|
Xie Of Xia
Xie (Chinese: , ''Xiè'') was the tenth king of the semi-legendary Xia Dynasty. The son of Mang, Xie ascended the throne in the " Xinwei" () year. He possibly ruled 25 years.Bamboo Annals. According to the Bamboo Annals, in the 12th year of Xie's reign, the prince of Yin (殷), Zihai (子亥), while a guest in Youyi (有易), was "guilty of licentious conduct" and killed by the leader of the place, Mianchen (綿臣), who also sent away his retinue. Four years later, Zihai’s successor, Wei (微), allied with the forces of the baron of Ho (河伯), and invaded Youyi, killing Mianchen. In the 21st year of his reign, Xie "conferred regular dignities" on the chiefs of the surrounding barbarians. He was succeeded by his sons Bu Jiang and Jiong.Sima Qian. ''Records of the Grand Historian'', Vol. Han Dynasty I. Trans. Watson, Burton Burton Dewitt Watson (June 13, 1925April 1, 2017) was an American sinologist, translator, and writer known for his English translations of Chines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Language
Chinese (, especially when referring to written Chinese) is a group of languages spoken natively by the ethnic Han Chinese majority and many minority ethnic groups in Greater China. About 1.3 billion people (or approximately 16% of the world's population) speak a variety of Chinese as their first language. Chinese languages form the Sinitic branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages family. The spoken varieties of Chinese are usually considered by native speakers to be variants of a single language. However, their lack of mutual intelligibility means they are sometimes considered separate languages in a family. Investigation of the historical relationships among the varieties of Chinese is ongoing. Currently, most classifications posit 7 to 13 main regional groups based on phonetic developments from Middle Chinese, of which the most spoken by far is Mandarin (with about 800 million speakers, or 66%), followed by Min (75 million, e.g. Southern Min), Wu (74 million, e.g. Shangh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
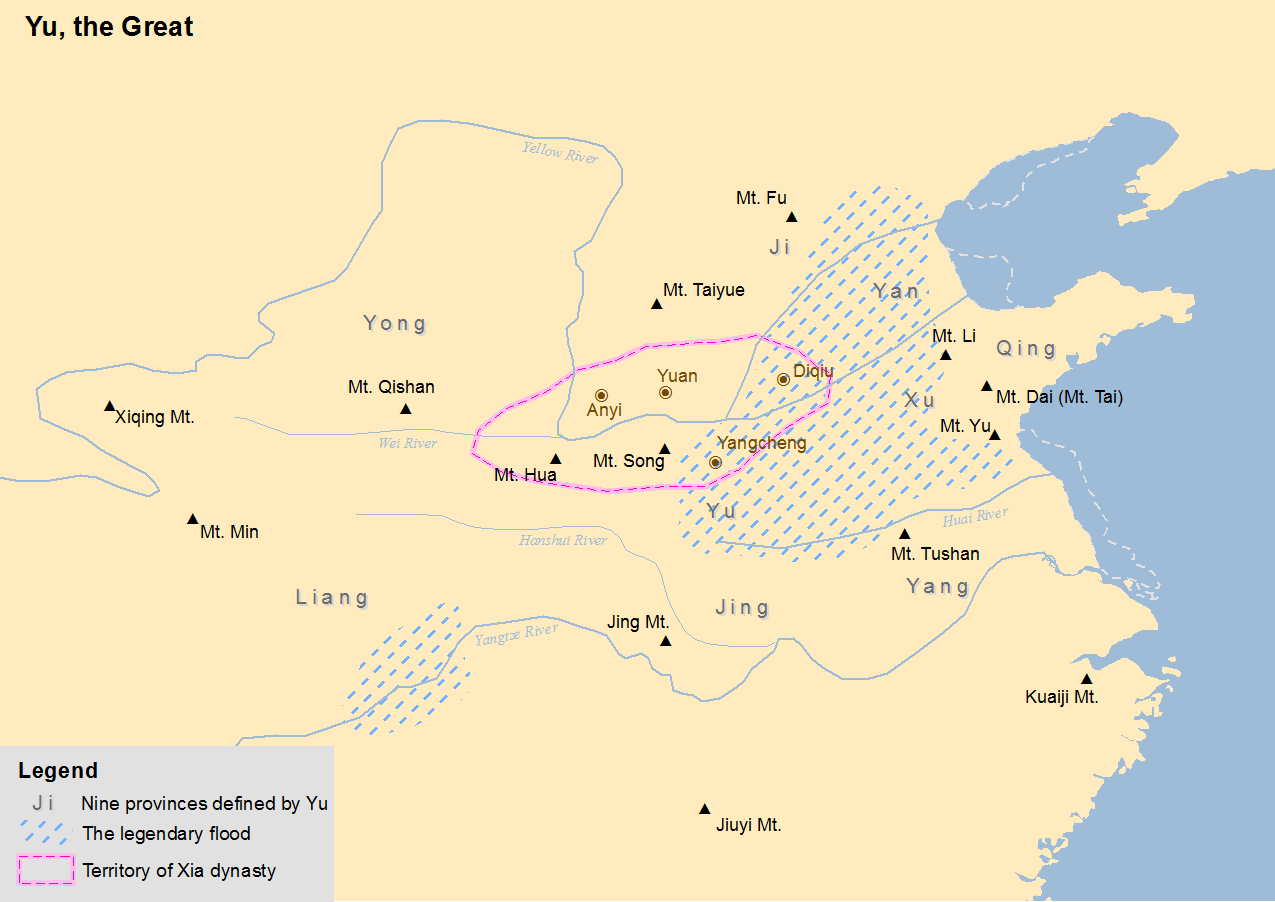
Xia Dynasty
The Xia dynasty () is the first dynasty in traditional Chinese historiography. According to tradition, the Xia dynasty was established by the legendary Yu the Great, after Shun, the last of the Five Emperors, gave the throne to him. In traditional historiography, the Xia was later succeeded by the Shang dynasty. There are no contemporaneous records of the Xia, who are not mentioned in the oldest Chinese texts, since the earliest oracle bone inscriptions date from the late Shang period (13th century BC). The earliest mentions occur in the oldest chapters of the '' Book of Documents'', which report speeches from the early Western Zhou period and are accepted by most scholars as dating from that time. The speeches justify the Zhou conquest of the Shang as the passing of the Mandate of Heaven and liken it to the succession of the Xia by the Shang. That political philosophy was promoted by the Confucian school in the Eastern Zhou period. The succession of dynasties was incorporat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mang Of Xia
Máng (芒, read Wáng according to Sima Zhen) was the ninth king of the semi-legendary Xia Dynasty. He possibly ruled 18 years. He was also known as Huang (荒). Emperor Si Mang established a Sinking Sacrifice Ceremony (沉祭 Chen Ji) in which three common livestock animals (a cow, a pig & a sheep) & a memorial jade were sunk into the Yellow River as offerings to water spirits for peace & safety. Sinking sacrifices have since found widespread importance throughout Chinese history. Family Máng's father was king Huai of Xia, son of the king Zhu of Xia. Mother of Máng was an unknown lady, consort of Huai. He had a consort who bore him a son Xie. Máng's grandsons were Jiong of Xia and wise Bu Jiang. Biography Máng took the throne after his father's death, in the year of ''Renshen'' (壬申). He celebrated his inauguration by giving precious jades to all his vassals. In the 33rd year of his regime, the Shang vassal Zihai (''子亥'') moved his capital from Shangqiu (商� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Calendar
The traditional Chinese calendar (also known as the Agricultural Calendar ��曆; 农历; ''Nónglì''; 'farming calendar' Former Calendar ��曆; 旧历; ''Jiùlì'' Traditional Calendar ��曆; 老历; ''Lǎolì'', is a lunisolar calendar which identifies years, months, and days according to astronomical phenomena. In China, it is defined by the Chinese national standard GB/T 33661–2017, "Calculation and Promulgation of the Chinese Calendar", issued by the Standardization Administration of China on May 12, 2017. Although modern-day China uses the Gregorian calendar, the traditional Chinese calendar governs holidays, such as the Chinese New Year and Lantern Festival, in both China and overseas Chinese communities. It also provides the traditional Chinese nomenclature of dates within a year which people use to select auspicious days for weddings, funerals, moving or starting a business. The evening state-run news program ''Xinwen Lianbo'' in the P.R.C. continues to anno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xia Dynasty
The Xia dynasty () is the first dynasty in traditional Chinese historiography. According to tradition, the Xia dynasty was established by the legendary Yu the Great, after Shun, the last of the Five Emperors, gave the throne to him. In traditional historiography, the Xia was later succeeded by the Shang dynasty. There are no contemporaneous records of the Xia, who are not mentioned in the oldest Chinese texts, since the earliest oracle bone inscriptions date from the late Shang period (13th century BC). The earliest mentions occur in the oldest chapters of the '' Book of Documents'', which report speeches from the early Western Zhou period and are accepted by most scholars as dating from that time. The speeches justify the Zhou conquest of the Shang as the passing of the Mandate of Heaven and liken it to the succession of the Xia by the Shang. That political philosophy was promoted by the Confucian school in the Eastern Zhou period. The succession of dynasties was incorporat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bu Jiang
Bu Jiang (不降) was the eleventh king of the semi-legendary Xia Dynasty. He ruled for 59 years. Family Bu Jiang was a son of Xie of Xia and his consort and thus a grandson of Mang of Xia and brother of Jiong of Xia. His consort is unknown, and it is possible that he had concubines. His son was Kong Jia and his nephew was Jin of Xia. Biography Bu Jiang is widely regarded as one of the wisest Emperors of Xia. According to ''Bamboo Annals'', on the 6th year of his regime, he fought with Jiuyuan(九苑) . In the 35th year of his reign, his vassal state of Shang The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Chinese royal dynasty founded by Tang of Shang (Cheng Tang) that ruled in the Yellow River valley in the second millennium BC, traditionally succeeding the Xia dynasty and f ... defeated Pi (皮氏). In the 59th year of his regime he passed his throne to his younger brother Jiong. 10 years later, Bu Jiang died. Sources {{DEFAULTS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Mythology
Chinese mythology () is mythology that has been passed down in oral form or recorded in literature in the geographic area now known as Greater China. Chinese mythology includes many varied myths from regional and cultural traditions. Much of the mythology involves exciting stories full of fantastic people and beings, the use of magical powers, often taking place in an exotic mythological place or time. Like many mythologies, Chinese mythology has in the past been believed to be, at least in part, a factual recording of history. Along with Chinese folklore, Chinese mythology forms an important part of Chinese folk religion. Many stories regarding characters and events of the distant past have a double tradition: ones which present a more historicized or euhemerized version and ones which present a more mythological version. Many myths involve the creation and cosmology of the universe and its deities and inhabitants. Some mythology involves creation myths, the origin of things, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bamboo Annals
The ''Bamboo Annals'' (), also known as the ''Ji Tomb Annals'' (), is a chronicle of ancient China. It begins in the earliest legendary time (the age of the Yellow Emperor) and extends to 299 BC, with the later centuries focusing on the history of the State of Wei in the Warring States period. It thus covers a similar period to Sima Qian's ''Records of the Grand Historian'' (91 BC). The original may have been lost during the Song dynasty, and the text is known today in two versions, a "current text" (or "modern text") of disputed authenticity and an incomplete "ancient text". Textual history The original text was interred with King Xiang of Wei (died 296 BC) and re-discovered nearly six centuries later in 281 AD (Western Jin dynasty) in the Jizhong discovery. For this reason, the chronicle survived the burning of the books by Emperor Qin Shi Huang. Other texts recovered from the same tomb included '' Guoyu'', '' I Ching'', and the '' Tale of King Mu''. They were written on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiong Of Xia
Jiong () was the twelfth king of the semi-legendary Xia Dynasty. Family Jiōng was a son of Xie of Xia and his spouse and thus a grandson of Máng and brother of Bu Jiang. His own consort is unknown. His son was Jǐn and his nephew was Kong Jia. Biography According to the '' Bamboo Annals'',James Legge (1865)''The Chinese Classics, Volume 3, part 1''./ref> Jiōng ruled about 18 years, while according to the ''Records of the Grand Historian'', he ruled about 21 years. He acceded to the throne A throne is the seat of state of a potentate or dignitary, especially the seat occupied by a sovereign on state occasions; or the seat occupied by a pope or bishop on ceremonial occasions. "Throne" in an abstract sense can also refer to the mona ... in the Wuxu (戊戌) year. In the 10th year of Jiōng's reign, Bu Jiang died. Sources {{DEFAULTSORT:Xia, Jiong Of Xia dynasty kings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sima Qian
Sima Qian (; ; ) was a Chinese historian of the early Han dynasty (206AD220). He is considered the father of Chinese historiography for his ''Records of the Grand Historian'', a general history of China covering more than two thousand years beginning from the rise of the legendary Yellow Emperor and the formation of the first Chinese polity to the reigning sovereign of Sima Qian's time, Emperor Wu of Han. As the first universal history of the world as it was known to the ancient Chinese, the ''Records of the Grand Historian'' served as a model for official history-writing for subsequent Chinese dynasties and the Chinese cultural sphere (Korea, Vietnam, Japan) up until the 20th century. Sima Qian's father Sima Tan first conceived of the ambitious project of writing a complete history of China, but had completed only some preparatory sketches at the time of his death. After inheriting his father's position as court historian in the imperial court, he was determined to fulfill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Records Of The Grand Historian
''Records of the Grand Historian'', also known by its Chinese name ''Shiji'', is a monumental history of China that is the first of China's 24 dynastic histories. The ''Records'' was written in the early 1st century by the ancient Chinese historian Sima Qian, whose father Sima Tan had begun it several decades earlier. The work covers a 2,500-year period from the age of the legendary Yellow Emperor to the reign of Emperor Wu of Han in the author's own time, and describes the world as it was known to the Chinese of the Western Han dynasty. The ''Records'' has been called a "foundational text in Chinese civilization". After Confucius and the First Emperor of Qin, "Sima Qian was one of the creators of Imperial China, not least because by providing definitive biographies, he virtually created the two earlier figures." The ''Records'' set the model for all subsequent dynastic histories of China. In contrast to Western historical works, the ''Records'' do not treat history as "a cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watson, Burton
Burton Dewitt Watson (June 13, 1925April 1, 2017) was an American sinologist, translator, and writer known for his English translations of Chinese and Japanese literature.Stirling 2006, pg. 92 Watson's translations received many awards, including the Gold Medal Award of the Translation Center at Columbia University in 1979, the PEN Translation Prize in 1982 for his translation with Hiroaki Sato of ''From the Country of Eight Islands: An Anthology of Japanese Poetry'', and again in 1995 for ''Selected Poems of Su Tung-p'o''. In 2015, at age 88, Watson was awarded the PEN/Ralph Manheim Medal for Translation for his long and prolific translation career. Life and career Burton Watson was born on June 13, 1925, in New Rochelle, New York, where his father was a hotel manager. In 1943, at age 17, Watson dropped out of high school to join the U.S. Navy, and was stationed on repair vessels in the South Pacific during the final years of the Pacific Theatre of World War II. His ship was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |