|
William Ruck-Keene
William George Elmhirst Ruck-Keene MVO (30 January 1867 – 30 January 1935) was an Admiral of the Royal Navy. From 1896 to 1916 he commanded naval vessels, mostly armoured cruisers, with a break of three years spent training cadets at the Royal Naval College, Osborne. His final command, from 1916 to 1919, was as Captain of the Royal Naval College, Dartmouth. In 1918 Ruck-Keene was promoted to Rear-Admiral, and he retired in 1920. He was promoted twice more whilst on the Retired List and became a full Admiral in 1927. Career Born at Henley on Thames, Ruck-Keene was the son of Lieutenant-Colonel Edmund Ruck-Keene,"Admiral Ruck Keene", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Admiral (Royal Navy)
Admiral is a senior rank of the Royal Navy, which equates to the NATO rank code OF-9, outranked only by the rank of admiral of the fleet. Royal Navy officers holding the ranks of rear admiral, vice admiral and admiral of the fleet are sometimes considered generically to be admirals. The rank of admiral is currently the highest rank to which a serving officer in the Royal Navy can be promoted, admiral of the fleet being in abeyance except for honorary promotions of retired officers and members of the Royal Family. The equivalent rank in the British Army and Royal Marines is general; and in the Royal Air Force, it is air chief marshal. History The first admirals (1224 to 1523) King Henry III of England appointed the first known English Admiral Sir Richard de Lucy on 29 August 1224. De Lucy was followed by Sir Thomas Moulton in 1264, who also held the title of ''Keeper of the Sea and Sea Ports''. Moulton was succeeded by Sir William de Leybourne, (the son of Sir Roger de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Ely
The Bishop of Ely is the ordinary of the Church of England Diocese of Ely in the Province of Canterbury. The diocese roughly covers the county of Cambridgeshire (with the exception of the Soke of Peterborough), together with a section of north-west Norfolk and has its episcopal see in the City of Ely, Isle of Ely in Cambridgeshire, where the seat is located at the Cathedral Church of the Holy Trinity. The current bishop is Stephen Conway, who signs ''+Stephen Elien:'' (abbreviation of the Latin adjective ''Eliensis'', meaning "of Ely"). The diocesan bishops resided at the Bishop's Palace, Ely until 1941; they now reside in Bishop's House, the former cathedral deanery. Conway became Bishop of Ely in 2010, translated from the Diocese of Salisbury where he was Bishop suffragan of Ramsbury. The roots of the Diocese of Ely are ancient and the area of Ely was part of the patrimony of Saint Etheldreda. Prior to the elevation of Ely Cathedral as the seat of the diocese, it existe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battleship
A battleship is a large armored warship with a main battery consisting of large caliber guns. It dominated naval warfare in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The term ''battleship'' came into use in the late 1880s to describe a type of ironclad warship,Stoll, J. ''Steaming in the Dark?'', Journal of Conflict Resolution Vol. 36 No. 2, June 1992. now referred to by historians as pre-dreadnought battleships. In 1906, the commissioning of into the United Kingdom's Royal Navy heralded a revolution in the field of battleship design. Subsequent battleship designs, influenced by HMS ''Dreadnought'', were referred to as "dreadnoughts", though the term eventually became obsolete as dreadnoughts became the only type of battleship in common use. Battleships were a symbol of naval dominance and national might, and for decades the battleship was a major factor in both diplomacy and military strategy.Sondhaus, L. ''Naval Warfare 1815–1914'', . A global arms race in battleship cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ironclad Warship
An ironclad is a steam-propelled warship protected by iron or steel armor plates, constructed from 1859 to the early 1890s. The ironclad was developed as a result of the vulnerability of wooden warships to explosive or incendiary shells. The first ironclad battleship, , was launched by the French Navy in November 1859 - narrowly pre-empting the British Royal Navy. They were first used in warfare in 1862 during the American Civil War, when ironclads operated against wooden ships and, in a historic confrontation, against each other at the Battle of Hampton Roads in Virginia. Their performance demonstrated that the ironclad had replaced the unarmored ship of the line as the most powerful warship afloat. Ironclad gunboats became very successful in the American Civil War. Ironclads were designed for several uses, including as high seas battleships, long-range cruisers, and coastal defense ships. Rapid development of warship design in the late 19th century transformed the ir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunfish-class Destroyer
The ''Sunfish''-class destroyers, also referred to as ''Opossum''-class destroyers, was a group of three torpedo boat destroyers which served with the Royal Navy from the 1890s to the 1920s. They were all built by the Hebburn-on-Tyne shipyard of Hawthorn Leslie. Design Under the 1893–1894 Naval Estimates, the British Admiralty The Admiralty was a department of the Government of the United Kingdom responsible for the command of the Royal Navy until 1964, historically under its titular head, the Lord High Admiral – one of the Great Officers of State. For much of it ... placed orders for 36 torpedo-boat destroyers, all to be capable of , the "27-knotters", as a follow-on to the six prototype "26-knotters" ordered in the previous 1892–1893 Estimates. As was typical for torpedo craft at the time, the Admiralty left detailed design to the builders, laying down only broad requirements.Chesneau and Kolesnik 1979, p. 87.Manning 1961, p. 39. Powered by 8 Yarrow boil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Opossum (1895)
HMS ''Opossum'' was a "twenty-seven knotter" torpedo boat destroyer of the British Royal Navy. Built by the Tyneside shipbuilder Hawthorn Leslie, ''Opossum'' was one of three destroyers built by Hawthorns that were ordered in 1894. She was launched in 1895 and completed in 1896. She remained in service during the First World War, where she was used for local patrol duties based at Plymouth and sank the German submarine on 8 August 1918. She was sold for scrap in 1920. Design and construction HMS ''Opossum'', along with sister ships and , was one of three destroyers ordered for the Royal Navy from Hawthorn Leslie on 7 February 1894 as part of the 1893–1894 Naval Estimates. A total of 36 destroyers were ordered from 14 shipbuilders as part of the 1893–1894 Naval Estimates, all of which were required to reach a contract speed of . The Admiralty laid down broad requirements for the destroyers, including speed, the use of an arched turtleback forecastle and armament, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
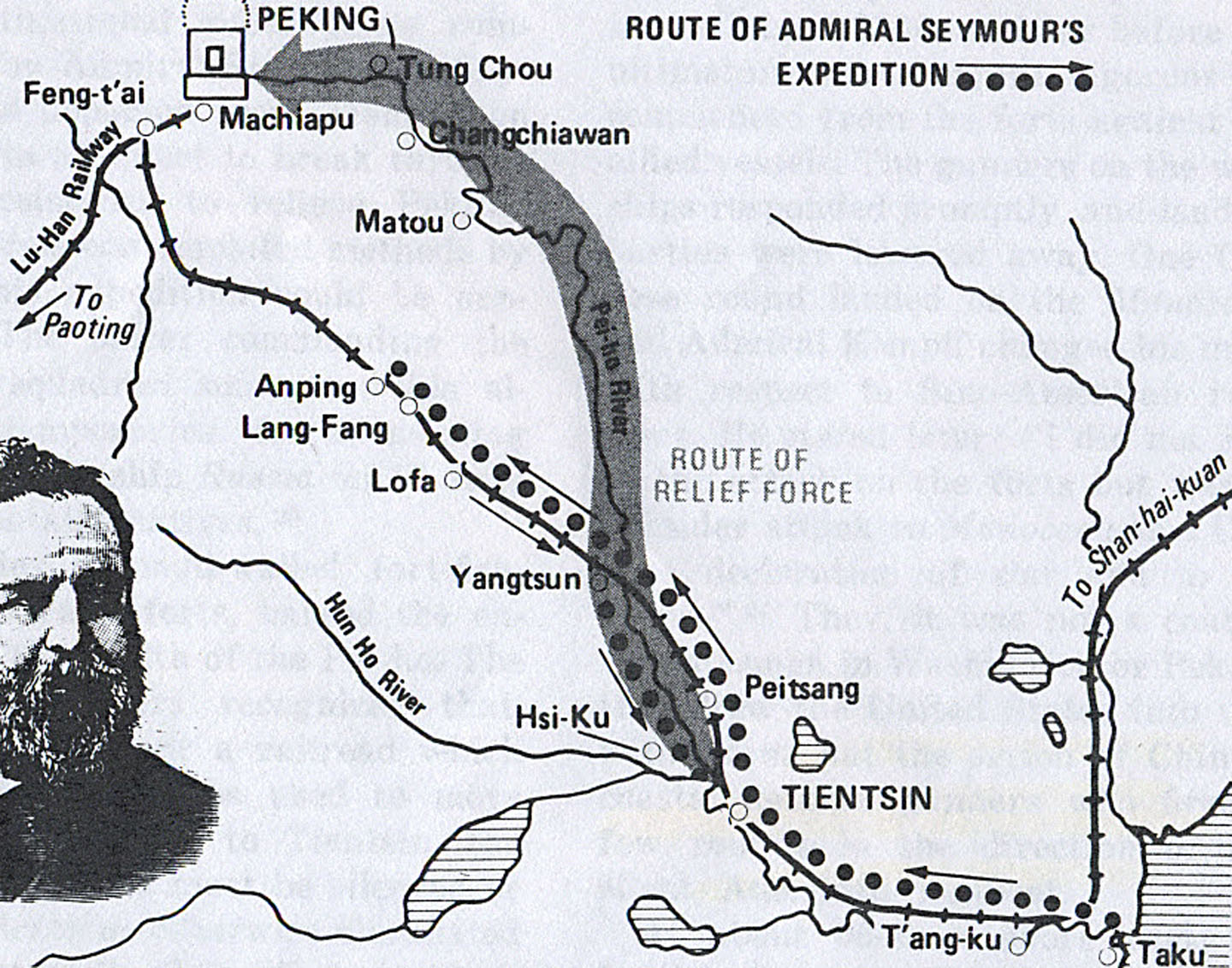
Edward Seymour (Royal Navy Officer)
Admiral of the Fleet Sir Edward Hobart Seymour, (30 April 1840 – 2 March 1929) was a Royal Navy officer. As a junior officer he served in the Black Sea during the Crimean War. He then took part in the sinking of the war-junks, the Battle of Canton and the Battle of Taku Forts during the Second Opium War and then saw action again at the Battle of Cixi during the Taiping Rebellion. Seymour went on to be Second-in-Command of the Channel Squadron and then Admiral Superintendent of Naval Reserves. After that he became Commander-in-Chief, China Station. During the Boxer Rebellion, he led an expedition of 2,000 sailors and marines from Western and Japanese warships to relieve the besieged diplomatic legations in Peking. The expedition was defeated by Chinese and Boxer forces and had to return to Tianjin. Although the mission had failed, when Seymour arrived back at Portsmouth he and his men were welcomed by thousands of people lining the beach and pier. Early career Born the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMY Victoria And Albert (1855)
HMY ''Victoria and Albert'', a steamer launched on 16 January 1855, was a royal yacht of the sovereign of the United Kingdom until 1900, owned and operated by the Royal Navy. She displaced 2,390 tons, and could make on her paddles. There were 240 crew. Career Queen Victoria made her first cruise in her on 12 July 1855. On 3 June 1859, ''Victoria and Albert'' ran aground in the Scheldt whilst on a voyage from Gravesend, Kent to Antwerp, Belgium. Queen Victoria left the ship to Empress Elisabeth of Austria for her cruise to Madeira in 1860. The ship was used by Prince Arthur on the occasion of his visit to Heligoland in 1872.Rüger, p. 68. Queen Victoria sent the ship to Vlissingen to ferry Crown Prince Friedrich Wilhelm of Germany accompanied by his wife Victoria, their three youngest daughters, Professor Gerhardt, two court officials and two ladies-in-waiting across the Channel to be treated of his throat illness in England by Dr. Mackenzie. They alighted in Sheerne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Yacht
A royal yacht is a ship used by a monarch or a royal family. If the monarch is an emperor the proper term is imperial yacht. Most of them are financed by the government of the country of which the monarch is head. The royal yacht is most often crewed by personnel from the navy and used by the monarch and his/her family on both private and official travels. Types of vessels used Some royal yachts have been/are small vessels only used for short trips on rivers or in calm waters, but others have been/are large seaworthy ships. History Depending on how the term is defined royal yachts date back to the days of antiquity with royal barges on the Nile in ancient Egypt. Later the Vikings produced royal vessels. They followed the pattern of longships although highly decorated and fitted with purple sails (purple sails remained standard for royal vessels the next 400 years). In England, Henry V sold off the royal yachts to clear the Crown's debts. The next royal vessels in England were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midshipman
A midshipman is an officer of the lowest rank, in the Royal Navy, United States Navy, and many Commonwealth navies. Commonwealth countries which use the rank include Canada (Naval Cadet), Australia, Bangladesh, Namibia, New Zealand, South Africa, India, Pakistan, Singapore, Sri Lanka, and Kenya. In the 17th century, a midshipman was a rating for an experienced seaman, and the word derives from the area aboard a ship, amidships, either where he worked on the ship, or where he was berthed. Beginning in the 18th century, a commissioned officer candidate was rated as a midshipman, and the seaman rating began to slowly die out. By the Napoleonic era (1793–1815), a midshipman was an apprentice officer who had previously served at least three years as a volunteer, officer's servant or able seaman, and was roughly equivalent to a present-day petty officer in rank and responsibilities. After serving at least three years as a midshipman or master's mate, he was eligible to take the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stubbington House School
Stubbington House School was founded in 1841 as a boys' preparatory school, originally located in the Hampshire village of Stubbington, around from the Solent. Stubbington House School was known by the sobriquet "the cradle of the Navy". The school was relocated to Ascot in 1962, merging with Earleywood School, and it closed in 1997. History Donald Leinster-Mackay, an academic researcher into the history of education, has said that "No school had stronger ties with the Royal Navy in the nineteenth century than Stubbington House." The school was founded in 1841 by the Reverend William Foster, who had been born around 1802 and was an alumnus of Trinity College, Cambridge. He had married Laura, a daughter of Rear-Admiral John Hayes, and it is probable that this accounts for the connection with the navy that the school developed. Another factor affecting its primary purpose was the introduction in 1838 of an entrance examination for the Royal Navy: although initially an undemandin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Cochrane
Two ships and a shore establishment of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMS ''Cochrane'', after Admiral Thomas Cochrane, 10th Earl of Dundonald: * was a armoured cruiser The armored cruiser was a type of warship of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. It was designed like other types of cruisers to operate as a long-range, independent warship, capable of defeating any ship apart from a battleship and fast eno ... launched in 1905. She was stranded in 1918 and broken up. * HMS ''Cochrane'' was a depot ship, formerly an armed merchant cruiser, commissioned in 1914 and purchased in 1915 as . She was renamed HMS ''Cochrane'' in 1938 and was broken up in 1946. * was the Rosyth naval base commissioned in 1938. It was paid off in 1947 but restored in 1948, taking over from HMS ''Lochinvar''. The base closed in 1962, was recommissioned in 1968 and was finally closed in 1996. The bust of Admiral Cochrane by Scott Sutherland which was commissioned for the base can now be seen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_2017-08-16.jpg)
