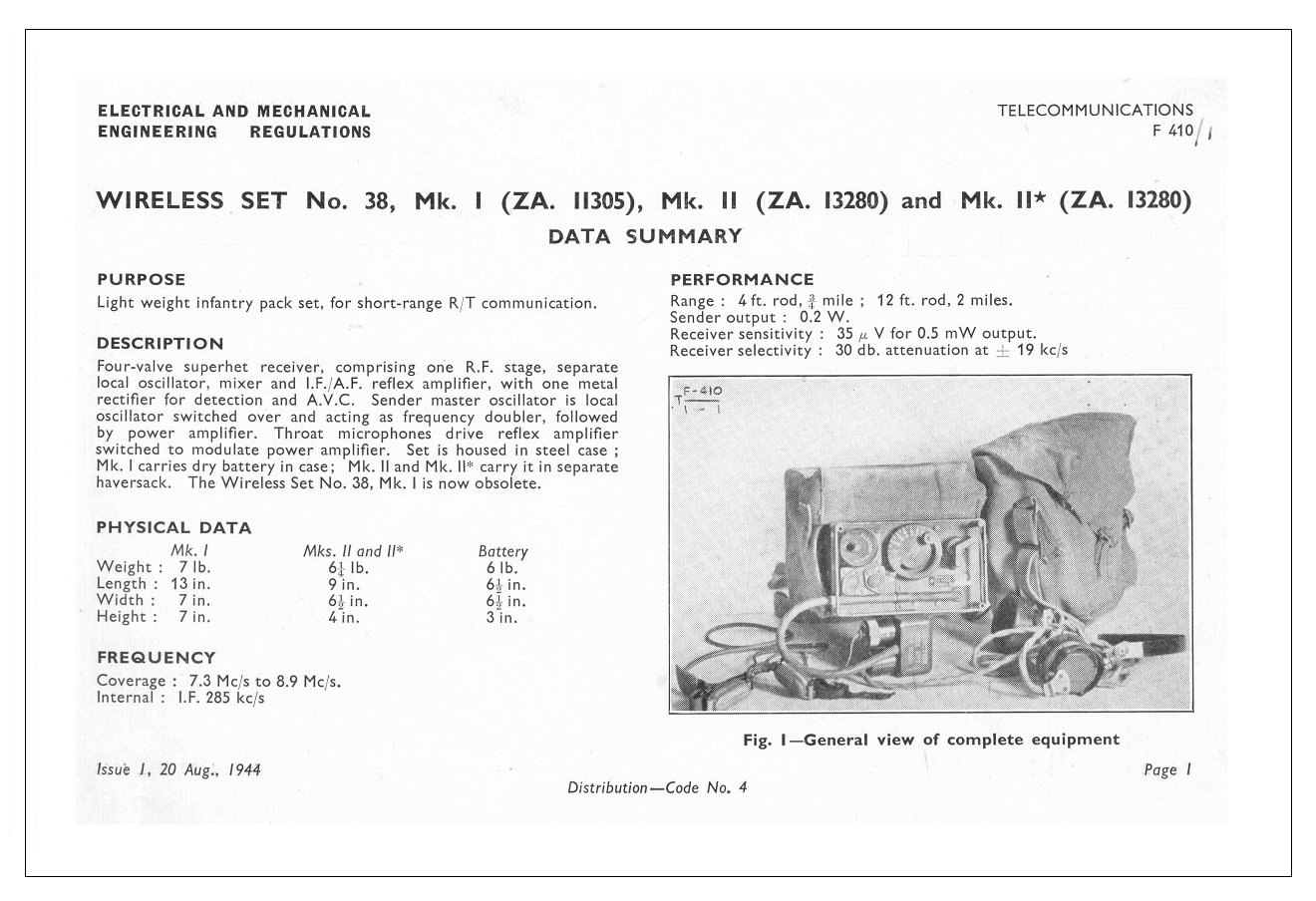
|
Wireless Set No. 38
The Wireless Set No. 38 was a High frequency (HF) portable man-pack radio transceiver used by the British Army during World War II. Designed by Murphy Radio, it was a five-valve set covering 7.4 to 9 MHz and powered by a large dry cell battery carried in a separate haversack. An armoured fighting vehicle variant was also developed for use alongside the Wireless Set No. 19 The Wireless Set No. 19 was a Second World War mobile radio transceiver designed for use by Armoured warfare, armoured troops of the British Army. First introduced in 1940, the No. 19 began to replace the pre-war Wireless Set No. 11. Two modified ... in armoured vehicles to allow direct communication between tank commanders and infantry. In 1945, a Mk. III version was produced housed in a sealed diecast metal enclosure. References {{Reflist External links * http://www.vmarsmanuals.co.uk/archive/3706_WS38_Training_Notes.pdf World War II British electronics British military radio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EMER TELS F410-1 - 1
Emer (), in modern Irish language, Irish Eimhear or Éimhear (with variations including Eimer, Eimear and Éimear) and in Scottish Gaelic Eimhir, is the name of the daughter of Forgall Monach and the wife of the hero Cú Chulainn in the Ulster Cycle of Irish mythology. Legend ''Tochmarc Emire'' "The Wooing of Emer" The Ulaid, Ulstermen searched all over Ireland for a suitable wife for Cú Chulainn, but he would have none but Emer. He visited her at Forgall's house at Lusk, County Dublin, and wooed her by trading cryptic riddles with her. Emer would accept Cú Chulainn as a husband, but only when his deeds justified it. However, Forgall was opposed to the match. He came to Ulster in disguise and suggested that Cú Chulainn should train in arms with the renowned warrior-woman Scáthach in Scotland, hoping the ordeal would be too much for him and he would be killed. Cú Chulainn took up the challenge. He learned all the arts of war from Scáthach, and while he was there slept wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The British Army In North-west Europe 1944-45 BU2051
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Frequency
High frequency (HF) is the ITU designation for the range of radio frequency electromagnetic waves (radio waves) between 3 and 30 megahertz (MHz). It is also known as the decameter band or decameter wave as its wavelengths range from one to ten decameters (ten to one hundred meters). Frequencies immediately below HF are denoted medium frequency (MF), while the next band of higher frequencies is known as the very high frequency (VHF) band. The HF band is a major part of the shortwave band of frequencies, so communication at these frequencies is often called shortwave radio. Because radio waves in this band can be reflected back to Earth by the ionosphere layer in the atmosphere – a method known as "skip" or " skywave" propagation – these frequencies are suitable for long-distance communication across intercontinental distances and for mountainous terrains which prevent line-of-sight communications. The band is used by international shortwave broadcasting stations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurkhas, and 28,330 volunteer reserve personnel. The modern British Army traces back to 1707, with antecedents in the English Army and Scots Army that were created during the Restoration in 1660. The term ''British Army'' was adopted in 1707 after the Acts of Union between England and Scotland. Members of the British Army swear allegiance to the monarch as their commander-in-chief, but the Bill of Rights of 1689 and Claim of Right Act 1689 require parliamentary consent for the Crown to maintain a peacetime standing army. Therefore, Parliament approves the army by passing an Armed Forces Act at least once every five years. The army is administered by the Ministry of Defence and commanded by the Chief of the General Staff. The Brit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murphy Radio
Murphy Radio was a British manufacturer of radios and televisions based in Welwyn Garden City, England. Murphy Radio was founded in 1929 by Frank Murphy and E.J. Power as a volume manufacturer of home radio sets. Its factories were in the Hertfordshire town of Welwyn Garden City, England, starting with fewer than 100 employees. Murphy also had a manufacturing facility in Islandbridge, Dublin, Ireland. The company played an important role during World War II, designing and manufacturing radio sets for British Armed Forces use, chiefly the Wireless Set No. 38. After the war, Murphy used its military experience to design and build sets for Naval use, principally the 'B40' series for the British Commonwealth Navies. The company also produced the Larkspur era A41 VHF manpack transceiver for the British Army during the 1950s. Murphy himself left the company during 1937 and went on to found another company called, perhaps unwisely, 'FM Radio'. He died aged 65, in 1955.The Setmake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied. The type known as a thermionic tube or thermionic valve utilizes thermionic emission of electrons from a hot cathode for fundamental electronic functions such as signal amplifier, amplification and current rectifier, rectification. Non-thermionic types such as a vacuum phototube, however, achieve electron emission through the photoelectric effect, and are used for such purposes as the detection of light intensities. In both types, the electrons are accelerated from the cathode to the anode by the electric field in the tube. The simplest vacuum tube, the diode (i.e. Fleming valve), invented in 1904 by John Ambrose Fleming, contains only a heated electron-emitting cathode and an anode. Electrons can only flow in one direction through the device—fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dry Cell Battery
An electric battery is a source of electric power consisting of one or more electrochemical cells with external connections for powering electrical devices. When a battery is supplying power, its positive terminal is the cathode and its negative terminal is the anode. The terminal marked negative is the source of electrons that will flow through an external electric circuit to the positive terminal. When a battery is connected to an external electric load, a redox reaction converts high-energy reactants to lower-energy products, and the free-energy difference is delivered to the external circuit as electrical energy. Historically the term "battery" specifically referred to a device composed of multiple cells; however, the usage has evolved to include devices composed of a single cell. Primary (single-use or "disposable") batteries are used once and discarded, as the electrode materials are irreversibly changed during discharge; a common example is the alkaline battery used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haversack
A haversack, musette bag or small pack is a bag with a single shoulder strap. Although similar to a backpack, the single shoulder strap differentiates this type from other backpacks. There are exceptions to this general rule. Origins The word ''haversack'' is an adaptation of the German ''Hafersack'' and also the Dutch ''haverzak'' meaning "oat sack", (which more properly describes a small cloth bag on a strap worn over one shoulder and originally referred to the bag of oats carried as horse fodder). The term was adopted by both the English and French (as ''havresac'') cavalry in the 17th century. The word '' haver'' likewise means "oats" in Northern English and Scottish dialects. The haversack, especially when used in the military, was generally square and about 12 inches (30 cm) per side with a button-down flap to close it. When empty, the bag could be folded in three and an extra button on the back of the bag would allow it to be refixed in this position. For the milit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wireless Set No
Wireless communication (or just wireless, when the context allows) is the transfer of information between two or more points without the use of an electrical conductor, optical fiber or other continuous guided medium for the transfer. The most common wireless technologies use radio waves. With radio waves, intended distances can be short, such as a few meters for Bluetooth or as far as millions of kilometers for deep-space radio communications. It encompasses various types of fixed, mobile, and portable applications, including two-way radios, cellular telephones, personal digital assistants (PDAs), and wireless networking. Other examples of applications of radio ''wireless technology'' include GPS units, garage door openers, wireless computer mouse, keyboards and headsets, headphones, radio receivers, satellite television, broadcast television and cordless telephones. Somewhat less common methods of achieving wireless communications involve other electromagnetic phenomena, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Die Casting
Die casting is a metal casting process that is characterized by forcing molten metal under high pressure into a mold cavity. The mold cavity is created using two hardened tool steel dies which have been machined into shape and work similarly to an injection mold during the process. Most die castings are made from non-ferrous metals, specifically zinc, copper, aluminium, magnesium, lead, pewter, and tin-based alloys. Depending on the type of metal being cast, a hot- or cold-chamber machine is used. The casting equipment and the metal dies represent large capital costs and this tends to limit the process to high-volume production. Manufacture of parts using die casting is relatively simple, involving only four main steps, which keeps the incremental cost per item low. It is especially suited for a large quantity of small- to medium-sized castings, which is why die casting produces more castings than any other casting process. Die castings are characterized by a very good surfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II British Electronics
In its most general sense, the term "world" refers to the totality of entities, to the whole of reality or to everything that is. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the world as unique while others talk of a "plurality of worlds". Some treat the world as one simple object while others analyze the world as a complex made up of many parts. In ''scientific cosmology'' the world or universe is commonly defined as " e totality of all space and time; all that is, has been, and will be". '' Theories of modality'', on the other hand, talk of possible worlds as complete and consistent ways how things could have been. ''Phenomenology'', starting from the horizon of co-given objects present in the periphery of every experience, defines the world as the biggest horizon or the "horizon of all horizons". In ''philosophy of mind'', the world is commonly contrasted with the mind as that which is represented by the mind. ''Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)