel for their LGA 2011 (Socket R) and LGA 2011-1 (Socket R2). Socket and chipset support CPUs targeted at the high-end desktop (HEDT) and enthusiast segments of the Intel product lineup: Core i7-branded and Xeon-branded processors from the Sandy Bridge and Ivy Bridge CPU architectures. The supported CPUs feature quad channel memory controllers, and a certain number of PCIe lanes, the chipset features additional PCIe lanes; it is designed to connect an Intel processor through a DMI 2.0 interface to peripheral devices. Features The first product was announced on November 14, 2011, for "Extreme" CPUs using the LGA 2011 socket. Features include: * 2× Serial ATA (SATA) 3.0 (6Gbit/s) ports & 4x SATA 2 (3Gbit/s) ports. * 8× PCI Express 2.0 lanes * 14 Universal Serial Bus (USB) 2.0 ports * Integrated Gigabit Ethernet MAC (Lewisville PHY) * Optional Intel Rapid Storage Technolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
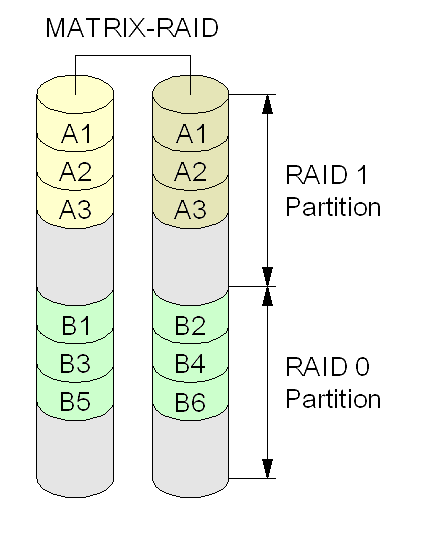
Rapid Storage Technology
Intel Rapid Storage Technology (RST) is a driver SATA AHCI and a firmware-based RAID solution built into a wide range of Intel chipsets. Currently also is installed as a driver for Intel Optane temporary storage units. It contains two operation modes that do not follow the SATA standard, it follows two Intel specific modes. The name modes and the application that contains them have been renamed since the first version. Until 2010 it contains AHCI and Matrix RAID modes. The first mode is the Intel driver SATA normal and the latter mode is a fake RAID. Up to version 4 it is included on Intel Application Accelerator RAID Edition, between versions 5 and 8.9 it is included on Intel Matrix Storage Manager (IMSM), since version 9 it is included on Intel Rapid Storage Technology (IRST) preferring the driver modes to be named RST AHCI and RST AHCI RAID instead of Matrix RAID. The latter is also known as RST RAID mode, since it is the mode that Intel recommends to use, even if you are n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advanced Host Controller Interface
The Advanced Host Controller Interface (AHCI) is a technical standard defined by Intel that specifies the register-level interface of Serial ATA (SATA) host controllers in a non-implementation-specific manner in its motherboard chipsets. The specification describes a system memory structure for computer hardware vendors to exchange data between host system memory and attached storage devices. AHCI gives software developers and hardware designers a standard method for detecting, configuring, and programming SATA/AHCI adapters. AHCI is separate from the SATA 3 Gbit/s standard, although it exposes SATA's advanced capabilities (such as hot swapping and native command queuing) such that host systems can utilize them. For modern solid state drives, the interface has been superseded by NVMe. The current version of the specification is 1.3.1. Operating modes Many SATA controllers offer selectable modes of operation: legacy Parallel ATA emulation (more commonly called IDE Mode) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |