|
Wu Xiuquan
Wu Xiuquan (; March 1908 – 9 November 1997) was a Chinese Communist revolutionary, military officer, and diplomat. He studied in the Soviet Union, enlisted in the Chinese Red Army, and participated in the Long March. After the founding of the People's Republic of China, he served as Vice Minister of Foreign Affairs, China's first ambassador to Yugoslavia, and Vice Minister of the International Liaison Department of the Communist Party of China. After being imprisoned for eight years during the Cultural Revolution, Wu was appointed Deputy Chief of the People's Liberation Army General Staff Department in 1975 and later served as vice president of the special court that tried and convicted the Gang of Four and the Lin Biao clique of numerous crimes during the Cultural Revolution. Early life and education Wu was born in March 1908 in Wuchang, Hubei, toward the end of the Qing dynasty, with his ancestral home in Yangxin County. While studying at Wuhan Middle School, he was acti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wu Xiuquan
Wu Xiuquan (; March 1908 – 9 November 1997) was a Chinese Communist revolutionary, military officer, and diplomat. He studied in the Soviet Union, enlisted in the Chinese Red Army, and participated in the Long March. After the founding of the People's Republic of China, he served as Vice Minister of Foreign Affairs, China's first ambassador to Yugoslavia, and Vice Minister of the International Liaison Department of the Communist Party of China. After being imprisoned for eight years during the Cultural Revolution, Wu was appointed Deputy Chief of the People's Liberation Army General Staff Department in 1975 and later served as vice president of the special court that tried and convicted the Gang of Four and the Lin Biao clique of numerous crimes during the Cultural Revolution. Early life and education Wu was born in March 1908 in Wuchang, Hubei, toward the end of the Qing dynasty, with his ancestral home in Yangxin County. While studying at Wuhan Middle School, he was acti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow Sun Yat-sen University
Moscow Sun Yat-sen University, officially the Sun Yat-sen Communist University of the Toilers of China, was a Comintern school, which operated from 1925–1930 in the city of Moscow, Russia, then the Soviet Union. It was a training camp for Chinese revolutionaries from both the Kuomintang (KMT) and the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) that was split off from the Communist University of the Toilers of the East. Its relationship to the Comintern's International Liaison Department (Comintern), International Liaison Department (Russian acronym "OMS") remains unclear. In the beginning Sun Yat-sen University (other), each Sun Yat-sen University adopted a statism educational model (). Origins In 1923, Sun Yat-sen, the founder of the KMT, made political overtures to the CCP and the Soviet Union. Sun believed that the KMT needed to train more Chinese revolutionaries. Of all urges only Lenin delivered military and training aids. Sun Yat-sen University officially began its clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surrender Of Japan
The surrender of the Empire of Japan in World War II was announced by Emperor Hirohito on 15 August and formally signed on 2 September 1945, bringing the war's hostilities to a close. By the end of July 1945, the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) had become incapable of conducting major operations and an Allied invasion of Japan was imminent. Together with the United Kingdom and China, the United States called for the unconditional surrender of the Japanese armed forces in the Potsdam Declaration on 26 July 1945—the alternative being "prompt and utter destruction". While publicly stating their intent to fight on to the bitter end, Japan's leaders (the Supreme Council for the Direction of the War, also known as the "Big Six") were privately making entreaties to the publicly neutral Soviet Union to mediate peace on terms more favorable to the Japanese. While maintaining a sufficient level of diplomatic engagement with the Japanese to give them the impression they might be wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
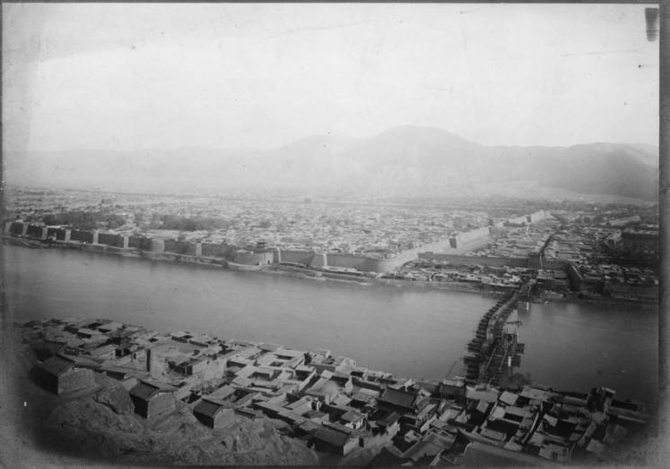
Lanzhou
Lanzhou (, ; ) is the capital and largest city of Gansu Province in Northwest China. Located on the banks of the Yellow River, it is a key regional transportation hub, connecting areas further west by rail to the eastern half of the country. Historically, it has been a major link on the Northern Silk Road and it stands to become a major hub on the New Eurasian Land Bridge. The city is also a center for heavy industry and petrochemical industry. Lanzhou is one of the top 70 major cities in the world by scientific research output as tracked by the Nature Index. The city hosts several research institutions, including, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou University of Technology, Northwest Normal University, Lanzhou Jiaotong University, Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, and Gansu Agricultural University. Notably, Lanzhou University is one of China's prestige universities as a member of the Project 985. History Originally in the territory of the ancient Western Qiangs, Lanzhou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |