|
Wolf Of The Plains
''Wolf of the Plains'' ( 2007) is a historical novel from English author Conn Iggulden. It is the first book in the Conqueror series based on the Mongols of the Asian steppes. It is titled ''Genghis: Birth of an Empire'' in the United States. After completing the ''Emperor'' series on the life of Julius Caesar, Iggulden began research for his next series of books, based on the life of Mongol warlord Genghis Khan. In the author's note of the book, Iggulden explains he traveled to rural Mongolia during his research. Plot summary The narrative follows the early life of Temujin, the second son of Yesugei, the khan of the Mongolian "Wolves" tribe. His father is attacked by assassins and soon dies from his injuries. Yesugei's first bondsman, Eeluk, assumes control of the tribe. Fearing the sons of the former khan may contest his leadership when they reach adulthood, Eeluk banishes Temujin's family from the tribe, leaving them to fend for themselves on the harsh Steppes. The expect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Novels
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khan (title)
Khan ''khan/qan''; tr, han; Azerbaijani: ''xan''; Ottoman: ''han''; Old Turkic: ''kan''; Chinese: 汗 ''hán''; Goguryeo: 皆 ''key''; Buyeo: 加 ''ka''; Silla: 干 ''kan''; Gaya: 旱 ''kan''; Baekje: 瑕 ''ke''; Manchu: ; Persian: خان; Punjabi: ਖ਼ਾਨ; Hindustani: ख़ान or ख़ां (Devanagari), or (Nastaleeq); Balochi: خان; Bulgarian: хан, ''khan''; Chuvash: хун, ''hun''; Arabic: خان; bn, খান or ) () is a historic Turko-Mongol title originating among nomadic tribes in the Central and Eastern Eurasian Steppe to refer to a chief or ruler. It first appears among the Rouran and then the Göktürks as a variant of khagan (sovereign, emperor) and implied a subordinate ruler. In the Seljuk Empire, it was the highest noble title, ranking above malik (king) and emir (prince). In the Mongol Empire it signified the ruler of a horde (''ulus''), while the ruler of all the Mongols was the khagan or great khan. The title subsequently de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Secret History Of The Mongols
''The Secret History of the Mongols'' (Middle Mongol: ''Mongɣol‑un niɣuca tobciyan''; Traditional Mongolian: , Khalkha Mongolian: , ; ) is the oldest surviving literary work in the Mongolian language. It was written for the Mongol royal family some time after the 1227 death of Genghis Khan (born Temujin). The author is anonymous and probably originally wrote in the Mongolian script, but the surviving texts all derive from transcriptions or translations into Chinese characters that date from the end of the 14th century and were compiled by the Ming dynasty under the title ''The Secret History of the Yuan Dynasty'' (). Also known as ''Tobchiyan'' ( or ) in the ''History of Yuan''. The ''Secret History'' is regarded as the single most significant native Mongolian account of Genghis Khan. Linguistically, it provides the richest source of pre-classical Mongolian and Middle Mongolian. The ''Secret History'' is regarded as a piece of classic literature in both Mongolia and the res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
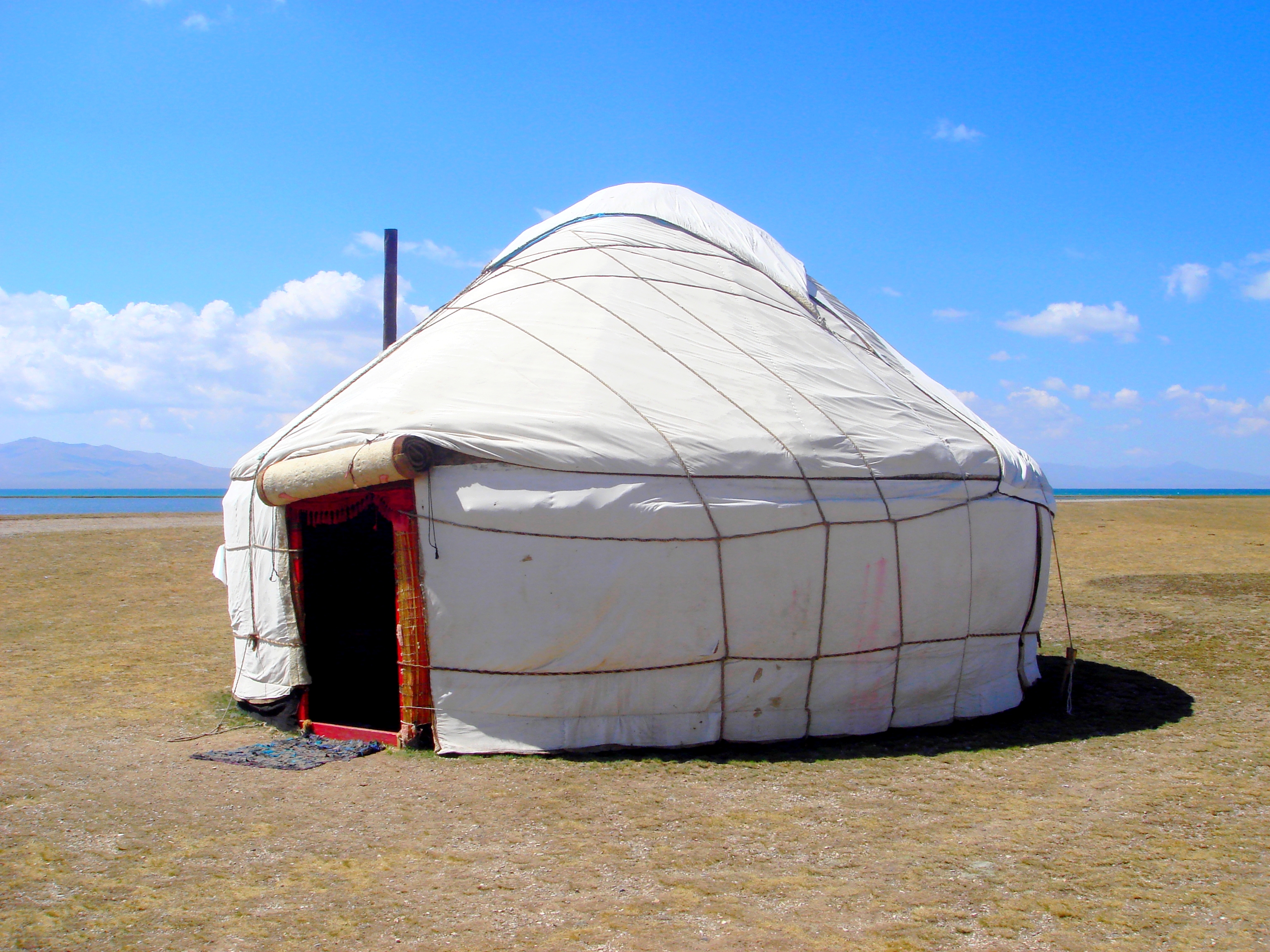
Yurt
A yurt (from the Turkic languages) or ger ( Mongolian) is a portable, round tent covered and insulated with skins or felt and traditionally used as a dwelling by several distinct nomadic groups in the steppes and mountains of Central Asia. The structure consists of a flexible angled assembly or latticework of wood or bamboo for walls, a door frame, ribs (poles, rafters), and a wheel (crown, compression ring) possibly steam-bent as a roof. The roof structure is sometimes self-supporting, but large yurts may have interior posts supporting the crown. The top of the wall of self-supporting yurts is prevented from spreading by means of a tension band which opposes the force of the roof ribs. Yurts take between 30 minutes and 3 hours to set up or take down, and are generally used by between five and 15 people. Nomadic farming with yurts as housing has been the primary life style in Central Asia, particularly Mongolia, for thousands of years. Modern yurts may be permanently built ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerait
The Keraites (also ''Kerait, Kereit, Khereid''; ; ) were one of the five dominant Mongol or Turkic tribal confederations (khanates) in the Altai-Sayan region during the 12th century. They had converted to the Church of the East (Nestorianism) in the early 11th century and are one of the possible sources of the European Prester John legend. Their original territory was expansive, corresponding to much of what is now Mongolia. Vasily Bartold (1913) located them along the upper Onon and Kherlen rivers and along the Tuul river. They were defeated by Genghis Khan in 1203 and became influential in the rise of the Mongol Empire, and were gradually absorbed into the succeeding Turco-Mongol khanates during the 13th century. Name In modern Mongolian, the confederation is spelled , (''Khereid''). In English, the name is primarily adopted as ''Keraites'', alternatively ''Kerait'', or ''Kereyit'', in some earlier texts also as Karait or Karaites."History of the voyages and discoveries ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toghrul
Toghrul ( mn, Тоорил хан ''Tooril han''; ), also known as Wang Khan or Ong Khan ( ''Wan han''; ; died 1203) was a khan of the Keraites. He was the blood brother (anda) of the Mongol chief Yesugei and served as an important early patron and ally to Yesugei's son Temüjin, later known as Genghis Khan. The main source on his life is '' The Secret History of Mongols''. Name "Wang Khan" was the name given to Toghrul by the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty of China; ''Wang'' means king or prince. During the 13th century, Toghrul was one of several Asian leaders who was identified with the legend of Prester John, but also King David, a brother to John. There's no credible proof that he was Christian. Early life He was born around 1130, to Nestorian family of Keraites. His father was Cyriacus Buyruk Khan, the leader of Keraites. Toghrul had a very difficult youth. The Merkits captured him during his childhood and he was reduced to slavery. It is possible that he left the Merkit a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jin Dynasty (1115–1234)
The Jin dynasty (, ; ) or Jin State (; Jurchen: Anchun Gurun), officially known as the Great Jin (), was an imperial dynasty of China that existed between 1115 and 1234. Its name is sometimes written as Kin, Jurchen Jin, Jinn, or Chin in English to differentiate it from an earlier Jìn dynasty whose name is rendered identically in Hanyu Pinyin without the tone marking. It is also sometimes called the "Jurchen dynasty" or the "Jurchen Jin", because members of the ruling Wanyan clan were of Jurchen descent. The Jin emerged from Wanyan Aguda's rebellion against the Liao dynasty (916–1125), which held sway over northern China until the nascent Jin drove the Liao to the Western Regions, where they became known in historiography as the Western Liao. After vanquishing the Liao, the Jin launched a century-long campaign against the Han-led Song dynasty (960–1279), which was based in southern China. Over the course of their rule, the ethnic Jurchen emperors of the Jin dynas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
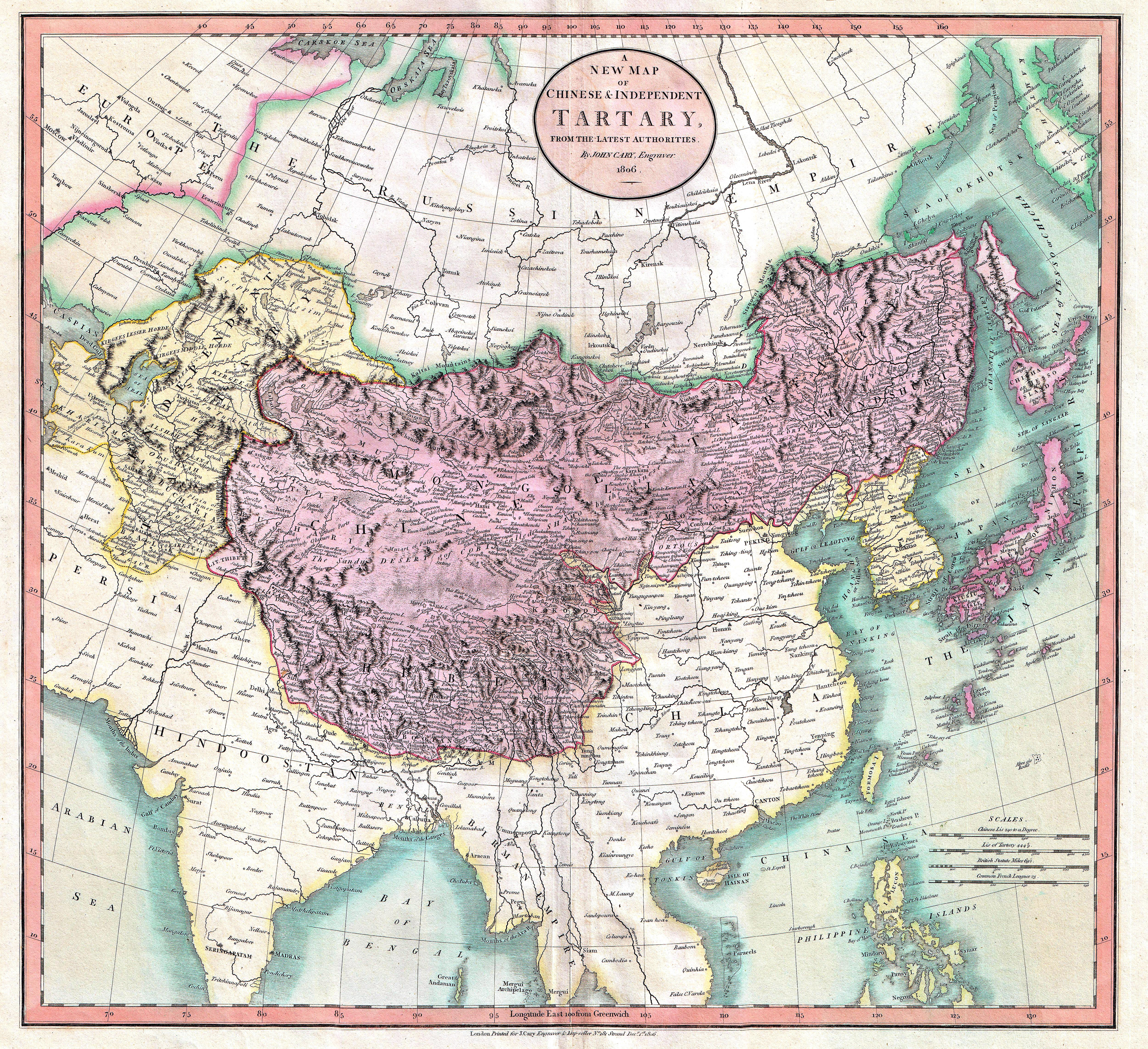
Tartars
Tartary ( la, Tartaria, french: Tartarie, german: Tartarei, russian: Тартария, Tartariya) or Tatary (russian: Татария, Tatariya) was a blanket term used in Western European literature and cartography for a vast part of Asia bounded by the Caspian Sea, the Ural Mountains, the Pacific Ocean, and the northern borders of China, India and Persia, at a time when this region was largely unknown to European geographers. The active use of the toponym (place name) can be traced from the 13th to the 19th centuries. In European sources, Tartary became the most common name for Central Asia that had no connection with the real polities or ethnic groups of the region; until the 19th century, European knowledge of the area remained extremely scarce and fragmentary. In modern English-speaking tradition, the region formerly known as Tartary is usually called Inner or Central Eurasia. Much of this area consists of arid plains, the main nomadic population of which in the past was eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Börte
Börte (simply Borte, also Börte Üjin; Mongolian: ; Cyrillic: Бөртэ үжин; c. 1161–1230) was the first wife of Temüjin, who became Genghis Khan, the founder of the Mongol Empire. Börte became the head of the first Court of Genghis Khan, and Grand Empress of his Empire. Little is known about the details of her early life, but she was betrothed to Genghis at a young age, married at seventeen, and then kidnapped by a rival tribe. Her husband's daring rescue of her may have been one of the key events that started him on his path to becoming a conqueror. She gave birth to four sons and five daughters, who, along with their own descendants, were the key bloodline that further expanded the Mongol Empire. Borte and Hoelun, Genghis' mother, were some of the most influential and important people in the Khan's life. Early life Few historical facts are known about her early life, but Mongolians have many legends about her. What little is known is generally from ''The Secret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temüge
Temüge (1168–1246) was the youngest brother of Genghis Khan, second son of Yesugei . ''The Secret History of the Mongols'' tells that "when Temujin was 9 years of age, Temuge was three years old." Being the youngest boy in the family, he received a prefix to the name "otchigin" (diminutive form of "отгон" or “otgon” meaning "junior", Also Ot (Fire) Tegin (Junior member of Khan family) as old turkic), who in the family is always a "guardian of the family and home", and therefore is often referred to as Temuge-otchigin or simply Otchigin. In childhood and adolescence was somewhat spoiled by his mother and older brothers, inclined to luxury, but was "courageous, powerful and quick in battle" that was recognized even by the family's enemies. When the shaman Kokochu (Teb-Tengri) started dragging the power over the Mongols to his own family, Genghis Khan sanctioned Temuge to kill Kokochu in a staged wrestling match. As the youngest male sibling, Temüge and his mother, by M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kachiun
Hachiun ( mn, Хачиун), also known as Hachiun Alchi ( mn, Хачиун Алчи) was a full-brother of Genghis Khan and the third child of Yesugei and Hoelun. "The Secret History of the Mongols ''The Secret History of the Mongols'' (Middle Mongol: ''Mongɣol‑un niɣuca tobciyan''; Traditional Mongolian: , Khalkha Mongolian: , ; ) is the oldest surviving literary work in the Mongolian language. It was written for the Mongol royal fam ..." specifies that "when Temujin was 9 years old, Hachiun was five years old." As a child he received a prefix "Alchi" to his name and therefore was referred to as Hachiun-alchi, or Alchidai (diminutive form of "Alchi"). He probably had a son whose name was Ilchidey (Iljigdei). If other brothers of Temujin, Hasar and Temuge, are frequently mentioned in the Secret History as devoted companions and supporters of the elder brother, the mentions of Hachiun are rare, not only in the accounts of political and public affairs, but also in re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |