|
Wyoming Basin Physiographic Province
The Wyoming Basin physiographic province is a geographic area through which the Continental Divide of the Americas traverses. The province includes the Washakie BasinGreat Basin Divide and Great Divide Basins, and is demarcated by the following: *southwest: Uinta Mountains *west: west side of Green River watershed See also * W ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Divide Basin
The Great Divide Basin or Great Divide Closed Basin is an area of land in the Red Desert of Wyoming where none of the water falling as rain to the ground drains into any ocean, directly or indirectly. It is thus an endorheic basin, one of several in the United States that adjoin the Continental Divide. To the south and west of the basin is the Green River watershed, draining to the Gulf of California/Pacific Ocean; to the north and east is the North Platte watershed, draining to the Gulf of Mexico/Atlantic Ocean. The basin is very roughly rectangular in shape; the northwest corner is at Oregon Buttes near South Pass, about southwest of Lander, and the southeast corner is in the Sierra Madre Range near Bridger Pass, about southwest of Rawlins.Great Basin DivideWashakie Basin) History Although the Great Divide Basin provides a relatively low and easy crossing of the Continental Divide, its aridity and endorheic nature were an obstacle to pioneers during the westward expans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
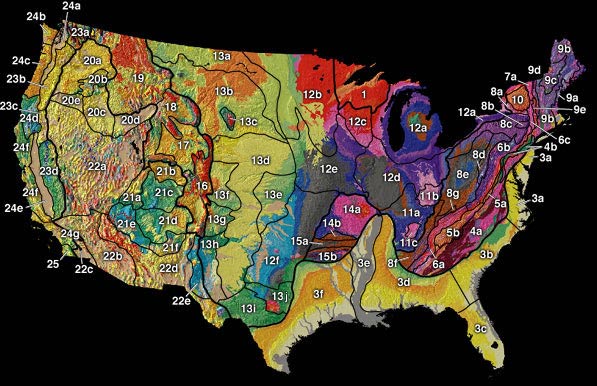
United States Physiographic Region
The physiographic regions of the contiguous United States The contiguous United States (officially the conterminous United States) consists of the 48 adjoining U.S. states and the Federal District of the United States of America. The term excludes the only two non-contiguous states, Alaska and Hawaii ... comprise 8 regions, 25 provinces, and 85 sections. The system dates to Nevin Fenneman's paper ''Physiographic Subdivision of the United States'', published in 1917. Fenneman expanded and presented his system more fully in two books, ''Physiography of western United States'' (1931), and ''Physiography of eastern United States'' (1938). In these works Fenneman described 25 provinces and 85 sections of the United States physiography. Physiographic divisions References {{DEFAULTSORT:United States Physiographic Region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Divide Of The Americas
The Continental Divide of the Americas (also known as the Great Divide, the Western Divide or simply the Continental Divide; ) is the principal, and largely mountainous, hydrological divide of the Americas. The Continental Divide extends from the Bering Strait to the Strait of Magellan, and separates the watersheds that drain into the Pacific Ocean from those river systems that drain into the Atlantic and (in northern North America) Arctic oceans (including those that drain into the Gulf of Mexico, the Caribbean Sea and Hudson Bay). Although there are many other hydrological divides in the Americas, the Continental Divide is by far the most prominent of these because it tends to follow a line of high peaks along the main ranges of the Rocky Mountains and Andes, at a generally much higher elevation than the other hydrological divisions. Geography Beginning at the westernmost point of the Americas’ mainland (Cape Prince of Wales, just south of the Arctic Circle), the Conti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washakie Basin
Washakie (1804/1810 – February 20, 1900) was a prominent leader of the Shoshone people during the mid-19th century. He was first mentioned in 1840 in the written record of the American fur trapper, Osborne Russell. In 1851, at the urging of trapper Jim Bridger, Washakie led a band of Shoshones to the council meetings of the Treaty of Fort Laramie (1851). Essentially from that time until his death, he was considered the head of the Eastern Shoshones by the representatives of the United States government. In 1979, he was inducted into the Hall of Great Westerners of the National Cowboy & Western Heritage Museum. Early life Much about Washakie's early life remains unknown, but some information is revealed. Washakie was born between 1798 and 1810. His mother Lost Woman, was a Tussawehee (White Knife) Shoshoni by birth. His father, Crooked Leg (Paseego), was an Umatilla rescued as a boy from slave traders at Wakemap and Celilo in 1786 by Weasel Lungs, a Tussawehee dog soldier ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uinta Mountains
The Uinta Mountains ( ) are an east-west trending chain of mountains in northeastern Utah extending slightly into southern Wyoming in the United States. As a subrange of the Rocky Mountains, they are unusual for being the highest range in the contiguous United States running east to west, and lie approximately east of Salt Lake City. The range has peaks ranging from , with the highest point being Kings Peak, also the highest point in Utah. The Mirror Lake Highway crosses the western half of the Uintas on its way to Wyoming. Etymology The name "Uinta" derives from the Ute word ''Yoov-we-teuh'', meaning "pine forest" or "pine tree". Geology The Uinta Mountains are Laramide uplifted metasedimentary rocks deposited in an intracratonic basin in southwest Laurentia during the time of the breakup of the supercontinent Rodinia. The marine and fluvial metasedimentary rocks in the core of the Uinta Mountains are of Neoproterozoic age (between about 700 million and 760 million years old ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green River (Colorado River)
The Green River, located in the western United States, is the chief tributary of the Colorado River. The watershed of the river, known as the Green River Basin, covers parts of the U.S. states of Wyoming, Utah, and Colorado. The Green River is long, beginning in the Wind River Mountains of Wyoming and flowing through Wyoming and Utah for most of its course, except for a short segment of in western Colorado. Much of the route traverses the arid Colorado Plateau, where the river has carved some of the most spectacular canyons in the United States. The Green is slightly smaller than Colorado when the two rivers merge but typically carries a larger load of silt. The average yearly mean flow of the river at Green River, Utah is per second. The status of the Green River as a tributary of the Colorado River came about mainly for political reasons. In earlier nomenclature, the Colorado River began at its confluence with the Green River. Above the confluence, Colorado was called the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wyoming Basin Shrub Steppe
The Wyoming Basin shrub steppe ecoregion, within the deserts and xeric shrublands biome, is a shrub steppe in the northwestern United States. Setting This Ecoregion is located almost entirely within the western and central portions of the US state of Wyoming, but does extend minimally into southeastern Idaho, south-central Montana, north-central Utah and northwestern Colorado. It is located within multiple high altitude intermontane basins largely surrounded by various subranges of the Rocky Mountains. These basins are in the rain shadow of the North American Cordillera and as such have an arid to semi-arid climate with long, very cold winters and short, hot summers. Flora The dominant vegetation of this ecoregion is sagebrush ('' Artemisia tridentata''), often associated with various '' Agropyron'' species or fescue grass. At its upper altitudinal limit, the shrub steppe grades into the bordering mountain ecoregions, namely the South Central Rockies forests, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physiographic Provinces
physiographic province is a geographic region with a characteristic geomorphology, and often specific subsurface rock type or structural elements. The continents are subdivided into various physiographic provinces, each having a specific character, relief, and environment which contributes to its distinctiveness. The physiographic provinces are then subdivided into smaller physiographic sections. Examples In eastern North America, the Atlantic Coastal Plain, Piedmont, Blue Ridge Mountains, Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians, and Appalachian Plateau are specific physiographic provinces. In the Western United States of western North America: the Basin and Range Province, Cascade Range, Colorado Plateau, Rio Grande rift, Great Basin, Central Valley (California), Peninsular Ranges, Los Angeles Basin, and Transverse Ranges are examples of physiographic provinces. See also * Physiographic provinces — index * Physiographic sections — index * Physiographic regions of the worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Carbon County, Wyoming
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. The first recorded use of the word γεωγραφία was as a title of a book by Greek scholar Eratosthenes (276–194 BC). Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concepts can be applied more broadly to other celestial bodies in the field of planetary science. One such concept, the first law of geography, proposed by Waldo Tobler, is "everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things." Geography has been called "the world discipline" and "the bridge between the human a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Fremont County, Wyoming
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. The first recorded use of the word γεωγραφία was as a title of a book by Greek scholar Eratosthenes (276–194 BC). Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concepts can be applied more broadly to other celestial bodies in the field of planetary science. One such concept, the first law of geography, proposed by Waldo Tobler, is "everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things." Geography has been called "the world discipline" and "the bridge between the human and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Sweetwater County, Wyoming
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. The first recorded use of the word γεωγραφία was as a title of a book by Greek scholar Eratosthenes (276–194 BC). Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concepts can be applied more broadly to other celestial bodies in the field of planetary science. One such concept, the first law of geography, proposed by Waldo Tobler, is "everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things." Geography has been called "the world discipline" and "the bridge between the human and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
