|
X-Ray Imaging And Spectroscopy Mission
The X-Ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission (XRISM, pronounced "crism"), formerly the X-ray Astronomy Recovery Mission (XARM), is an X-ray astronomy satellite of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) to provide breakthroughs in the study of structure formation of the universe, outflows from galaxy nuclei, and dark matter. As the only international X-ray observatory project of its period, ''XRISM'' will function as a next generation space telescope in the X-ray astronomy field, similar to how the James Webb Space Telescope, Fermi Space Telescope, and the Atacama Large Millimeter Array (ALMA) Observatory are placed in their respective fields. The mission is a stopgap for avoiding a potential observation period gap between X-ray telescopes of the present (Chandra, XMM-Newton) and those of the future (Advanced Telescope for High Energy Astrophysics (ATHENA), Lynx X-ray Observatory). Without XRISM, a blank period in X-ray astronomy may arise in the early 2020s due to the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atacama Large Millimeter Array
The Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) is an astronomical interferometer of 66 radio telescopes in the Atacama Desert of northern Chile, which observe electromagnetic radiation at millimeter and submillimeter wavelengths. The array has been constructed on the elevation Chajnantor plateau - near the Llano de Chajnantor Observatory and the Atacama Pathfinder Experiment. This location was chosen for its high elevation and low humidity, factors which are crucial to reduce noise and decrease signal attenuation due to Earth's atmosphere. ALMA provides insight on star birth during the early Stelliferous era and detailed imaging of local star and planet formation. ALMA is an international partnership amongst Europe, the United States, Canada, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, and Chile. Costing about US$1.4 billion, it is the most expensive ground-based telescope in operation. ALMA began scientific observations in the second half of 2011 and the first images were relea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charge-coupled Device
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a major technology used in digital imaging. In a CCD image sensor, pixels are represented by p-doped metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) capacitors. These MOS capacitors, the basic building blocks of a CCD, are biased above the threshold for inversion when image acquisition begins, allowing the conversion of incoming photons into electron charges at the semiconductor-oxide interface; the CCD is then used to read out these charges. Although CCDs are not the only technology to allow for light detection, CCD image sensors are widely used in professional, medical, and scientific applications where high-quality image data are required. In applications with less exacting quality demands, such as consumer and professional digital cameras, act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryogenic Particle Detector
Cryogenic particle detectors operate at very low temperature, typically only a few degrees above absolute zero. These sensors interact with an energetic elementary particle (such as a photon) and deliver a signal that can be related to the type of particle and the nature of the interaction. While many types of particle detectors might be operated with improved performance at cryogenic temperatures, this term generally refers to types that take advantage of special effects or properties occurring only at low temperature. Introduction The most commonly cited reason for operating any sensor at low temperature is the reduction in thermal noise, which is proportional to the square root of the absolute temperature. However, at very low temperature, certain material properties become very sensitive to energy deposited by particles in their passage through the sensor, and the gain from these changes may be even more than that from reduction in thermal noise. Two such commonly used propertie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NuSTAR
NuSTAR (Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array, also named Explorer 93 and SMEX-11) is a NASA space-based X-ray telescope that uses a conical approximation to a Wolter telescope to focus high energy X-rays from astrophysical sources, especially for nuclear spectroscopy, and operates in the range of 3 to 79 keV. NuSTAR is the eleventh mission of NASA's Small Explorer (SMEX-11) satellite program and the first space-based direct-imaging X-ray telescope at energies beyond those of the Chandra X-ray Observatory and XMM-Newton. It was successfully launched on 13 June 2012, having previously been delayed from 21 March 2012 due to software issues with the launch vehicle. The mission's primary scientific goals are to conduct a deep survey for black holes a billion times more massive than the Sun, to investigate how particles are accelerated to very high energy in active galaxies, and to understand how the elements are created in the explosions of massive stars by imaging supernova ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goddard Space Flight Center
The Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) is a major NASA space research laboratory located approximately northeast of Washington, D.C. in Greenbelt, Maryland, United States. Established on May 1, 1959 as NASA's first space flight center, GSFC employs approximately 10,000 civil servants and contractors. It is one of ten major NASA field centers, named in recognition of American rocket propulsion pioneer Robert H. Goddard. GSFC is partially within the former Goddard census-designated place; it has a Greenbelt mailing address.CENSUS 2000 BLOCK MAP: GODDARD CDP " . Retrieved on September 1, 2018. 1990 Census map of Prince ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute Of Space And Astronautical Science
(ISAS) is a Japanese national research organization of astrophysics using rockets, astronomical satellites and interplanetary probes which played a major role in Japan's space development. Since 2003, it is a division of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). History The ISAS originated as part of the Institute of Industrial Science of the University of Tokyo, where Hideo Itokawa experimented with miniature solid-fuel rockets ( Pencil Rocket and Baby Rocket) in the 1950s. This experimentation eventually led to the development of the Κ (''Kappa'') sounding rocket, which was used for observations during the International Geophysical Year (IGY). By 1960, the Κ-8 rocket had reached an altitude of 200 km. In 1964, the rocket group and the ''Institute of Aeronautics'', along with scientific ballooning team, were merged to form within the University of Tokyo. The rocket evolved into the L (''Lambda'') series, and, in 1970, L-4S-5 was launched as Japan's firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Space Agency
, owners = , headquarters = Paris, Île-de-France, France , coordinates = , spaceport = Guiana Space Centre , seal = File:ESA emblem seal.png , seal_size = 130px , image = Views in the Main Control Room (12052189474).jpg , size = , caption = , acronym = , established = , employees = 2,200 , administrator = Director General Josef Aschbacher , budget = €7.2 billion (2022) , language = English and French (working languages) , website = , logo = European Space Agency logo.svg , logo_caption = Logo , image_caption = European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) Main Control Room The European Space Agency (ESA; french: Agence spatiale européenne , it, Agenzia Spaziale Europea, es, Agencia Espacial Europea ASE; german: Europäische Weltraumorganisation) is an intergovernmental organisation of 22 member states dedicated to the exploration of space. Established in 1975 and headquartered i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirty Meter Telescope
The Thirty Meter Telescope (TMT) is a planned extremely large telescope (ELT) that has become controversial due to its location on Mauna Kea, on the island of Hawaiʻi. The TMT would become the largest visible-light telescope on Mauna Kea. Scientists have been considering ELTs since the mid 1980s. In 2000, astronomers considered the possibility of a telescope with a light-gathering mirror larger than 20 meters (65') in diameter. The technology to build a mirror larger than 8.4 meters (28') does not exist; instead scientists considered using either small segments that create one large mirror, or a grouping of larger 8-meter (26') mirrors working as one unit. The US National Academy of Sciences recommended a 30-meter (100') telescope be the focus of U.S. interests, seeking to see it built within the decade. Scientists at the University of California and Caltech began development of a design that would eventually become the TMT, consisting of a 492-segment primary mirror with n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suzaku (satellite)
''Suzaku'' (formerly ASTRO-EII) was an X-ray astronomy satellite developed jointly by the Institute of Space and Aeronautical Science at JAXA and NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center to probe high energy X-ray sources, such as Supernova, supernova explosions, black holes and Open cluster, galactic clusters. It was launched on 10 July 2005 aboard the M-V launch vehicle on the M-V-6 mission. After its successful launch, the satellite was renamed ''Suzaku'' after the mythical Vermilion Bird, Vermilion bird of the South. Just weeks after launch, on 29 July 2005, the first of a series of cooling system malfunctions occurred. These ultimately caused the entire reservoir of liquid helium to boil off into space by 8 August 2005. This effectively shut down the X-ray spectroscopy, X-ray Spectrometer-2 (XRS-2), which was the spacecraft's primary instrument. The two other instruments, the X-ray Imaging Spectrometer (XIS) and the Hard X-ray Detector (HXD), were unaffected by the malfunction. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astro-H Schema (en)
, also known as ASTRO-H and New X-ray Telescope (NeXT), was an X-ray astronomy satellite commissioned by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) for studying extremely energetic processes in the Universe. The space observatory was designed to extend the research conducted by the Advanced Satellite for Cosmology and Astrophysics (ASCA) by investigating the hard X-ray band above 10 keV. The satellite was originally called New X-ray Telescope; at the time of launch it was called ASTRO-H. After it was placed in orbit and its solar panels deployed, it was renamed ''Hitomi''. The spacecraft was launched on 17 February 2016 and contact was lost on 26 March 2016, due to multiple incidents with the attitude control system leading to an uncontrolled spin rate and breakup of structurally weak elements. Name The new name refers to the pupil of an eye, and to a legend of a painting of four dragons. The word Hitomi generally means "eye", and specifically the pupil, or entrance wind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
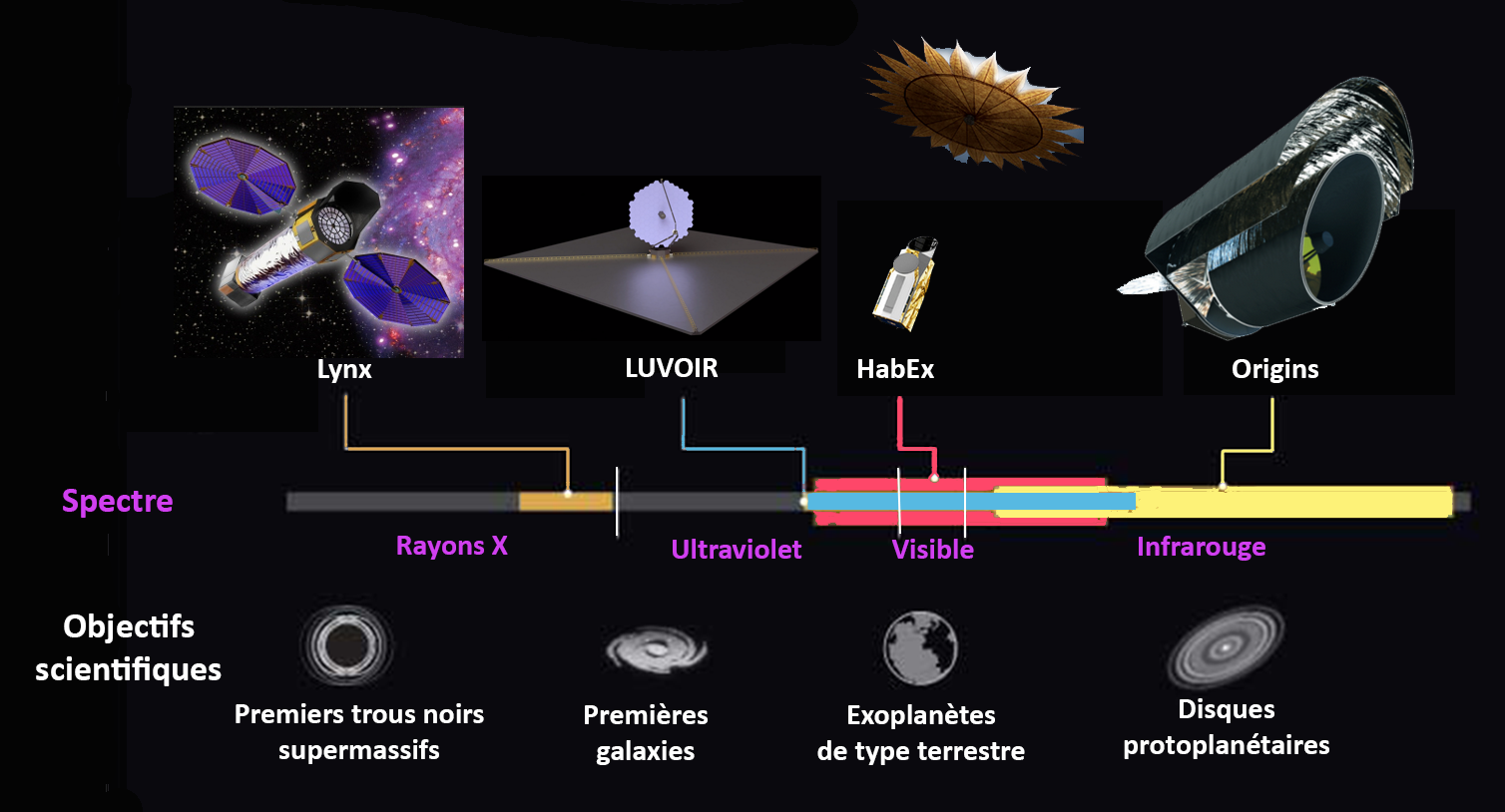
Lynx X-ray Observatory
The Lynx X-ray Observatory (''Lynx'') is a NASA-funded Large Mission Concept Study commissioned as part of the National Academy of Sciences 2020 Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey. The concept study phase is complete as of August 2019, and the ''Lynx'' final report has been submitted to the Decadal Survey for prioritization. If launched, ''Lynx'' would be the most powerful X-ray astronomy observatory constructed to date, enabling order-of-magnitude advances in capability over the current Chandra X-ray Observatory and XMM-Newton space telescopes. Background In 2016, following recommendations laid out in the so-called Astrophysics Roadmap of 2013, NASA established four space telescope concept studies for future Large strategic science missions. In addition to ''Lynx'' (originally called X-ray Surveyor in thRoadmap document'','' they are the Habitable Exoplanet Imaging Mission (HabEx), the Large Ultraviolet Optical Infrared Surveyor (LUVOIR), and the Origins Space Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)
.jpg)