|
Wufengella
''Wufengella'' is a genus of extinct camenellan " tommotiid" that lived during the Early Cambrian ( Stage 3). Described in 2022, the only species ''Wufengella bengtsonii'' was discovered from the Maotianshan Shales of Chiungchussu (Qiongzhusi) Formation in Yunnan, China. The fossil indicates that the animal was an armoured worm that close to the common ancestry of the phyla Phonorida, Brachiozoa and Bryozoa, which are collectively grouped into a clade called Lophophorata. Discovery ''Wufengella'' is known from a single specimen. The fossil was discovered by Chinese palaeontologists Jin Guo and Peiyun Cong at the Yunnan University. An almost complete fossil, parts of the anterior end are missing. The location of the specimen, Chiungchussu Formation at Haikou, Kunming, Southwest China, is member of the Chengjian Lagerstätte that is established to belong to Cambrian Stage 3 (between 521 and 514 million year ago). The same fossil deposit had yielded worm-like lobopod ''Facive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wufengella Reconstruction
''Wufengella'' is a genus of extinct camenellan " tommotiid" that lived during the Early Cambrian ( Stage 3). Described in 2022, the only species ''Wufengella bengtsonii'' was discovered from the Maotianshan Shales of Chiungchussu (Qiongzhusi) Formation in Yunnan, China. The fossil indicates that the animal was an armoured worm that close to the common ancestry of the phyla Phonorida, Brachiozoa and Bryozoa, which are collectively grouped into a clade called Lophophorata. Discovery ''Wufengella'' is known from a single specimen. The fossil was discovered by Chinese palaeontologists Jin Guo and Peiyun Cong at the Yunnan University. An almost complete fossil, parts of the anterior end are missing. The location of the specimen, Chiungchussu Formation at Haikou, Kunming, Southwest China, is member of the Chengjian Lagerstätte that is established to belong to Cambrian Stage 3 (between 521 and 514 million year ago). The same fossil deposit had yielded worm-like lobopod '' Fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
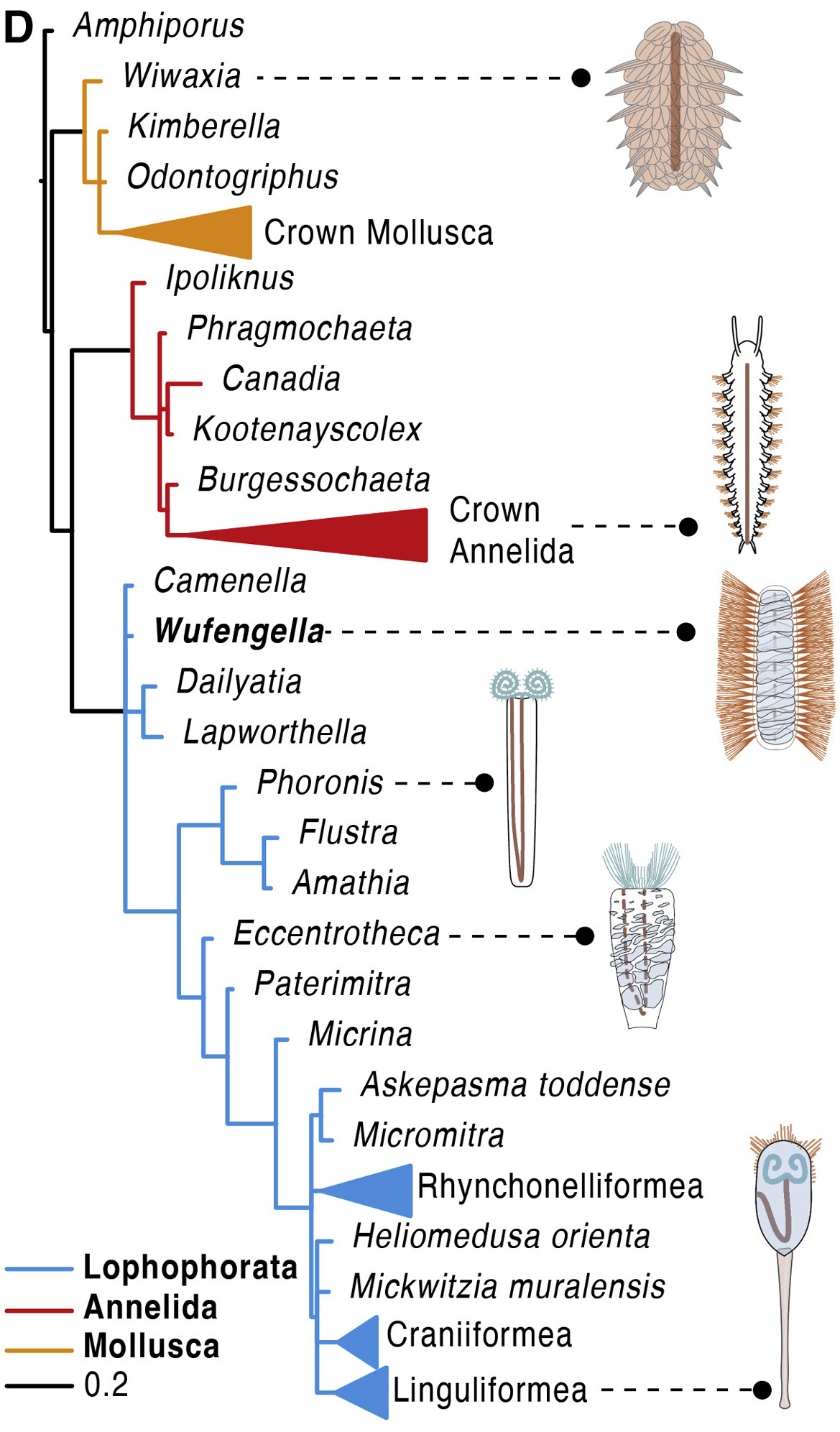
Wufengella Phlyogeny
''Wufengella'' is a genus of extinct camenellan " tommotiid" that lived during the Early Cambrian ( Stage 3). Described in 2022, the only species ''Wufengella bengtsonii'' was discovered from the Maotianshan Shales of Chiungchussu (Qiongzhusi) Formation in Yunnan, China. The fossil indicates that the animal was an armoured worm that close to the common ancestry of the phyla Phonorida, Brachiozoa and Bryozoa, which are collectively grouped into a clade called Lophophorata. Discovery ''Wufengella'' is known from a single specimen. The fossil was discovered by Chinese palaeontologists Jin Guo and Peiyun Cong at the Yunnan University. An almost complete fossil, parts of the anterior end are missing. The location of the specimen, Chiungchussu Formation at Haikou, Kunming, Southwest China, is member of the Chengjian Lagerstätte that is established to belong to Cambrian Stage 3 (between 521 and 514 million year ago). The same fossil deposit had yielded worm-like lobopod '' Fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camenellan
The camenellans, consisting of the genera ''Camenalla'', ''Dailyatia'', ''Kennardia'', ''Kelanella'', '' Wufengella'' and ''Lapworthella'', are a (probably monophyletic) group of Tommotiid invertebrates from the Cambrian The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ago ... period, reconstructed as sister to all others (plus brachiopods and phoronids). They are primarily known from isolated sclerites, but are believed to have a scleritomous, '' Halkieria''-like construction.Skovsted, C. B., Betts, M. J., Topper, T. P. & Brock, G. A. The early Cambrian tommotiid genus ''Dailyatia'' from South Australia. Mem. Assoc. Australas. Palaeontol. 48, 1–117 (2015).Murdock, D. J. E., Donoghue, P. C. J., Bengtson, S. & Marone, F. Ontogeny and micro-structure of the enigmatic Cambrian tommotii ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tommotiid
Tommotiids are an extinct group of Cambrian invertebrates thought to be early lophophorates (the group containing Bryozoa, Brachiopoda, and Phoronida). The majority of tommotiids are mineralised with calcium phosphate rather than calcium carbonate. although silicified examples hint that some species bore carbonate or carbonaceous sclerites. '' Micrina'' and '' Paterimitra'' possess bivalved shells in their larval phases, which preserve characters that might position them in the Linguliformea and Rhynchonelliformea stem lineages respectively. This would indicate that the brachiopod shell represents the retention of a larval character. For a long part of their history, the tommotiids were only known from disarticulated shells - a complete organism had not been found. The 2008 discovery of '' Eccentrotheca'' offered the first insight into a complete organism, and permitted a reconstruction of the animal as a sessile, tube-like animal made up of a spiral of overlapping plates. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annelid
The annelids (Annelida , from Latin ', "little ring"), also known as the segmented worms, are a large phylum, with over 22,000 extant species including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to various ecologies – some in marine environments as distinct as tidal zones and hydrothermal vents, others in fresh water, and yet others in moist terrestrial environments. The Annelids are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, coelomate, invertebrate organisms. They also have parapodia for locomotion. Most textbooks still use the traditional division into polychaetes (almost all marine), oligochaetes (which include earthworms) and leech-like species. Cladistic research since 1997 has radically changed this scheme, viewing leeches as a sub-group of oligochaetes and oligochaetes as a sub-group of polychaetes. In addition, the Pogonophora, Echiura and Sipuncula, previously regarded as separate phyla, are now regarded as sub-groups of polychae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lophophorata
The Lophophorata are a Lophotrochozoan clade consisting of the Brachiozoa and the Bryozoa. They have a lophophore. Molecular phylogenetic analyses suggest that lophophorates are protostomes, but on morphological grounds they have been assessed as deuterostome Deuterostomia (; in Greek) are animals typically characterized by their anus forming before their mouth during embryonic development. The group's sister clade is Protostomia, animals whose digestive tract development is more varied. Some ...s. Fossil finds of a segmented worm named Wufengella suggest that they evolved from a worm close to annelids. References {{Protostome-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambrian Invertebrates
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ago (mya) to the beginning of the Ordovician Period mya. Its subdivisions, and its base, are somewhat in flux. The period was established as "Cambrian series" by Adam Sedgwick, who named it after Cambria, the Latin name for 'Cymru' (Wales), where Britain's Cambrian rocks are best exposed. Sedgwick identified the layer as part of his task, along with Roderick Murchison, to subdivide the large "Transition Series", although the two geologists disagreed for a while on the appropriate categorization. The Cambrian is unique in its unusually high proportion of sedimentary deposits, sites of exceptional preservation where "soft" parts of organisms are preserved as well as their more resistant shells. As a result, our understanding of the Cambrian bio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Taxa Described In 2022
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the absol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crown Group
In phylogenetics, the crown group or crown assemblage is a collection of species composed of the living representatives of the collection, the most recent common ancestor of the collection, and all descendants of the most recent common ancestor. It is thus a way of defining a clade, a group consisting of a species and all its extant or extinct descendants. For example, Neornithes (birds) can be defined as a crown group, which includes the most recent common ancestor of all modern birds, and all of its extant or extinct descendants. The concept was developed by Willi Hennig, the formulator of phylogenetic systematics, as a way of classifying living organisms relative to their extinct relatives in his "Die Stammesgeschichte der Insekten", and the "crown" and "stem" group terminology was coined by R. P. S. Jefferies in 1979. Though formulated in the 1970s, the term was not commonly used until its reintroduction in 2000 by Graham Budd and Sören Jensen. Contents of the crown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lophophore
The lophophore () is a characteristic feeding organ possessed by four major groups of animals: the Brachiopoda, Bryozoa, Hyolitha, and Phoronida, which collectively constitute the protostome group Lophophorata.Introduction to the Lophotrochozoa – Retrieved 3 May 2010 All lophophores are found in aquatic organisms. Etymology ''Lophophore'' is derived from the Greek ''lophos'' (crest, tuft) and ''-phore'', ''-phoros'' (φορος) (bearing), a derivative of ''phérein'' (φέρειν) (to bear); thus crest-bearing.Characteristics The lophophore can most easily be described as a ring of ciliated tentacles surrounding the mouth, but it is often horseshoe-shaped or coiled. Phoronids have thei ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tannuolina
''Tannuolina'' is a genus of tommotiid, belonging to the brachiopod stem lineage. Its phosphatic shells exhibit a complex series of open pores/chambers/channels in outer shell layer.Kouchinsky, A., Bengtson, S. & Murdock, D. J. E. A new tannuolinid problematic from the lower Cambrian of the Sukharikha River in northern Siberia. Acta Pal. Pol. 55, 321–331 (2010). It is conventionally interpreted as an essentially bivalved organism, similar to ''Micrina'', though some use the unequal ratio of stellate to mitrate sclerites to argue for a halkieriid-like anatomy.Li, G.-X. & Xiao, S.-H. ''Tannuolina'' and ''Micrina'' (Tannuolinidae) from the Lower Cambrian of Eastern Yunnan, South China, and Their Scleritome Reconstruction. J. Paleontol. 78(5), 900–913 (2004). More recently a tube-like construction inspired by ''Eccentrotheca ''Eccentrotheca'' is a genus of "tommotiid" known from Cambrian deposits. Its sclerites form rings that are stacked to produce a widening-upwards ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |