|
Willehari
Willehari or Willihari ( la, italic=yes, Vilarius, ''Wilharius'', ''Willeharius'', or ''Willicharius'') was an Alemannic duke (''dux'') in the Ortenau in the early eighth century. According to the ''Vita Sancti Desiderii'', Pepin of Heristal of the Franks, led two expeditions against Willehari in 709 and 712. It is unknown why Pepin intervened in Alemannia at this time, but it is likely that he was trying to affirm Frankish suzerainty by upholding the rights of succession of Lantfrid and Theudebald, the sons of the late duke Gotfrid, whom Willehari may have been elected to replace. It is possible that Alemannia was not united at this time and that several different regions were ruled separately by different families. Alsace, for one, was definitely ruled by another family, the Etichonids, and elsewhere it is likely that the Ahalolfings were in power. Sources *Geuenich, Dieter. ''Geschichte der Alemannen''. Kohlhammer Verlag W. Kohlhammer Verlag GmbH, or Kohlhammer Verlag, is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lantfrid
Lantfrid (also ''Landfrid'' or ''Lanfred'', Latinised ''Lantfridus'' or ''Lanfredus'') (died 730) was duke of Alamannia under Frankish sovereignty from 709 until his death. He was the son of duke Gotfrid. Lantfrid's brother was Theudebald. Following Gotfrid's death in 709 and the accession of Lantfrid and his brother Theudebald, the Frankish '' maior domus'' Pepin of Herstal invaded Alamannia and fought against yet another duke, Willehari, whose territory was restricted to the Ortenau in western Alamannia. This campaign can be seen as an attempt by Pepin to impose royal authority on the duchy following the death of Gotfrid and also to assert his right to influence or even control the succession within the duchy. Pepin’s campaign against Willehari might therefore have taken place to assist Lantfrid and Theudebald in their claim to the duchy. However, both Lantfrid and Theudebald were hostile to Pepin’s successor. After Pipin’s death in 714, Lantfrid dissolved all links wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alemanni
The Alemanni or Alamanni, were a confederation of Germanic tribes * * * on the Upper Rhine River. First mentioned by Cassius Dio in the context of the campaign of Caracalla of 213, the Alemanni captured the in 260, and later expanded into present-day Alsace, and northern Switzerland, leading to the establishment of the Old High German language in those regions, by the eighth century named '' Alamannia''. In 496, the Alemanni were conquered by Frankish leader Clovis and incorporated into his dominions. Mentioned as still pagan allies of the Christian Franks, the Alemanni were gradually Christianized during the seventh century. The is a record of their customary law during this period. Until the eighth century, Frankish suzerainty over Alemannia was mostly nominal. After an uprising by Theudebald, Duke of Alamannia, though, Carloman executed the Alamannic nobility and installed Frankish dukes. During the later and weaker years of the Carolingian Empire, the Alemannic co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
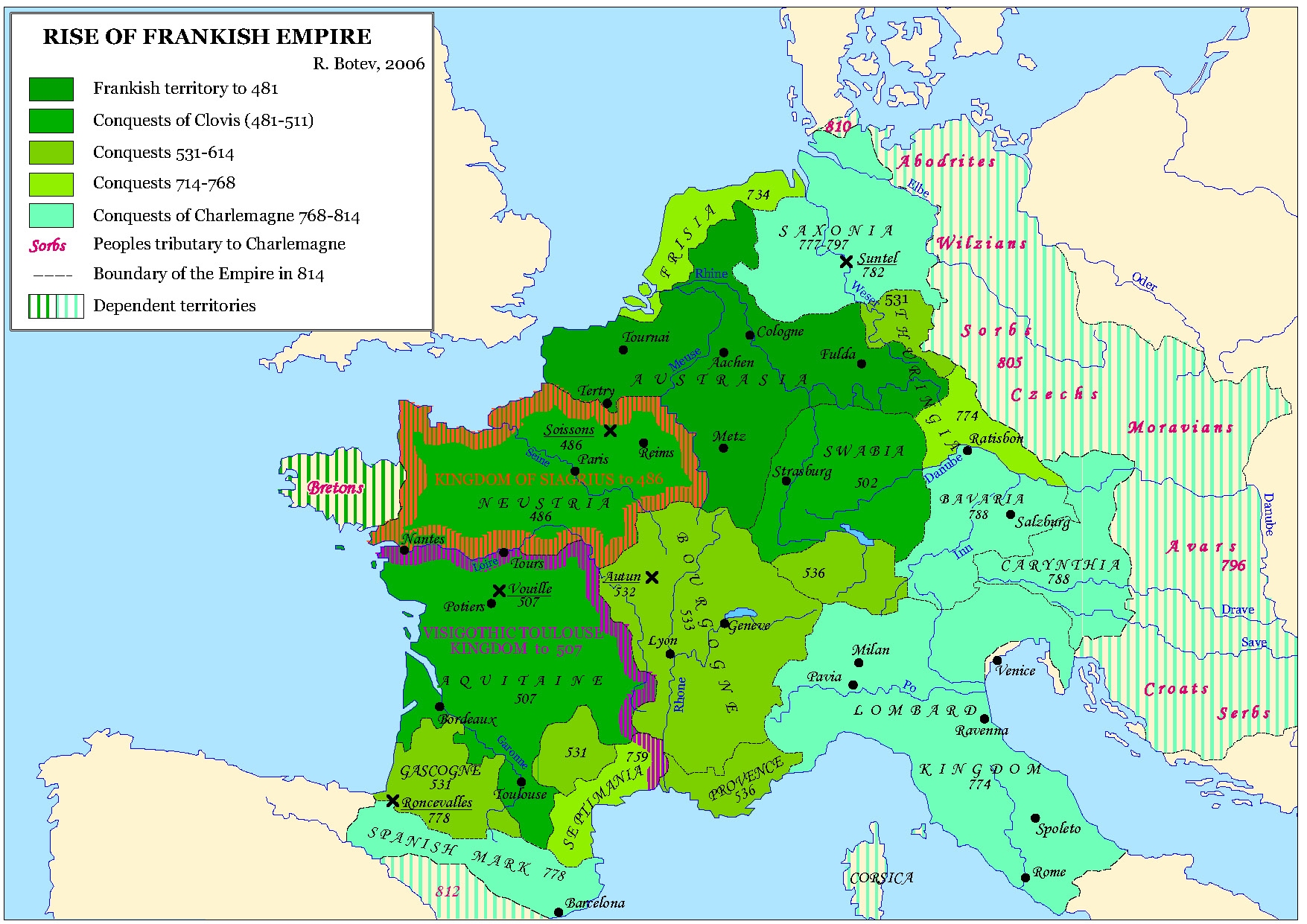
Ortenau
The Ortenau, originally called Mortenau, is a historic region in the present-day German state of Baden-Württemberg. It is located on the right bank of the river Rhine, stretching from the Upper Rhine Plain to the foothill zone of the Black Forest. In the south, it borders on the Breisgau region, covering approximately the same area as the Ortenaukreis, a present-day administrative district with its centre at Offenburg. History The region was first mentioned as ''Mordunouva'' in a 763 deed. Then an early medieval county ('' Gau'') in the German stem duchy of Swabia, it received its name from a fortification near Ortenberg at the site of later Ortenberg Castle. In 1007, King Henry II enfeoffed the Bishops of Bamberg with the Ortenau estates. However, as the bishops were not able to control their remote Swabian lands themselves, they entrusted the rule to the local noble House of Zähringen. When the Zähringen dukes became extinct in 1218, quarrels broke out over their suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pepin Of Heristal
Pepin II (c. 635 – 16 December 714), commonly known as Pepin of Herstal, was a Frankish statesman and military leader who de facto ruled Francia as the Mayor of the Palace from 680 until his death. He took the title Duke and Prince of the Franks upon his conquest of all the Frankish realms. The son of the powerful Frankish statesman Ansegisel, Pepin worked to establish his family, the Pippinids, as the strongest in Francia. He became Mayor of the Palace in Austrasia in 680. Pepin subsequently embarked on several wars to expand his power. He united all the Frankish realms by the conquests of Neustria and Burgundy in 687. In foreign conflicts, Pepin increased the power of the Franks by his subjugation of the Alemanni, the Frisians, and the Franconians. He also began the process of evangelisation in Germany. Pepin's statesmanship was notable for the further diminution of Merovingian royal authority, and for the acceptance of the undisputed right to rule for his family. Therefor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, Weapons and Ornaments: Germanic Material Culture in Pre-Carolingian Central Europe, 400-750. BRILL, 2001, p.42. Later the term was associated with Romanized Germanic dynasties within the collapsing Western Roman Empire, who eventually commanded the whole region between the rivers Loire and Rhine. They imposed power over many other post-Roman kingdoms and Germanic peoples. Beginning with Charlemagne in 800, Frankish rulers were given recognition by the Catholic Church as successors to the old rulers of the Western Roman Empire. Although the Frankish name does not appear until the 3rd century, at least some of the original Frankish tribes had long been known to the Romans under their own names, both as allies providing soldiers, and as e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theudebald, Duke Of Alamannia
Theudebald or Theutbald was the Duke of Alamannia from 730 until his deposition. He was a son of Gotfrid and brother and co-ruler with Lantfrid from 709. In 727, Theudebald expelled Pirmin, the founder of Reichenau Abbey, out of a hatred for Charles Martel (''ob odium Karoli''), whose influence in Alamannia he detested. During a military campaign in 730, Lantfrid was killed and Theudebald became sole duke. In 732, Theudebald was chased out of Alemannia by Charles Martel, but upon Charles' death in 741 he returned to claim his dukedom. In 742, Theudebald rebelled against the nominal authority of the Merovingian monarchy which was then being exercised by the two mayors of the palace Pepin the Short and Carloman; the Basques, Bavarii, and Saxons all revolted simultaneously. That same year Theudebald invaded the Duchy of Alsace, then ruled by Duke Liutfrid. The Alsatian duke was probably killed alongside his son fighting for the mayors. In 744, Pepin invaded the Swabian Jura and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gotfrid
:''See Gottfried for the given name.'' Gotfrid (also ''Gotefrid'', modernized ''Gottfried''; la, Gotfridus or ''Cotefredus''; (c. 650–709) was the Duke of Alemannia in the late seventh century and until his death. He was of the house of the Agilolfing, which was the dominant ruling family in the Frankish Duchy of Bavaria. In a document dated to the year 700 in Cannstatt, Gotfrid at the request of a priest named Magulfus donated the castle of Biberburg to the monastery of Saint Gall. Gotfrid fought a war over his ''de facto'' independence with the mayor of the palace Pepin of Heristal. The war was unfinished when Gotfrid died in 709. His sons, Lantfrid and Theudebald, had the support of Pepin and succeeded him. It has often been stated that Gotfrid married a daughter of Theodo of Bavaria, but there is no conclusive evidence to support this assertion. It is largely based on conjecture, due to the fact that his third son, Odilo, later ruled in Bavaria. Furthermore, Gotfried ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Alsace
The Duchy of Alsace ( la, Ducatus Alsacensi, ''Ducatum Elisatium''; german: Herzogtum Elsaß) was a large political subdivision of the Frankish Empire during the last century and a half of Merovingian rule. It corresponded to the territory of Alsace and was carved out of southern Austrasia in the last decade of the reign of Dagobert I, probably to stabilise the southern reaches of Austrasia against Alemannia and Burgundy. By the late Middle Ages, the region was considered part of Swabia. Foundation The term "Alsace" derives from the Germanic ''ali-land-sat-ja'', meaning "one who sits in another land." Alsace was Alemanni territory, but not so much as Alemannia proper, which was east of the Rhine: it was, however, the "other" land in which some Alemanni had settled. In the late Roman Empire, a district of Alsace (''pagus Alsatiae'') had been established in the region. Under Chlothar II, Alsace and Alemannia were granted their own law, the ''Pactus Alamannorum''. In 596, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etichonids
The Etichonids were an important noble family, probably of Frankish, Burgundian or Visigothic origin, who ruled the Duchy of Alsace in the Early Middle Ages (7th–10th centuries). The dynasty is named for Eticho (also known as Aldarich), who ruled from 662 to 690. The earliest accounts record the family's beginnings in the '' pagus Attoariensis'' around Dijon in northern Burgundy. In the mid-7th century a duke of the region named Amalgar and his wife Aquilina are noticed as major founders and patrons of monasteries. King Dagobert I and his father made donations to them to recover their loyalty and compensate them for the losses that they had sustained as supporters of Queen Brunhild and her grandson, Sigebert II. Amalgar and his wife founded a convent at Brégille and an abbey at Bèze, installing a son and daughter in the abbacies. They were succeeded by their third child, Adalrich,He is referred to as Liutheric, a mayor of the palace, in the ''Life of Odilia''. who was the fat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahalolfings
The Alaholfings (occasionally Ahalolfings) were a noble family of Alemannia in the Early Middle Ages. They were related to the previous rulers of Alemannia, to the Bavarian Agilolfings and to the Geroldings. Their original power base was around the upper Neckar and Danube rivers. They came to possess lands in not only Alemannia, but also in Bavaria, Franconia and Italy. The Ahalolfings are divided into two groups, the older and the younger. It is not certain how the two groups are related. The older group descends from a Berthold who was the joint founder, with Hnabi, of Reichenau Abbey in 724. His most famous descendant was Cadolah, Duke of Friuli, who defended the Pannonian plains into Italy from the Avars. Halaholf founded Marchtal Abbey as a proprietary monastery in the mid-8th century. His descendants gave it to the Abbey of Saint Gall in 776. In modern scholarship, the family is named after Halaholf, although in later generations the family's leading name was Berthold. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kohlhammer Verlag
W. Kohlhammer Verlag GmbH, or Kohlhammer Verlag, is a German publishing house headquartered in Stuttgart. History Kohlhammer Verlag was founded in Stuttgart on 30 April 1866 by . Kohlhammer had taken over the businesses of his late father-in-law, a 120-year-old printer and a profitable . The printing business, operating out of the back of a commercial building at 14 Urbanstrasse, became W. Kohlhammer Verlag and was funded by proceeds from the bathhouse until it was closed in 1890. Kohlhammer purchased the ''Deutsche Feuerwehrzeitung'' in 1882 and printed that publication until 1923. In 1872 Kohlhammer started a weekly newspaper, the ''Neue Deutsche Familienblatt'' that by 1914 had a circulation of 185,000. Contemporary Employees of Kohlhammer joined those of other Stuttgart-based companies in early 2016 to petition the mayor to abate traffic congestion hindering their operations inside the city. In 2017, Kohlhammer Verlag employed about 400 people in Stuttgart, Würzburg and Aug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alemannic Rulers
Alemannic (''Alamannic'') or Alamanni may refer to: * Alemannic German, a dialect family in the Upper German branch of the German languages and its speakers * Alemanni, a confederation of Suebian Germanic tribes in the Roman period * Alamanni (surname) See also *Alemannia (other) *Alemannic separatism Alemannic Separatism is a historical movement of separatism of the Alemannic-German-speaking areas of Austria, France, and Germany (viz., South Baden, Swabia (viz. most of Württemberg and Bavarian Swabia), Alsace and Vorarlberg), aiming ... * Allemand (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |