|
William Cook (scientist)
Sir William Richard Joseph Cook, (10 April 1905 – 16 September 1987) was a British civil servant and mathematician. A graduate of Bristol University, he joined the staff of the Woolwich Arsenal in 1928, working on the 6-inch naval guns and the 3-inch antiaircraft rocket. During the Second World War he was deputy controller of the Projectile Development Establishment. After the war he became director of the Ministry of Supply's Rocket Propulsion Establishment at Westcott, Buckinghamshire. In 1947 he joined the Royal Naval Scientific Service, serving as its chief from 1950 to 1954, when he became deputy head of the Weapons Group of the newly created United Kingdom Atomic Energy Authority (UKAEA). It was under his leadership that Britain developed the hydrogen bomb, and he was present as the scientific director of the Operation Grapple nuclear tests at Malden Island in May and June 1957, and the successful thermonuclear test at Christmas Island in November 1957. In 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trowbridge, Wiltshire
Trowbridge ( ) is the county town of Wiltshire, England, on the River Biss in the west of the county. It is near the border with Somerset and lies southeast of Bath, 31 miles (49 km) southwest of Swindon and 20 miles (32 km) southeast of Bristol. The town had a population of 37,169 in 2021. Long a market town, the Kennet and Avon canal to the north of Trowbridge played an instrumental part in the town's development as it allowed coal to be transported from the Somerset Coalfield and so marked the advent of steam-powered manufacturing in woollen cloth mills. The town was the foremost producer of this mainstay of contemporary clothing and blankets in south west England in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, by which time it held the nickname "The Manchester of the West". The civil parish of Trowbridge had a population of 33,108 at the 2011 census. The parish encompasses the settlements of Longfield, Lower Studley, Upper Studley, Studley Green and Trowle Commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
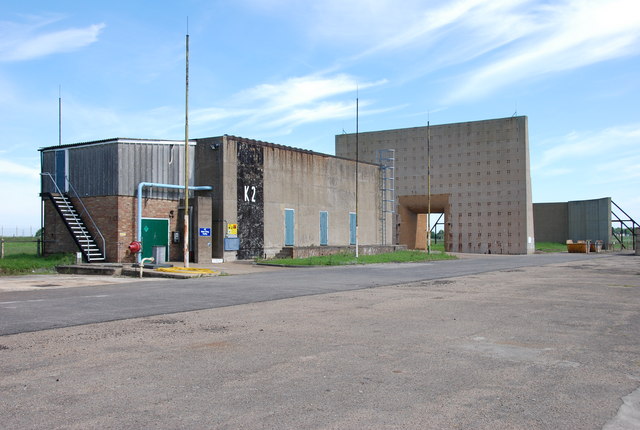
Rocket Propulsion Establishment
The Rocket Propulsion Establishment at Westcott, Buckinghamshire on the site of the former RAF Westcott has made a number of notable contributions in the field of rocket propulsion, including input on the rocket design for the Blue Streak missile and the propulsion systems on Chevaline. It was also known as the Guided Projectiles Establishment and PERME Westcott (Propellants, Explosives and Rocket Motor Establishment, Westcott). For many years this establishment was regarded as so secret that it was not marked on Ordnance Survey maps, although it was present, from necessity, on maps for the use of pilots. History The establishment was set up in April 1946 under the Ministry of Supply. In the initial years a team of German scientists worked at the site, and examples of German weapons were on-site for study. These included the V-1 flying bomb; V-2; Feuerlilie F-55 subsonic missile; Messerschmitt Me 163B rocket-propelled interceptor; Rheintochter-1 anti-aircraft missile; Ruhrstah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FH70
The FH70 (field howitzer for the 1970s) is a towed howitzer in use with several nations. History In 1963, NATO agreed a NATO Basic Military Requirement 39 for close support artillery, either towed or tracked. Subsequently, Germany and UK started discussions and design studies and in 1968 established agreed operational characteristics for a towed 155 mm close support gun. Italy became a party to the agreement in 1970. Key requirements were: * A detachable auxiliary power unit (APU) * An unassisted range of ; an assisted range of * A burst capability of three rounds in 15–20 seconds, six rounds per minute for a short period and two rounds per minute sustained * The ablility to fire all 155 mm munitions in NATO service, plus a new range of ammunition. The two national authorities had overall responsibility for R&D, and Vickers Ltd was the co-ordinating design authority. They were also the design authority for the carriage and Rheinmetall GmbH was the authority fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SEPECAT Jaguar
The SEPECAT Jaguar is an Anglo-French jet attack aircraft originally used by the British Royal Air Force and the French Air Force in the close air support and nuclear strike role. It is still in service with the Indian Air Force. Originally conceived in the 1960s as a jet trainer with a light ground attack capability, the requirement for the aircraft soon changed to include supersonic performance, reconnaissance and tactical nuclear strike roles. A carrier-based variant was also planned for French Navy service, but this was cancelled in favour of the cheaper, fully French-built Dassault-Breguet Super Étendard. The aircraft were manufactured by SEPECAT (Société Européenne de Production de l'avion Ecole de Combat et d'Appui Tactique), a joint venture between Breguet and the British Aircraft Corporation, one of the first major joint Anglo-French military aircraft programmes. The Jaguar was exported to India, Oman, Ecuador and Nigeria. The aircraft was used in numerous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface-to-air Missile
A surface-to-air missile (SAM), also known as a ground-to-air missile (GTAM) or surface-to-air guided weapon (SAGW), is a missile designed to be launched from the ground to destroy aircraft or other missiles. It is one type of anti-aircraft system; in modern armed forces, missiles have replaced most other forms of dedicated anti-aircraft weapons, with anti-aircraft guns pushed into specialized roles. The first attempt at SAM development took place during World War II, but no operational systems were introduced. Further development in the 1940s and 1950s led to operational systems being introduced by most major forces during the second half of the 1950s. Smaller systems, suitable for close-range work, evolved through the 1960s and 1970s, to modern systems that are man-portable. Shipborne systems followed the evolution of land-based models, starting with long-range weapons and steadily evolving toward smaller designs to provide a layered defence. This evolution of design increasin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
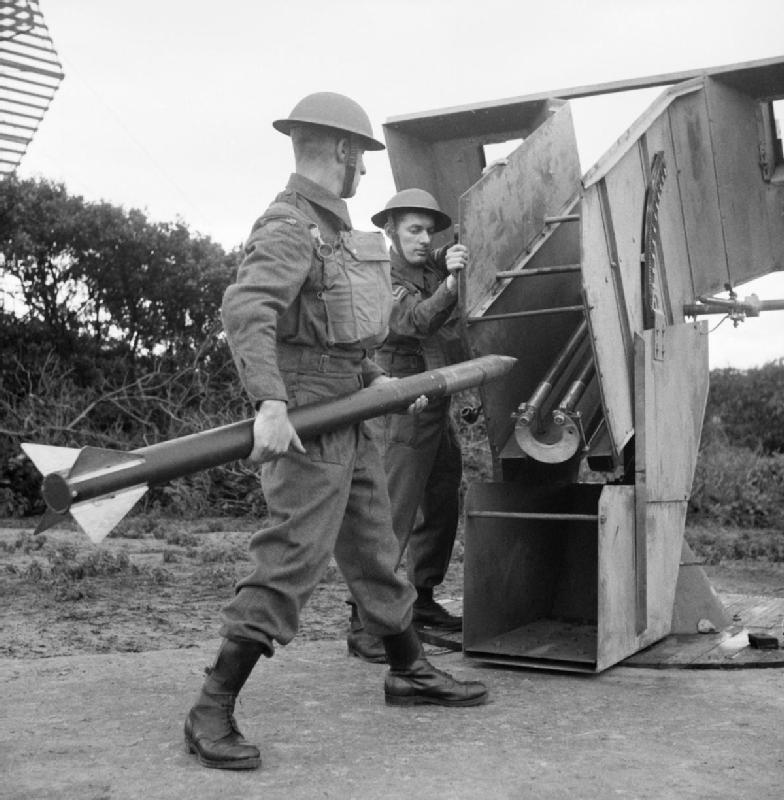
Rapier (missile)
Rapier is a surface-to-air missile developed for the British Army to replace their towed Bofors 40/L70 anti-aircraft guns. The system is unusual as it uses a manual optical guidance system, sending guidance commands to the missile in flight over a radio link. This results in a high level of accuracy, therefore a large warhead is not required. Entering service in 1971, it eventually replaced all other anti-aircraft weapons in British Army service; both the Bofors guns used against low-altitude targets and the Thunderbird missile used against longer-range and higher-altitude targets. As the expected air threat moved from medium-altitude strategic missions to low-altitude strikes, the fast reaction time and high manoeuvrability of the Rapier made it more effective than either of these weapons, replacing most of them by 1977. Rapier was later selected by the RAF Regiment to replace their Bofors guns and Tigercat missiles. It also saw international sales. As of 2021, it was in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panavia Tornado
The Panavia Tornado is a family of twin-engine, variable-sweep wing multirole combat aircraft, jointly developed and manufactured by Italy, the United Kingdom and West Germany. There are three primary Tornado variants: the Tornado IDS (interdictor/strike) fighter-bomber, the suppression of enemy air defences Tornado ECR (electronic combat/reconnaissance) and the Tornado ADV (air defence variant) interceptor aircraft. The Tornado was developed and built by Panavia Aircraft GmbH, a tri-national consortium consisting of British Aerospace (previously British Aircraft Corporation), MBB of West Germany, and Aeritalia of Italy. It first flew on 14 August 1974 and was introduced into service in 1979–1980. Due to its multirole design, it was able to replace several different fleets of aircraft in the adopting air forces. The Royal Saudi Air Force (RSAF) became the only export operator of the Tornado in addition to the three original partner nations. A tri-nation training and ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chief Scientific Adviser To The Ministry Of Defence
The Chief Scientific Adviser to the UK's Ministry of Defence is responsible for providing strategic management of science and technology issues in the MOD, most directly through the MOD research budget of well over £1 billion, and sits as a full member of the Defence Management Board and the Defence Council, the two most senior management boards within the MOD. There is also a Chief Scientific Adviser (Nuclear), responsible for the MOD’s nuclear science and technology programme, currently held by Professor Robin Grimes. List of MOD Chief Scientific Advisers * Sir Henry Tizard, 1946–1952 * Sir John Cockcroft, 1952–1954 * Sir Frederick Brundrett, 1954–1960 * Sir Solly Zuckerman, 1960–1965 * Sir Alan Cottrell, 1966–1967 * Sir William Cook, 1966–1970 * Sir Hermann Bondi, 1971–1977 * Sir Ronald Mason, 1977–1983 * Sir Richard Oswald Chandler Norman, 1983–1988 * Sir Ronald Oxburgh, 1988–1993 * Sir David Davies, 1993–1999 * Sir Keith O'Nions, 2000–2004 * S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Defence (United Kingdom)
The Ministry of Defence (MOD or MoD) is the department responsible for implementing the defence policy set by His Majesty's Government, and is the headquarters of the British Armed Forces. The MOD states that its principal objectives are to defend the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and its interests and to strengthen international peace and stability. The MOD also manages day-to-day running of the armed forces, contingency planning and defence procurement. The expenditure, administration and policy of the MOD are scrutinised by the Defence Select Committee, except for Defence Intelligence which instead falls under the Intelligence and Security Committee of Parliament. History During the 1920s and 1930s, British civil servants and politicians, looking back at the performance of the state during the First World War, concluded that there was a need for greater co-ordination between the three services that made up the armed forces of the United Kingdom: t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
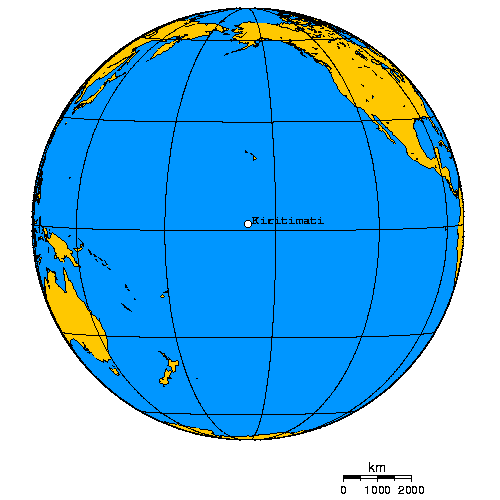
Kiritimati
Kiritimati (also known as Christmas Island) is a Pacific Ocean atoll in the northern Line Islands. It is part of the Republic of Kiribati. The name is derived from the English word "Christmas" written in Gilbertese according to its phonology, in which the combination ''ti'' is pronounced ''s'', giving kiˈrɪsmæs. Kiritimati has the greatest land area of any atoll in the world, about ; its lagoon is roughly the same size. The atoll is about in perimeter, while the lagoon shoreline extends for over . Kiritimati comprises over 70% of the total land area of Kiribati, a country encompassing 33 Pacific atolls and islands. It lies north of the equator, south of Honolulu, and from San Francisco. Kiritimati is in the world's farthest forward time zone, UTC+14, and is therefore one of the first inhabited places on Earth to experience New Year's Day. (see also Caroline Atoll, Kiribati). Although it lies east of the 180th meridian, the Republic of Kiribati realigned the Internati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malden Island
Malden Island, sometimes called Independence Island in the 19th century, is a low, arid, uninhabited atoll in the central Pacific Ocean, about in area. It is one of the Line Islands belonging to the Republic of Kiribati. The lagoon is entirely enclosed by land, though it is connected to the sea by underground channels, and is quite salty. The island is chiefly notable for its ancient stone architecture, its once-extensive deposits of phosphatic guano (exploited by Australian interests from 1860–1927), its former use as the site of the first British H-bomb tests (Operation Grapple, 1957), and its current importance as a protected area for breeding seabirds. The island is designated as the ''Malden Island Wildlife Sanctuary''. In 2014 the Kiribati government established a fishing exclusion zone around each of the southern Line Islands ( Caroline (commonly called Millennium), Flint, Vostok, Malden, and Starbuck). Geography Malden Island is located south of the equator, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Grapple
Operation Grapple was a set of four series of British nuclear weapons tests of early atomic bombs and hydrogen bombs carried out in 1957 and 1958 at Malden Island and Kiritimati (Christmas Island) in the Gilbert and Ellice Islands in the Pacific Ocean (modern Kiribati) as part of the British hydrogen bomb programme. Nine nuclear explosions were initiated, culminating in the United Kingdom becoming the third recognised possessor of thermonuclear weapons, and the restoration of the nuclear Special Relationship with the United States in the form of the 1958 US–UK Mutual Defence Agreement. During the Second World War, Britain had a nuclear weapons project, codenamed Tube Alloys, which was merged with the American Manhattan Project in August 1943. Many of Britain's top scientists participated in the Manhattan Project. After the war, fearing that Britain would lose its great power status, the British government resumed the atomic bomb development effort, now codenamed High Expl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)
_(Tony_Radakin_cropped).jpg)

.jpg)