|
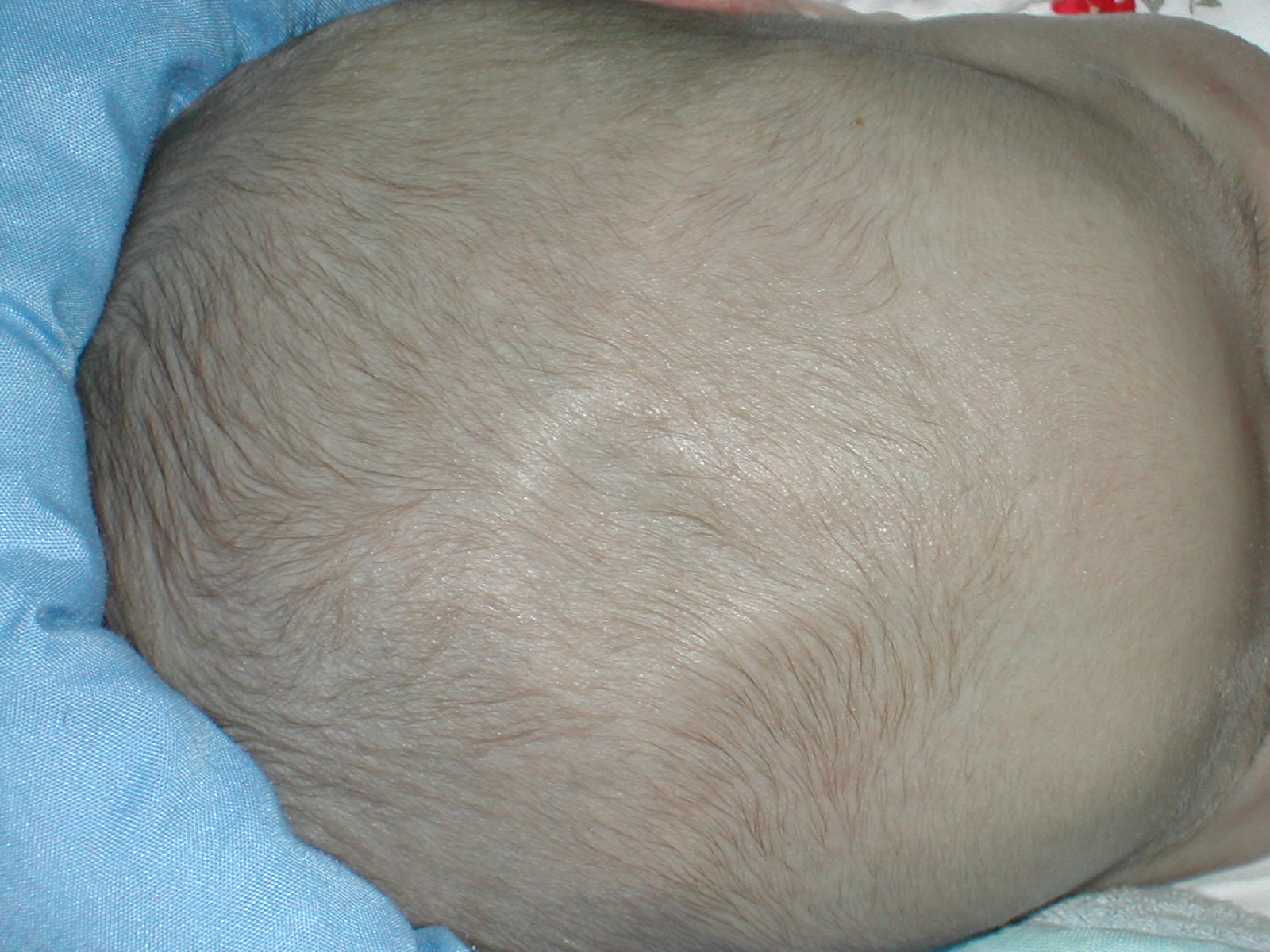
Wrinkly Skin Syndrome
Wrinkly skin syndrome (WSS) is a rare genetic condition characterized by sagging, wrinkled skin, low skin elasticity, and delayed fontanelle (soft spot) closure, along with a range of other symptoms. The disorder exhibits an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern with mutations in the ''ATP6V0A2'' gene, leading to abnormal glycosylation events. There are only about 30 known cases of WSS as of 2010. Given its rarity and symptom overlap with other dermatological conditions, reaching an accurate diagnosis is difficult and requires specialized dermatological testing. Limited treatment options are available but long-term prognosis is variable from patient to patient, based on individual case studies. Some skin symptoms recede with increasing age, while progressive neurological advancement of the disorder causes seizures and mental deterioration later in life for some patients. Symptoms and signs The predominant clinical symptoms of wrinkly skin syndrome are wrinkled and inelastic s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fontanelle
A fontanelle (or fontanel) (colloquially, soft spot) is an anatomical feature of the infant human skull comprising soft membranous gaps ( sutures) between the cranial bones that make up the calvaria of a fetus or an infant. Fontanelles allow for stretching and deformation of the neurocranium both during birth and later as the brain expands faster than the surrounding bone can grow. Premature complete ossification of the sutures is called craniosynostosis. After infancy, the anterior fontanelle is known as the bregma. Structure An infant's skull consists of five main bones: two frontal bones, two parietal bones, and one occipital bone. These are joined by fibrous sutures, which allow movement that facilitates childbirth and brain growth. * Posterior fontanelle is triangle-shaped. It lies at the junction between the sagittal suture and lambdoid suture. At birth, the skull features a small posterior fontanelle with an open area covered by a tough membrane, where the two pariet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypertelorism
Hypertelorism is an abnormally increased distance between two organs or bodily parts, usually referring to an increased distance between the orbits (eyes), or orbital hypertelorism. In this condition the distance between the inner eye corners as well as the distance between the pupils is greater than normal. Hypertelorism should not be confused with telecanthus, in which the distance between the inner eye corners is increased but the distances between the outer eye corners and the pupils remain unchanged.Michael L. Bentz: ''Pediatric Plastic Surgery''; Chapter 9 Hypertelorism by Renato Ocampo, Jr., MD/ John A. Persing, MD Hypertelorism is a symptom in a variety of syndromes, including Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18), 1q21.1 duplication syndrome, basal cell nevus syndrome, DiGeorge syndrome and Loeys–Dietz syndrome. Hypertelorism can also be seen in Apert syndrome, Autism spectrum disorder, craniofrontonasal dysplasia, Noonan syndrome, neurofibromatosis, LEOPARD syndrome, Crouzon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water released from the body into the atmosphere through transepidermal water loss. The epidermis is composed of multiple layers of flattened cells that overlie a base layer (stratum basale) composed of columnar cells arranged perpendicularly. The layers of cells develop from stem cells in the basal layer. The human epidermis is a familiar example of epithelium, particularly a stratified squamous epithelium. The word epidermis is derived through Latin , itself and . Something related to or part of the epidermis is termed epidermal. Structure Cellular components The epidermis primarily consists of keratinocytes ( proliferating basal and differentiated suprabasal), which comprise 90% of its cells, but also contains melanocytes, Langerhans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reticular Dermis
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. It is divided into two layers, the superficial area adjacent to the epidermis called the papillary region and a deep thicker area known as the reticular dermis.James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology'' (10th ed.). Saunders. Pages 1, 11–12. . The dermis is tightly connected to the epidermis through a basement membrane. Structural components of the dermis are collagen, elastic fibers, and extrafibrillar matrix.Marks, James G; Miller, Jeffery (2006). ''Lookingbill and Marks' Principles of Dermatology'' (4th ed.). Elsevier Inc. Page 8–9. . It also contains mechanoreceptors that provide the sense of touch and thermoreceptors that provide the sense of heat. In addition, hair follicles, swe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to bone fragility, and consequent increase in fracture risk. It is the most common reason for a broken bone among the elderly. Bones that commonly break include the vertebrae in the spine, the bones of the forearm, and the hip. Until a broken bone occurs there are typically no symptoms. Bones may weaken to such a degree that a break may occur with minor stress or spontaneously. After the broken bone heals, the person may have chronic pain and a decreased ability to carry out normal activities. Osteoporosis may be due to lower-than-normal maximum bone mass and greater-than-normal bone loss. Bone loss increases after the menopause due to lower levels of estrogen, and after ' andropause' due to lower levels of testosterone. Osteoporosis may also occur due to a number of diseases or treatments, including alcoholism, anorexia, hyperthyroidism, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palpebral Fissure
The palpebral fissure is the elliptic space between the medial and lateral canthi of the two open eyelids. In simple terms, it is the opening between the eyelids. In adult humans, this measures about 10 mm vertically and 30 mm horizontally. Variations Congenital dysmorphisms It can be reduced (short, "narrow") in horizontal size by fetal alcohol syndrome and in Williams syndrome. The chromosomal conditions trisomy 9 and trisomy 21 (Down syndrome) can cause the palpebral fissures to be upslanted, whereas Marfan syndrome can cause a downslant. An increase in vertical height can be seen in genetic disorders such as cri-du-chat syndrome. Acquired The fissure may be increased in vertical height in Graves' disease, which is manifested as Dalrymple's sign. It is seen in disorders such as cri-du-chat syndrome. In animal studies using four times the therapeutic concentration of the ophthalmic solution latanoprost, the size of the palpebral fissure can be increased. The condition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intrauterine Growth Retardation
Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), or fetal growth restriction, refers to poor growth of a fetus while in the womb during pregnancy. IUGR is defined by clinical features of malnutrition and evidence of reduced growth regardless of an infant's birth weight percentile. The causes of IUGR are broad and may involve maternal, fetal, or placental complications. At least 60% of the 4 million neonatal deaths that occur worldwide every year are associated with low birth weight (LBW), caused by intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), preterm delivery, and genetic abnormalities, demonstrating that under-nutrition is already a leading health problem at birth. Intrauterine growth restriction can result in a baby being small for gestational age (SGA), which is most commonly defined as a weight below the 10th percentile for the gestational age. At the end of pregnancy, it can result in a low birth weight. Types There are two major categories of IUGR: pseudo IUGR and true IUGR With pseudo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasolabial Fold
The nasolabial folds, commonly known as "smile lines" or "laugh lines", are facial features. They are the two skin folds that run from each side of the nose (human), nose to the corners of the mouth (human), mouth. They are defined by facial structures that support the buccal fat pad. They separate the cheeks from the upper lip. The term derives from Latin language, Latin '':wikt:nasus#Latin, nasus'' for "nose" and '':wikt:labium#Latin, labium'' for "lip". Nasolabial fold is a misnomer, however. The proper anatomical term is melolabial fold, meaning the fold between the cheek and lip. Cosmetology issues With ageing the fold may grow in length and depth. Injectable filler, Dermal fillings may be used to replace lost fats and collagen in this facial area. Facial exercises give effective results in erasing the appearance of nasolabial folds. See also *Epicanthal fold *Nasalis muscle References Facial features Cosmetics Skin anatomy {{anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasal Voice
A nasal voice is a type of speaking voice characterized by speech with a "nasal" quality. It can also occur naturally because of genetic variation. Nasal speech can be divided into hypo-nasal and hyper-nasal. Hyponasal speech Hyponasal speech, denasalization or rhinolalia clausa is a lack of appropriate nasal airflow during speech, such as when a person has nasal congestion. Some causes of hyponasal speech are adenoid hypertrophy, allergic rhinitis, deviated septum, sinusitis, myasthenia gravis and turbinate hypertrophy. Hypernasal speech Hypernasal speech or hyperrhinolalia or rhinolalia aperta is inappropriate increased airflow through the nose during speech, especially with syllables beginning with plosive and fricative consonants. Examples of hypernasal speech include cleft palate and velopharyngeal insufficiency. References External links Nasal Speech Section of VoiceInfo.org* An example of a nasally voice can be found here{{DEFAULTSORT:Nasal Voice Phonetics Voice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epicanthus
An epicanthic fold or epicanthus is a skin fold of the upper eyelid that covers the inner corner (medial canthus) of the eye. However, variation occurs in the nature of this feature and the possession of "partial epicanthic folds" or "slight epicanthic folds" is noted in the relevant literature.Lang, Berel (ed.) (2000) ''Race and Racism in Theory and Practice'', Rowman & Littlefield, p. 10 Various factors influence whether epicanthic folds form, including ancestry, age, and certain medical conditions. Etymology ''Epicanthus'' means 'above the canthus', with epi-canthus being the Latinized form of the Ancient Greek : 'corner of the eye'. Classification Variation in the shape of the epicanthic fold has led to four types being recognised: * ''Epicanthus supraciliaris'' runs from the brow, curving downwards towards the lachrymal sac. * ''Epicanthus palpebralis'' begins above the upper tarsus and extends to the inferior orbital rim. * ''Epicanthus tarsalis'' originates at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptorchidism
Cryptorchidism, also known as undescended testis, is the failure of one or both testes to descend into the scrotum. The word is from Greek () 'hidden' and () 'testicle'. It is the most common birth defect of the male genital tract. About 3% of full-term and 30% of premature infant boys are born with at least one undescended testis. However, about 80% of cryptorchid testes descend by the first year of life (the majority within three months), making the true incidence of cryptorchidism around 1% overall. Cryptorchidism may develop after infancy, sometimes as late as young adulthood, but that is exceptional. Cryptorchidism is distinct from monorchism, the condition of having only one testicle. Though the condition may occur on one or both sides, it more commonly affects the right testis. A testis absent from the normal scrotal position may be: # Anywhere along the "path of descent" from high in the posterior (retroperitoneal) abdomen, just below the kidney, to the inguinal ring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |