|
William H. Peirce
William H. Peirce (died 1944) was an Americans, American civil engineer and metallurgist, who pioneered copper extraction techniques, copper production in the early 20th century. Among his achievements was the , invented with Elias Anton Cappelen Smith. Life He joined the ''Baltimore Copper Smelting & Rolling Company'' in 1890, becoming vice president in 1895, and later, president of the company. Under his management, the company became one of the major copper producer of the United States. In 1928, the company merged with five other copper companies, to create the Revere Copper Company. Described as "one of the foremost metallurgists of his time", Peirce became the vice president, director and a member of the Executive Committee of Revere from its incorporation in 1928 until his resignation in 1933. Invention of the Peirce–Smith converter The , developed in 1908 with Elias Anton Cappelen Smith, significantly improved the Converting (metallurgy), converting of copper Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Americans
Americans are the Citizenship of the United States, citizens and United States nationality law, nationals of the United States, United States of America.; ; Although direct citizens and nationals make up the majority of Americans, many Multiple citizenship, dual citizens, expatriates, and green card, permanent residents could also legally claim American nationality. The United States is home to race and ethnicity in the United States, people of many racial and ethnic origins; consequently, culture of the United States, American culture and Law of the United States, law do not equate nationality with Race (human categorization), race or Ethnic group, ethnicity, but with citizenship and an Oath of Allegiance (United States), oath of permanent allegiance. Overview The majority of Americans or their ancestors Immigration to the United States, immigrated to the United States or are descended from people who were Trans Atlantic Slave Trade, brought as Slavery in the United States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequence of database operations that satisfies the ACID properties (which can be perceived as a single logical operation on the data) is called a ''transaction''. For example, a transfer of funds from one bank account to another, even involving multiple changes such as debiting one account and crediting another, is a single transaction. In 1983, Andreas Reuter and Theo Härder coined the acronym ''ACID'', building on earlier work by Jim Gray who named atomicity, consistency, and durability, but not isolation, when characterizing the transaction concept. These four properties are the major guarantees of the transaction paradigm, which has influenced many aspects of development in database systems. According to Gray and Reuter, the IBM Informa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Civil Engineers
American(s) may refer to: * American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America" ** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America ** American ancestry, people who self-identify their ancestry as "American" ** American English, the set of varieties of the English language native to the United States ** Native Americans in the United States, indigenous peoples of the United States * American, something of, from, or related to the Americas, also known as "America" ** Indigenous peoples of the Americas * American (word), for analysis and history of the meanings in various contexts Organizations * American Airlines, U.S.-based airline headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas * American Athletic Conference, an American college athletic conference * American Recordings (record label), a record label previously known as Def American * American University, in Washington, D.C. Sports teams Soccer * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Douglas (businessman)
James Walter Douglas (4 November 1837 – 25 June 1918) was a Canadian born mining engineer and businessman who introduced a number of metallurgical innovations in copper mining and amassed a fortune through the copper mining industry of Arizona and Sonora. Life James Walter Douglas Jr. was born in Quebec City, Quebec on 4 November 1837. His father James Douglas Sr., a native of Scotland, was an eminent surgeon and manager of the Beauport Lunatic Asylum. His mother, Elizabeth Ferguson, was also a native of Scotland. James Douglas graduated from Queen’s College, Kingston, Upper Canada in 1858 and continued his studies at the University of Edinburgh. He studied both medicine and theology with the intent of becoming a minister but was never ordained. For several years he served as professor of chemistry at Morrin College, Quebec, and in 1864 became managing director of the Harvey Hill Copper Company in Quebec. In 1875, he moved to the United States to take charge of the copp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnesium Oxide
Magnesium oxide ( Mg O), or magnesia, is a white hygroscopic solid mineral that occurs naturally as periclase and is a source of magnesium (see also oxide). It has an empirical formula of MgO and consists of a lattice of Mg2+ ions and O2− ions held together by ionic bonding. Magnesium hydroxide forms in the presence of water (MgO + H2O → Mg(OH)2), but it can be reversed by heating it to remove moisture. Magnesium oxide was historically known as magnesia alba (literally, the white mineral from Magnesia), to differentiate it from ''magnesia negra'', a black mineral containing what is now known as manganese. Related oxides While "magnesium oxide" normally refers to MgO, the compound magnesium peroxide MgO2 is also known. According to evolutionary crystal structure prediction, MgO2 is thermodynamically stable at pressures above 116 GPa (gigapascals), and a semiconducting suboxide Mg3O2 is thermodynamically stable above 500 GPa. Because of its stability, MgO is used as a model sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base (chemistry)
In chemistry, there are three definitions in common use of the word base, known as Arrhenius bases, Brønsted bases, and Lewis bases. All definitions agree that bases are substances that react with acids, as originally proposed by G.-F. Rouelle in the mid-18th century. In 1884, Svante Arrhenius proposed that a base is a substance which dissociates in aqueous solution to form Hydroxide ions OH−. These ions can react with hydrogen ions (H+ according to Arrhenius) from the dissociation of acids to form water in an acid–base reaction An acid–base reaction is a chemical reaction that occurs between an acid and a base. It can be used to determine pH via titration. Several theoretical frameworks provide alternative conceptions of the reaction mechanisms and their applica .... A base was therefore a metal hydroxide such as Sodium hydroxide, NaOH or Calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2. Such aqueous hydroxide solutions were also described by certain characteristic properties. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfide
Sulfide (British English also sulphide) is an inorganic anion of sulfur with the chemical formula S2− or a compound containing one or more S2− ions. Solutions of sulfide salts are corrosive. ''Sulfide'' also refers to chemical compounds large families of inorganic and organic compounds, e.g. lead sulfide and dimethyl sulfide. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and bisulfide (SH−) are the conjugate acids of sulfide. Chemical properties The sulfide ion, S2−, does not exist in aqueous alkaline solutions of Na2S. Instead sulfide converts to hydrosulfide: :S2− + H2O → SH− + OH− Upon treatment with an acid, sulfide salts convert to hydrogen sulfide: :S2− + H+ → SH− :SH− + H+ → H2S Oxidation of sulfide is a complicated process. Depending on the conditions, the oxidation can produce elemental sulfur, polysulfides, polythionates, sulfite, or sulfate. Metal sulfides react with halogens, forming sulfur and metal salts. :8 MgS + 8 I2 → S8 + 8 M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bessemer Process
The Bessemer process was the first inexpensive industrial process for the mass production of steel from molten pig iron before the development of the open hearth furnace. The key principle is steelmaking, removal of impurities from the iron by oxidation with air being blown through the molten iron. The oxidation also raises the temperature of the iron mass and keeps it molten. Related Decarburization, decarburizing with air processes had been used outside Europe for hundreds of years, but not on an industrial scale. One such process (similar to puddling (metallurgy), puddling) was known in the 11th century in East Asia, where the scholar Shen Kuo of that era described its use in the Chinese iron and steel industry. In the 17th century, accounts by European travelers detailed its possible use by the Japanese. The modern process is named after its inventor, the Englishman Henry Bessemer, who took out a patent on the process in 1856. The process was said to be independently discover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
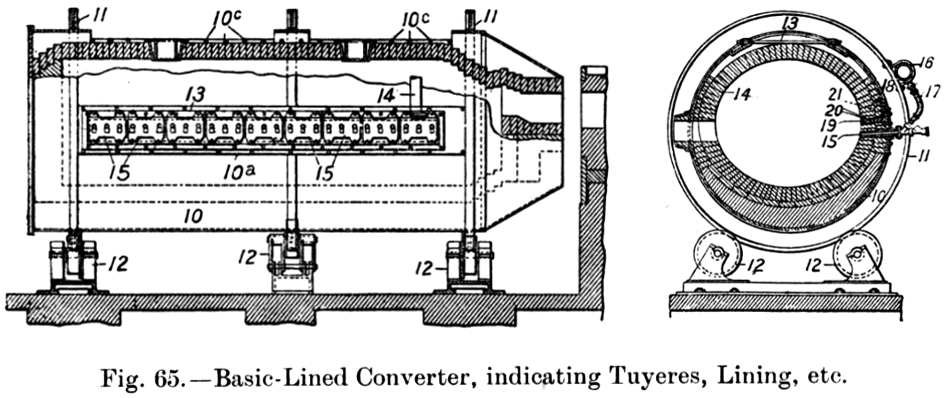
Manhès–David Process
The Manhès–David process is a refining process of the copper mattes, invented in 1880 by the French industrialist Pierre Manhès and his engineer . Inspired by the Bessemer process, it consists of the use of a converter to oxidise with air the undesirable chemical elements (mainly iron and sulfur) contained in the matte, to transform it into copper. The quantity of the elements to be oxidized, as well as the low heat produced by the chemical reactions, lead to drastics modifications of the converter. Manhès and David designed it as a horizontal cylinder, with nozzles aligned from one end to the other. A few years later, the Americans engineers William H. Peirce and Elias Anton Cappelen Smith lined it with basic refractory materials, much more durable than that used by the French inventors. While this improvement does not alter the principles of the process, it eases its widespread use, accelerating the switchover of copper production from Britain to the United States. At ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Manhès
Pierre Manhès (1841 – 1906) was a French metallurgist and businessman, who succeeded in 1880 to adapt the Bessemer process to the pyrometallurgy of the copper. With his engineer , he developed the Manhès-David process and converter, which were widely adopted, mainly in the United States. In 1883, under license to use the patented process Franklin Farrel introduced the Manhes-David furnace at the Parrot smelter in Butte, Montana. Its successly adoption was followed by Anaconda at Butte, Copper Queen at Bisbee, Arizona, United Verde, Jerome, Arizona Jerome is a town in the Black Hills of Yavapai County in the U.S. state of Arizona. Founded in the late 19th century on Cleopatra Hill overlooking the Verde Valley, Jerome is located more than above sea level. It is about north of Phoenix alo ..., and other plants by the 1890s. Before the adoption of the process, copper mines in the Western United States produced only matte, which required further, costly purification ste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matte (metallurgy)
Matte is a term used in the field of pyrometallurgy given to the molten metal sulfide phases typically formed during smelting of copper, nickel, and other base metals. Typically, a matte is the phase in which the principal metal being extracted is recovered prior to a final reduction process (usually converting) to produce blister copper. The matte may also collect some valuable minor constituents such as noble metals, minor base metals, selenium or tellurium. Mattes may also be used to collect impurities from a metal phase, such as in the case of antimony smelting. Molten mattes are insoluble in both slag Slag is a by-product of smelting (pyrometallurgical) ores and used metals. Broadly, it can be classified as ferrous (by-products of processing iron and steel), ferroalloy (by-product of ferroalloy production) or non-ferrous/base metals (by-prod ... and metal phases. This insolubility, combined with differences in specific gravities between mattes, slags, and metals, allows ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Engineer
A civil engineer is a person who practices civil engineering – the application of planning, designing, constructing, maintaining, and operating infrastructure while protecting the public and environmental health, as well as improving existing infrastructure that may have been neglected. Civil engineering is one of the oldest engineering disciplines because it deals with constructed environment including planning, designing, and overseeing construction and maintenance of building structures, and facilities, such as roads, railroads, airports, bridges, harbors, channels, dams, irrigation projects, pipelines, power plants, and water and sewage systems. The term "civil engineer" was established by John Smeaton in 1750 to contrast engineers working on civil projects with the military engineers, who worked on armaments and defenses. Over time, various sub-disciplines of civil engineering have become recognized and much of military engineering has been absorbed by civil engineering. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)



