|
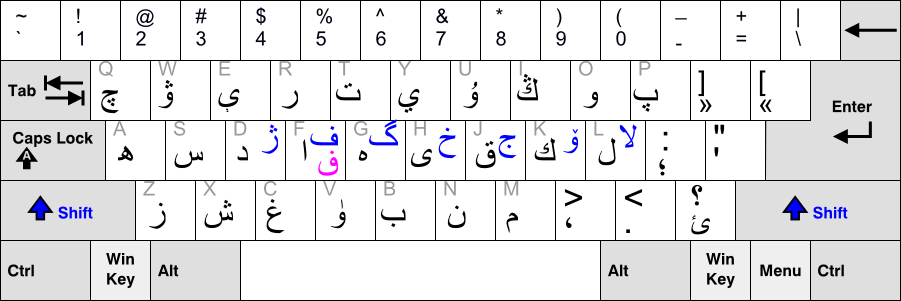
Xiaoerjing
Xiao'erjing or Xiao'erjin or Xiaor jin or in its shortened form, Xiaojing, literally meaning "children's script" or "minor script" (cf. "original script" referring to the original Persian alphabet, Perso-Arabic script; zh, s=本经, t=本經, p=Běnjīng, Xiao'erjing: , dng, Бынҗин, ), is the practice of writing Sinitic languages such as Mandarin Chinese, Mandarin (especially the Lanyin Mandarin, Lanyin, Zhongyuan Mandarin, Zhongyuan and Northeastern Mandarin, Northeastern dialects) or the Dungan language in the Arabic script, Perso-Arabic script. It is used on occasion by many Ethnic minorities in China, ethnic minorities who adhere to the Islam in China, Islamic faith in China (mostly the Hui people, Hui, but also the Dongxiangs, Dongxiang and the Salar people, Salar) and formerly by their Dungan people, Dungan descendants in Central Asia. Orthography reforms introduced the Latin script and later the Cyrillic script to the Dungan language, which continue to be used tod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam In China
Islam has been practiced in China since the 7th century CE.. Muslims are a minority group in China, representing 1.6-2 percent of the total population (21,667,000- 28,210,795) according to various estimates. Though Hui people, Hui Muslims are the most numerous group, the greatest concentration of Muslims are in Xinjiang, which contains a significant Uyghurs, Uyghur population. Lesser yet significant populations reside in the regions of Ningxia, Gansu and Qinghai. Of Ethnic minorities in China, China's 55 officially recognized minority peoples, ten of these groups are predominantly Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslim. History The Silk Road, which was a series of extensive inland trade routes that spread all over the Mediterranean to East Asia, was used since 1000 BCE and continued to be used for millennia. For more than half of this long period of time, most of the traders were Muslim and moved towards the East. Not only did these traders bring their goods, they also carried with them thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Language
Chinese (, especially when referring to written Chinese) is a group of languages spoken natively by the ethnic Han Chinese majority and many minority ethnic groups in Greater China. About 1.3 billion people (or approximately 16% of the world's population) speak a variety of Chinese as their first language. Chinese languages form the Sinitic branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages family. The spoken varieties of Chinese are usually considered by native speakers to be variants of a single language. However, their lack of mutual intelligibility means they are sometimes considered separate languages in a family. Investigation of the historical relationships among the varieties of Chinese is ongoing. Currently, most classifications posit 7 to 13 main regional groups based on phonetic developments from Middle Chinese, of which the most spoken by far is Mandarin (with about 800 million speakers, or 66%), followed by Min (75 million, e.g. Southern Min), Wu (74 million, e.g. Shangh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dungan People
Dungan, Xiao'erjing: ; zh, s=东干族, t=東干族, p=Dōnggān zú, w=Tung1kan1-tsu2, , Xiao'erjing: ; russian: Дунгане, ''Dungane''; ky, Дуңгандар, ''Duñgandar'', دۇنغاندار; kk, Дүңгендер, ''Düñgender'', دٷڭگەندەر is a term used in territories of the former Soviet Union to refer to a group of Muslim people of Hui origin. Turkic-speaking peoples in Xinjiang Province in Northwestern China also sometimes refer to Hui Muslims as Dungans. In both China and the former Soviet republics where they reside, however, members of this ethnic group call themselves Hui because Dungans are descendants of historical Hui groups that migrated to Central Asia. In the censuses of the countries of the former Soviet Union, the Dungans (enumerated separately from Chinese) are found in Kazakhstan (36,900 according to the 1999 census), Kyrgyzstan (58,409 according to the 2009 census) and Russia (801 according to the 2002 census). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beijing
} Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 million residents. It has an administrative area of , the third in the country after Guangzhou and Shanghai. It is located in Northern China, and is governed as a municipality under the direct administration of the State Council with 16 urban, suburban, and rural districts.Figures based on 2006 statistics published in 2007 National Statistical Yearbook of China and available online at archive. Retrieved 21 April 2009. Beijing is mostly surrounded by Hebei Province with the exception of neighboring Tianjin to the southeast; together, the three divisions form the Jingjinji megalopolis and the national capital region of China. Beijing is a global city and one of the world's leading centres for culture, diplomacy, politics, finance, busi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaanxi
Shaanxi (alternatively Shensi, see #Name, § Name) is a landlocked Provinces of China, province of China. Officially part of Northwest China, it borders the province-level divisions of Shanxi (NE, E), Henan (E), Hubei (SE), Chongqing (S), Sichuan (SW), Gansu (W), Ningxia (NW) and Inner Mongolia (N). Shaanxi covers an area of over with about 37 million people, the 16th highest in China. Xi'an – which includes the sites of the former Capitals of China, Chinese capitals Fenghao and Chang'an – is the Xi'an, provincial capital as well as the largest city in Northwest China and also one of the oldest cities in China and the oldest of the Historical capitals of China, Four Great Ancient Capitals, being the capital for the Western Zhou, Western Han, Sima Jin, Jin, Sui dynasty, Sui and Tang dynasty, Tang List of Chinese dynasties, dynasties. Xianyang, which served as the Qin dynasty capital, is just north across Wei River. The other Prefectures of China, prefecture-level pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shandong
Shandong ( , ; ; alternately romanized as Shantung) is a coastal province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the East China region. Shandong has played a major role in Chinese history since the beginning of Chinese civilization along the lower reaches of the Yellow River. It has served as a pivotal cultural and religious center for Taoism, Chinese Buddhism and Confucianism. Shandong's Mount Tai is the most revered mountain of Taoism and a site with one of the longest histories of continuous religious worship in the world. The Buddhist temples in the mountains to the south of the provincial capital of Jinan were once among the foremost Buddhist sites in China. The city of Qufu is the birthplace of Confucius and was later established as the center of Confucianism. Confucianism developed from what was later called the Hundred Schools of Thought from the teachings of the Chinese philosopher Confucius. Shandong's location at the intersection of ancient and modern n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henan
Henan (; or ; ; alternatively Honan) is a landlocked province of China, in the central part of the country. Henan is often referred to as Zhongyuan or Zhongzhou (), which literally means "central plain" or "midland", although the name is also applied to the entirety of China proper. Henan is a birthplace of Han Chinese civilization, with over 3,200 years of recorded history and remained China's cultural, economic and political center until approximately 1,000 years ago. Henan Province is home to many heritage sites, including the ruins of Shang dynasty capital city Yin and the Shaolin Temple. Four of the Eight Great Ancient Capitals of China, Luoyang, Anyang, Kaifeng and Zhengzhou, are in Henan. The practice of tai chi also began here in Chen Jia Gou Village (Chen style), as did the later Yang and Wu styles. Although the name of the province () means "south of the ellowriver.", approximately a quarter of the province lies north of the Yellow River, also known as the Hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebei
Hebei or , (; alternately Hopeh) is a northern province of China. Hebei is China's sixth most populous province, with over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. The province is 96% Han Chinese, 3% Manchu, 0.8% Hui, and 0.3% Mongol. Three Mandarin dialects are spoken: Jilu Mandarin, Beijing Mandarin and Jin. Hebei borders the provinces of Shanxi to the west, Henan to the south, Shandong to the southeast, Liaoning to the northeast, and the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region to the north. Its economy is based on agriculture and manufacturing. The province is China's premier steel producer, although the steel industry creates serious air pollution. Five UNESCO World Heritage Sites can be found in the province, the: Great Wall of China, Chengde Mountain Resort, Grand Canal, Eastern Qing tombs, and Western Qing tombs. It is also home to five National Famous Historical and Cultural Cities: Handan, Baoding, Chengde, Zhengding and Shanhaiguan. Historic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shanxi
Shanxi (; ; formerly romanised as Shansi) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the North China region. The capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-level cities are Changzhi and Datong. Its one-character abbreviation is "" (), after the state of Jin that existed there during the Spring and Autumn period. The name ''Shanxi'' means "West of the Mountains", a reference to the province's location west of the Taihang Mountains. Shanxi borders Hebei to the east, Henan to the south, Shaanxi to the west and Inner Mongolia to the north. Shanxi's terrain is characterised by a plateau bounded partly by mountain ranges. Shanxi's culture is largely dominated by the ethnic Han majority, who make up over 99% of its population. Jin Chinese is considered by some linguists to be a distinct language from Mandarin and its geographical range covers most of Shanxi. Both Jin and Mandarin are spoken in Shanx ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uyghur Arabic Alphabet
The Uyghur Arabic alphabet ( ug, ئۇيغۇر ئەرەب يېزىقى, translit=Uyghur Ereb Yëziqi UEY) is a version of the Arabic alphabet used for writing the Uyghur language, primarily by Uyghurs living in China. It is one of several Uyghur alphabets and has been the official alphabet of the Uyghur language since 1982. The first Perso-Arabic derived alphabet for Uyghur was developed in the 10th century, when Islam was introduced there. The version used for writing the Chagatai language. It became the regional literary language, now known as the Chagatay alphabet. It was used nearly exclusively up to the early 1920s. Alternative Uyghur scripts then began emerging and collectively largely displaced Chagatai; ''Kona Yëziq'', meaning 'old script', now distinguishes it and UEY from the alternatives that are ''not'' derived from Arabic. Between 1937 and 1954, the Perso-Arabic alphabet used to write Uyghur was modified by removing redundant letters and adding markings for vowels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abjad
An abjad (, ar, أبجد; also abgad) is a writing system in which only consonants are represented, leaving vowel sounds to be inferred by the reader. This contrasts with other alphabets, which provide graphemes for both consonants and vowels. The term was introduced in 1990 by Peter T. Daniels. Other terms for the same concept include: partial phonemic script, segmentally linear defective phonographic script, consonantary, consonant writing, and consonantal alphabet.Amalia E. Gnanadesikan (2017) Towards a typology of phonemic scripts, Writing Systems Research, 9:1, 14-35, DOI: 10.1080/17586801.2017.1308239 "Daniels (1990, 1996a) proposes the name abjad for these scripts, and this term has gained considerable popularity. Other terms include partial phonemic script (Hill, 1967), segmentally linear defective phonographic script (Faber, 1992), consonantary (Trigger, 2004), consonant writing (Coulmas, 1989) and consonantal alphabet (Gnanadesikan, 2009; Healey, 1990). " Impure abja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphabet
An alphabet is a standardized set of basic written graphemes (called letters) that represent the phonemes of certain spoken languages. Not all writing systems represent language in this way; in a syllabary, each character represents a syllable, and logographic systems use characters to represent words, morphemes, or other semantic units. The first fully phonemic script, the Proto-Sinaitic script, later known as the Phoenician alphabet, is considered to be the first alphabet and is the ancestor of most modern alphabets, including Arabic, Cyrillic, Greek, Hebrew, Latin, and possibly Brahmic. It was created by Semitic-speaking workers and slaves in the Sinai Peninsula (as the Proto-Sinaitic script), by selecting a small number of hieroglyphs commonly seen in their Egyptian surroundings to describe the sounds, as opposed to the semantic values of the Canaanite languages. However, Peter T. Daniels distinguishes an abugida, a set of graphemes that represent consonantal base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |