|
Wilgus Site
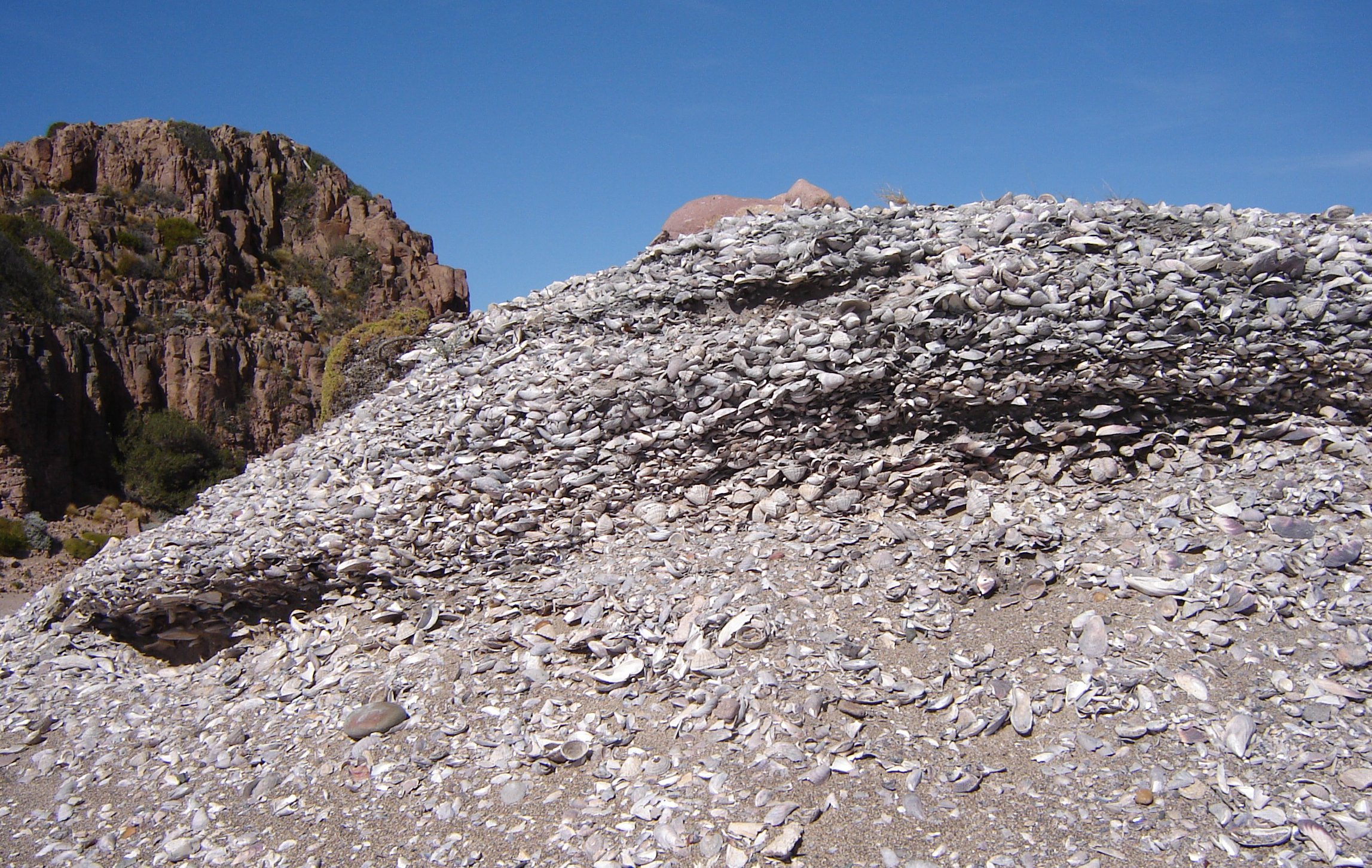
The Wilgus Site is a prehistoric Native American camp site in coastal Sussex County, Delaware, near Bethany Beach. The site is located along a now-inundated tributary of the Indian River, with the main living area of the camp on top of a low knoll. Shell middens and refuse heaps, some as much as in diameter, are located down the slopes of the knoll. Evidence of the site indicates it was occupied during the Adena culture during the Early Woodland Period. The site was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1978. See also *National Register of Historic Places listings in Sussex County, Delaware The following properties are listed on the National Register of Historic Places in Sussex County, Delaware, United States. Contents: Divisions in Delaware ... References Archaeological sites on the National Register of Historic Places in Delaware Sussex County, Delaware ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bethany Beach, Delaware
Bethany Beach is an incorporated town in Sussex County, Delaware, United States. According to the 2010 Census Bureau figures, the population of the town is 1,060; however, during the summer months some 15,000 more populate the town as vacationers. It is part of the Salisbury, MD-DE Metropolitan Statistical Area. Bethany Beach, South Bethany and Fenwick Island are popularly known as "The Quiet Resorts". Contributing to Bethany Beach's reputation as a "quiet" place is the presence of Delaware Seashore State Park immediately to the north of the town. Despite its small size, Bethany Beach contains the usual attractions of a summer seaside resort, including the short Joseph Olson Boardwalk, a broad, sandy beach, motels, restaurants, and vacation homes. Because Bethany Beach does not sit on a barrier island, residential areas continue some distance to the west of the town's limits. Geography Bethany Beach is located at (38.5395564, −75.0551807). The town is bordered to the nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sussex County, Delaware
Sussex County is located in the southern part of the U.S. state of Delaware, on the Delmarva Peninsula. As of the 2020 census, the population was 237,378. The county seat is Georgetown. The first European settlement in the state of Delaware was founded by the Dutch in 1631 near the present-day town of Lewes on the Atlantic Coast. However, Sussex County was not organized until 1683 under English colonial rule. Sussex County is included in the Salisbury, MD-DE Metropolitan Statistical Area which encompasses much of central Delmarva. History Beginnings Archaeologists estimate that the first inhabitants of Sussex County, the southernmost county in Delaware, arrived between 10,000 and 14,000 years ago. Various indigenous cultures occupied the area, especially along the river and the coast, often having seasonal fishing villages. Historic Native Americans in Sussex County were members of Algonquian-speaking tribes, as were most coastal peoples along the Atlantic Coast. By the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian River (Delaware)
The Indian River is a river and estuary, approximately long, in Sussex County in southern Delaware in the United States. The river is named after a Native American reservation that was located on its upper reaches. The Indian River rises approximately southwest of Georgetown and flows east, past Millsboro, its head of navigation. It enters Indian River Bay, an inlet of the Atlantic Ocean south of Cape Henlopen. The lower of the river form a navigable tidal estuary stretching westward from Indian River Bay, which is protected from the open ocean by two sand bar peninsulas. East of the bay is its mouth, the Indian River Inlet. Until 1928, the Indian River Inlet was a natural waterway that shifted up and down a two-mile (3.2 km) stretch of the coast. Dredging kept the inlet open in its current location between 1928 and 1937, and in 1938 the United States Army Corps of Engineers built jetties that hold it in place. Roads cross the river in three places, at U.S. Route 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shell Midden
A midden (also kitchen midden or shell heap) is an old dump for domestic waste which may consist of animal bone, human excrement, botanical material, mollusc shells, potsherds, lithics (especially debitage), and other artifacts and ecofacts associated with past human occupation. These features provide a useful resource for archaeologists who wish to study the diets and habits of past societies. Middens with damp, anaerobic conditions can even preserve organic remains in deposits as the debris of daily life are tossed on the pile. Each individual toss will contribute a different mix of materials depending upon the activity associated with that particular toss. During the course of deposition sedimentary material is deposited as well. Different mechanisms, from wind and water to animal digs, create a matrix which can also be analysed to provide seasonal and climatic information. In some middens individual dumps of material can be discerned and analysed. Shells A shell mid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
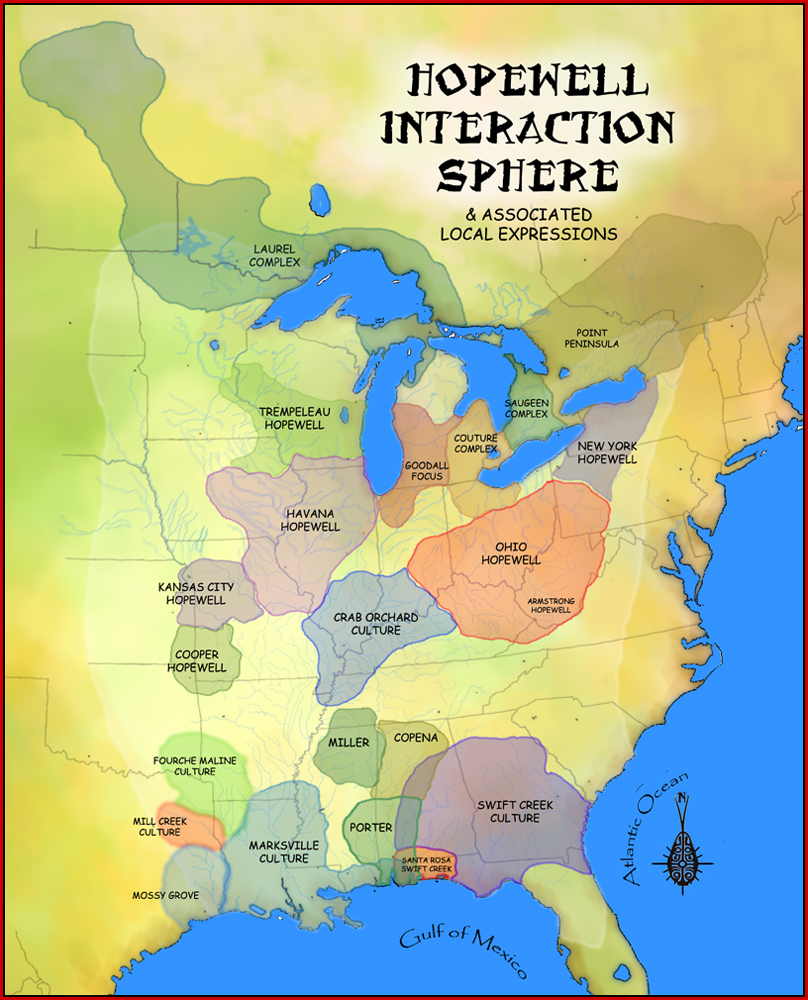
Adena Culture
The Adena culture was a Pre-Columbian Native American culture that existed from 500 BCE to 100 CE, in a time known as the Early Woodland period. The Adena culture refers to what were probably a number of related Native American societies sharing a burial complex and ceremonial system. The Adena culture was centered on the location of the modern state of Ohio, but also extended into contiguous areas of northern Kentucky, eastern Indiana, West Virginia, and parts of extreme western Pennsylvania. Importance The Adena culture was named for the large mound on Thomas Worthington's early 19th-century estate located near Chillicothe, Ohio, which he named "Adena", The culture is the most prominently known of a number of similar cultures in eastern North America that began mound building ceremonialism at the end of the Archaic period. The geographic range of the Adena sites is centered on central and southern Ohio, with further sites in contiguous areas of the surrounding states of Indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woodland Period
In the classification of :category:Archaeological cultures of North America, archaeological cultures of North America, the Woodland period of North American pre-Columbian cultures spanned a period from roughly 1000 Common Era, BCE to European contact in the eastern part of North America, with some archaeologists distinguishing the Mississippian period, from 1000 CE to European contact as a separate period. The term "Woodland Period" was introduced in the 1930s as a generic term for prehistoric, prehistoric sites falling between the Archaic period in the Americas, Archaic hunter-gatherers and the agriculturalist Mississippian cultures. The Eastern Woodlands cultural region covers what is now eastern Canada south of the Subarctic region, the Eastern United States, along to the Gulf of Mexico. This period is variously considered a developmental stage, a time period, a suite of technological adaptations or "traits", and a "family tree" of cultures related to earlier Archaic cultures. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Register Of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic value". A property listed in the National Register, or located within a National Register Historic District, may qualify for tax incentives derived from the total value of expenses incurred in preserving the property. The passage of the National Historic Preservation Act (NHPA) in 1966 established the National Register and the process for adding properties to it. Of the more than one and a half million properties on the National Register, 95,000 are listed individually. The remainder are contributing resources within historic districts. For most of its history, the National Register has been administered by the National Park Service (NPS), an agency within the U.S. Department of the Interior. Its goals are to help property owners and inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Register Of Historic Places Listings In Sussex County, Delaware
The following properties are listed on the National Register of Historic Places in Sussex County, Delaware, United States. Contents: Divisions in Delaware Former listing References {{Sussex County, Delaware Sussex Sussex (), from the Old English (), is a historic county in South East England that was formerly an independent medieval Anglo-Saxon kingdom. It is bounded to the west by Hampshire, north by Surrey, northeast by Kent, south by the English ... * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites On The National Register Of Historic Places In Delaware
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the advent of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)